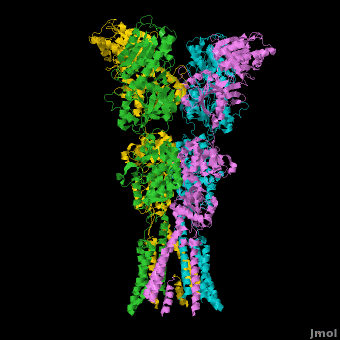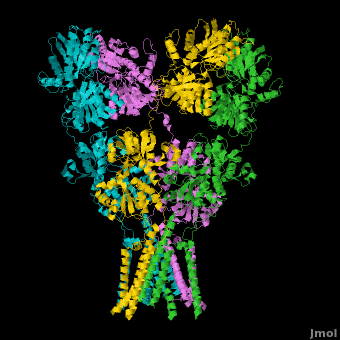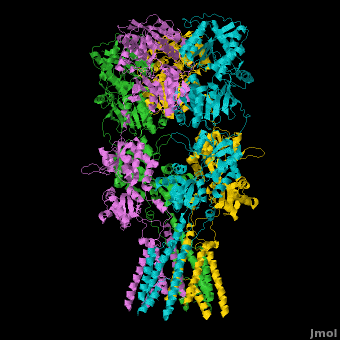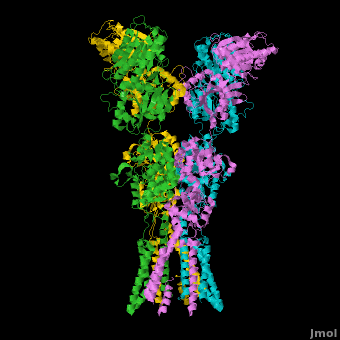Ionotropic Glutamate Receptors
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 118: | Line 118: | ||
**[[1vso]] - rIGluR5 ligand-binding domain + antagonist<br /> | **[[1vso]] - rIGluR5 ligand-binding domain + antagonist<br /> | ||
| - | + | *Ionotropic glutamate receptor 6 | |
| - | [[3h6g]], [[3h6h]] – rIGluR6 N-terminal domain<br /> | + | **[[3h6g]], [[3h6h]] – rIGluR6 N-terminal domain<br /> |
| - | [[3g3f]], [[1sd3]], [[1s50]], [[1s7y]] – rIGluR6 ligand-binding domain + Glu<br /> | + | **[[3g3f]], [[1sd3]], [[1s50]], [[1s7y]] – rIGluR6 ligand-binding domain + Glu<br /> |
| - | [[3g3g]], [[3g3h]], [[3g3i]], [[3g3j]], [[3g3k]], [[2i0b]], [[2i0c]] - rIGluR6 ligand-binding domain (mutant) + Glu<br /> | + | **[[3g3g]], [[3g3h]], [[3g3i]], [[3g3j]], [[3g3k]], [[2i0b]], [[2i0c]] - rIGluR6 ligand-binding domain (mutant) + Glu<br /> |
| - | [[1s9t]] – rIGluR6 ligand-binding domain + positive allosteric modulator<br /> | + | **[[1s9t]] – rIGluR6 ligand-binding domain + positive allosteric modulator<br /> |
| - | [[1tt1]] – rIGluR6 ligand-binding domain + partial agonist<br /> | + | **[[1tt1]] – rIGluR6 ligand-binding domain + partial agonist<br /> |
*Metabotropic glutamate receptor see [[Metabotropic glutamate receptor]] | *Metabotropic glutamate receptor see [[Metabotropic glutamate receptor]] | ||
Revision as of 08:05, 26 November 2014
| |||||||||||
Contents |
Page Development
This article was developed based on lectures given in Chemistry 543 by Prof. Clarence E. Schutt at Princeton University.
3D structures of glutamate receptor
Updated on 26-November-2014
A topic page describing in detail the GluA2 structure described in 3kg2
Topic Page on Glutamate Receptor GluA2 structure
There is a topic page describing in detail the GluA2 structure described in 3kg2. The page is meant to complement the original publication of the structure by Sobolevsky et al.[2][8] with matching colors, etc..
See Also
- Glutamate Receptor Symmetry Analysis
- Glutamate receptor (GluA2) structure in detail
- Metabotropic glutamate receptor
- Membrane Channels & Pumps
- Alzheimer's Disease
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Jin R, Clark S, Weeks AM, Dudman JT, Gouaux E, Partin KM. Mechanism of positive allosteric modulators acting on AMPA receptors. J Neurosci. 2005 Sep 28;25(39):9027-36. PMID:16192394 doi:25/39/9027
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 2.3 2.4 2.5 2.6 2.7 Sobolevsky AI, Rosconi MP, Gouaux E. X-ray structure, symmetry and mechanism of an AMPA-subtype glutamate receptor. Nature. 2009 Dec 10;462(7274):745-56. Epub . PMID:19946266 doi:10.1038/nature08624
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 Purcell AE, Jeon OH, Zimmerman AW, Blue ME, Pevsner J. Postmortem brain abnormalities of the glutamate neurotransmitter system in autism. Neurology. 2001 Nov 13;57(9):1618-28. PMID:11706102
- ↑ Welsh JP, Ahn ES, Placantonakis DG. Is autism due to brain desynchronization? Int J Dev Neurosci. 2005 Apr-May;23(2-3):253-63. PMID:15749250 doi:10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2004.09.002
- ↑ Zuo J, De Jager PL, Takahashi KA, Jiang W, Linden DJ, Heintz N. Neurodegeneration in Lurcher mice caused by mutation in delta2 glutamate receptor gene. Nature. 1997 Aug 21;388(6644):769-73. PMID:9285588 doi:10.1038/42009
- ↑ Rubenstein JL, Merzenich MM. Model of autism: increased ratio of excitation/inhibition in key neural systems. Genes Brain Behav. 2003 Oct;2(5):255-67. PMID:14606691
- ↑ Jin R, Singh SK, Gu S, Furukawa H, Sobolevsky AI, Zhou J, Jin Y, Gouaux E. Crystal structure and association behaviour of the GluR2 amino-terminal domain. EMBO J. 2009 Jun 17;28(12):1812-23. Epub 2009 May 21. PMID:19461580 doi:10.1038/emboj.2009.140
- ↑ Wollmuth LP, Traynelis SF. Neuroscience: Excitatory view of a receptor. Nature. 2009 Dec 10;462(7274):729-31. PMID:20010675 doi:10.1038/462729a
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, David Canner, Wayne Decatur, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman