This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 954
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | '''<big>SQUAMOUS CELL CARICNOMA ANTIGEN 1</big>''' | ||
| - | |||
==Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')== | ==Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')== | ||
| - | < | + | <StructureSection load='3rec' size='350' side='right' caption='Escherichia coli reca protein-bound DNA (PDB entry [[3rec]])' scene=''>==Introduction== |
| - | + | Squamous cell carcinoma antigen is a tumor associated protein of squamous cell carcinoma of various organs. SCCA was originally purified from SCC of the uterine cervix <ref>Martz, E. Book review of ''Introduction to protein science—architecture, function, and genomics: Lesk, Arthur M. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ.'' 33:144-5 (2006). [http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-1-4612-0401-5_21#page-1 DOI :10.1007/978-1-4612-0401-5_21#page-1]</ref>. SCCA is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tumor_marker tumor marker] to detect malignant tumor and to understand biological behaviors of squamous cells. SCCA is classified as a serine protease inhibitor called [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serpin serpin] B3. It also inhibits [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chymotrypsin chymotripsin], [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cathepsin cathepsin] L, K and S and papain like cysteine proteases. In the case of tumor development SCCA 1 inhibits NK cells(natural killer), TNFalfa and apoptosis of tumor cells induced by treatment. It can also play a role in tumor growth. The chromosomal location is the locus 18q21.3.<ref>PMID:9817978</ref> | |
| - | + | ||
| - | Squamous cell carcinoma antigen is a tumor associated protein of squamous cell carcinoma of various organs. SCCA was originally purified from SCC of the uterine cervix <ref>Martz, E. Book review of ''Introduction to protein science—architecture, function, and genomics: Lesk, Arthur M. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ.'' 33:144-5 (2006). [http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-1-4612-0401-5_21#page-1 DOI :10.1007/978-1-4612-0401-5_21#page-1]</ref>. SCCA is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tumor_marker tumor marker] to detect malignant tumor and to understand biological behaviors of squamous cells. SCCA is classified as a serine protease inhibitor called [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serpin serpin] B3. It also inhibits [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chymotrypsin chymotripsin], [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cathepsin cathepsin] L, K and S and papain like cysteine proteases. In the case of tumor development SCCA 1 inhibits NK cells(natural killer), TNFalfa and apoptosis of tumor cells induced by treatment. It can also play a role in tumor growth. The chromosomal location is the locus 18q21.3.<ref>PMID:9817978</ref | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | |||
| - | ==General structure== | ||
| - | |||
| - | Serpins are a superfamily of functionally distinct but structurally conserved proteins. <ref>JBC Papers in Press. Published on July 2, 2001 as Manuscript R100016200 THE SERPINS ARE AN EXPANDING SUPERFAMILY OF | ||
| - | STRUCTURALLY SIMILAR BUT FUNCTIONALLY DIVERSE PROTEINShttp://www.jbc.org/content/early/2001/07/02/jbc.R100016200.full.pdf DOI : 2001/07/02/jbc.R100016200.full.pdf </ref> | ||
| - | SerpinB3 means serin protease inhibitor, clade B (ovalbumin), member 3. The particularity of Serpin B3 is to target proteases wich have a nucleophilic cysteine instead of serine in their catalytic site. | ||
| - | SCCA1 is a <scene name='60/604473/Trimeric/1'>trimeric protein</scene><ref> PMID : 19166818 </ref> | ||
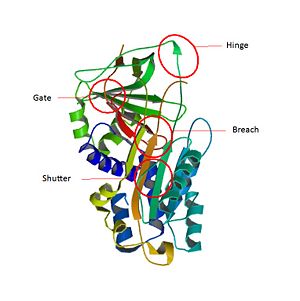
| - | . Like all for serpins, <scene name='60/604473/One_subunit/1'>one subunit</scene> has three β sheets termed <scene name='60/604473/A_beta_sheet/3'>A (7 stranded)</scene>, <scene name='60/604473/B_beta_sheet/2'>B (5 stranded)</scene> and <scene name='60/604473/C_beta_sheet/2'>C (6 stranded)</scene> and <scene name='60/604473/Alpha_helices/1'>11 α helices (hA to hK)</scene> <ref>Gary A. Silverman1*, Phillip I. Bird2 | ||
| - | , Robin W. Carrell3 | ||
| - | , Frank C. Church4 | ||
| - | , Paul B. Coughlin5 | ||
| - | , Peter G.W. Gettins6 | ||
| - | , | ||
| - | James A Irving2 | ||
| - | , David A. Lomas3 | ||
| - | , Cliff J. Luke1 | ||
| - | , Richard W. Moyer7 | ||
| - | , Philip A. Pemberton8 | ||
| - | , Eileen RemoldO'Donnell9 | ||
| - | , Guy S. Salvesen10, James Travis11 and James C. Whisstock, THE SERPINS ARE AN EXPANDING SUPERFAMILY OF | ||
| - | STRUCTURALLY SIMILAR BUT FUNCTIONALLY DIVERSE PROTEINS, http://www.jbc.org/content/early/2001/07/02/jbc.R100016200.full.pdf DOI : 2001/07/02/jbc.R100016200.full.pdf </ref> <ref>PDB, Crystal structure of human squamous cell carcinoma antigen 1 http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/remediatedSequence.do?structureId=2ZV6&bionumber=1 DOI : pdb/explore/remediatedSequence.do?structureId=2ZV6&bionumber=1</ref> . | ||
| - | The most important part of Serpins is an exposed region of 20 amino acids near the C terminus named the reactive center loop (<scene name='60/604473/The_rcl_loop_scene/3'>RCL</scene>). The amino-acids of <scene name='60/604473/The_rcl_loop_scene/3'>RCL</scene> are very conservated for Serpin B3 and allow the specificity interaction of the inhibitor for the target protease<ref> PMID : PMC24842</ref>. | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===Conformational changes of serpins=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | Structural studies on serpins revealed that inhibitory members of the family undergo an unusual conformational change, termed the Stressed to Relaxed (S to R) transition. During this structural transition the <scene name='60/604473/The_rcl_loop_scene/3'>RCL</scene> inserts into <scene name='60/604473/A_beta_sheet/3'>A β-sheet</scene> and forms an extra fourth β strand . The serpin conformational change is key to the mechanism of inhibition of target proteases. <scene name='60/604473/Rcl_insertion_into_beta_sheet/1'>Some amino-acids of RCL</scene> wich belong to a consensus sequence for inhibitory serpins are thought to permit efficient and rapid insertion of the <scene name='60/604473/The_rcl_loop_scene/3'>RCL</scene> into the <scene name='60/604473/A_beta_sheet/3'>A β-sheet</scene>.<ref> James C Whisstocka, 2, Richard Skinnera, 2, Robin W Carrella, Arthur M Leska, Conformational changes in serpins: I. the native and cleaved conformations of α1-antitrypsin1, http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022283699935209 DOI:pii/S0022283699935209</ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[Image:Structure region.jpg|300px]] [[Image:Fontion3.jpg|400px]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | ==Function== | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===Cysteine proteases mecanism=== | ||
| - | |||
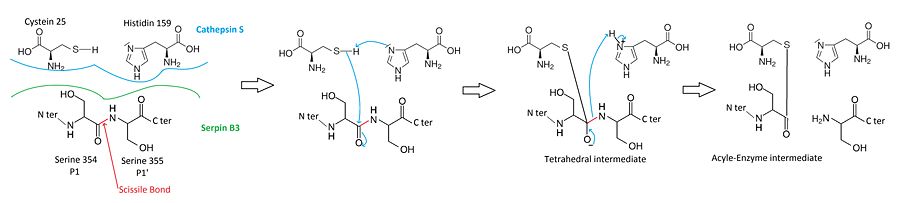
| - | When attacking a substrate, proteases catalyze peptide bond cleavage in a two-step process. Initially, the catalytic cysteine performs a nucleophilic attack on the peptide bond of the substrate. This releases the new N-terminus and forms an new bond between the enzyme and the substrate. This covalent enzyme-substrate complex is called an acyl enzyme intermediate. Subsequent to this, this bond is hydrolysed and the new C-terminus is released. | ||
| - | |||
| - | http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serpin | ||
| - | |||
| - | ===Protease inhibition=== | ||
| - | |||
| - | The <scene name='60/604473/The_rcl_loop_scene/3'>RCL</scene> of a serpin acts as a substrate for its cognate protease. | ||
| - | The <scene name='60/604473/The_rcl_loop_scene/3'>RCL</scene> is cleaved at a scissile bond between two residues <scene name='60/604473/P1_scene/3'>Ser354 termed P1 (N-terminal of the cleavage event) and Ser355 termed P1’ (C-terminal of the cleavage event)</scene>. The <scene name='60/604473/P1_scene/3'>P1 and P1' residues</scene> are critical for serpin specificity and mutation of these residues results in the loss or conversion of inhibitory activity. The protease recognize <scene name='60/604473/Amino_acids_for_protease_recog/1'>amino-acids of the RCL</scene> that allow its docking. | ||
| - | <ref>M. S. J. Mangan, D. Kaiserman & P. I. Bird, The role of serpins in vertebrate immunity | ||
| - | Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Monash University, Clayton, Victoria, Australiahttp://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1399-0039.2008.01059.x/pdf DOI : 10.1111/j.1399-0039.2008.01059.x/pdf </ref> http://genome.cshlp.org/content/10/12/1845 | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[Image:Fonction2.jpg|600px]] [[Image:fonction1.jpg|900px]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | Prior to hydrolysis of the acyl-enzyme intermediate, the serpin rapidly undergoes the S-to-R transition. Since the <scene name='60/604473/The_rcl_loop_scene/3'>RCL</scene> is still covalently attached to the protease via the ester bond, the S-to-R transition moves the protease from the top to the bottom of the serpin. http://www.plosone.org/article/info%3Adoi%2F10.1371%2Fjournal.pone.0104935 At the same time, the protease is distorted into a conformation, where the acyl enzyme intermediate is hydrolysed extremely slowly. The the active site of the enzyme would be expected to break.The protease thus remains covalently attached to the target protease and is thereby inhibited. | ||
| - | |||
| - | [[Image:Gb-2006-7-5-216-1-l_-_Copie.jpg|600px]] | ||
| - | |||
| - | Further, since the serpin has to be cleaved to inhibit the target protases, inhibition consumes the serpin as well. Serpins are therefore irreversible enzyme inhibitors. | ||
| - | <ref>J. A. HUNTINGTON,Department of Haematology, Cambridge Institute for Medical Research, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK, Serpin structure, function and dysfunction, | ||
| - | http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1538-7836.2011.04360.x/pdf DOI : 10.1111/j.1538-7836.2011.04360.x/pdf</ref> | ||
| - | The increase of the SCCA1 residing in the cytosol of squamous carcinoma cell may protect the tumor by neutralizing harmful proteases. | ||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | |||
| - | ==Introduction== | ||
| - | |||
| - | Squamous cell carcinoma antigen is a tumor associated protein of squamous cell carcinoma of various organs. SCCA was originally purified from SCC of the uterine cervix <ref>Martz, E. Book review of ''Introduction to protein science—architecture, function, and genomics: Lesk, Arthur M. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Educ.'' 33:144-5 (2006). [http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-1-4612-0401-5_21#page-1 DOI :10.1007/978-1-4612-0401-5_21#page-1]</ref>. SCCA is a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tumor_marker tumor marker] to detect malignant tumor and to understand biological behaviors of squamous cells. SCCA is classified as a serine protease inhibitor called [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serpin serpin] B3. It also inhibits [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chymotrypsin chymotripsin], [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cathepsin cathepsin] L, K and S and papain like cysteine proteases. In the case of tumor development SCCA 1 inhibits NK cells(natural killer), TNFalfa and apoptosis of tumor cells induced by treatment. It can also play a role in tumor growth. The chromosomal location is the locus 18q21.3.<ref>PMID:9817978</ref> | ||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
==General structure== | ==General structure== | ||
| Line 177: | Line 111: | ||
| - | + | ||
= References = | = References = | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Anything in this section will appear adjacent to the 3D structure and will be scrollable. | ||
Revision as of 12:08, 8 January 2015
Your Heading Here (maybe something like 'Structure')
| |||||||||||