Magainin 2
From Proteopedia
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| - | Magainin are a class of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) found in the African clawed frog Xenopus Laevis. | + | '''Magainin''' are a class of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) found in the African clawed frog Xenopus Laevis. |
AMPs consists of 10-50 amino acids, and are produced by Eukaryotes, as part of their defence mechanism from bacteria. For informatoin about AMPs you can visit the Proteopedia page [[Antimicrobial peptides]] | AMPs consists of 10-50 amino acids, and are produced by Eukaryotes, as part of their defence mechanism from bacteria. For informatoin about AMPs you can visit the Proteopedia page [[Antimicrobial peptides]] | ||
Magainin 1 and 2 were discovered by Dr. Michael Zasloff and first reported in 1987. They have an alpha helix structure, and are water soluble and Potentially amphiphilic. | Magainin 1 and 2 were discovered by Dr. Michael Zasloff and first reported in 1987. They have an alpha helix structure, and are water soluble and Potentially amphiphilic. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of magainin 2== | ||
| + | Updated on {{REVISIONDAY2}}-{{MONTHNAME|{{REVISIONMONTH}}}}-{{REVISIONYEAR}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[2mag]], [[2lsa]] – Mag2 – frog - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | [[1dum]] – Mag2 (mutant) - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | [[4mgp]], [[5cgn]], [[5cgo]] – Mag2 (mutant) <br /> | ||
| + | [[1d9j]], [[1d9l]], [[1d9o]], [[1d9m]], [[1d9p]], [[1f0d]], [[1f0e]], [[1f0f]], [[1f0g]], [[1f0h]] – Mag2/cecropin A - NMR<br /> | ||
| + | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
1-'''J. Gesella., M. Zasloffb and S. J. Opellaa'''., Two-dimensional H NMR experiments show that the 23-residue magainin antibiotic peptide is an α-helix in dodecylphosphocholine micelles, sodium dodecylsulfate micelles, and trifluoroethanol/water solution. ''Journal of Biomolecular NMR'', 1997. 9: 127–135. | 1-'''J. Gesella., M. Zasloffb and S. J. Opellaa'''., Two-dimensional H NMR experiments show that the 23-residue magainin antibiotic peptide is an α-helix in dodecylphosphocholine micelles, sodium dodecylsulfate micelles, and trifluoroethanol/water solution. ''Journal of Biomolecular NMR'', 1997. 9: 127–135. | ||
Revision as of 13:15, 6 January 2016
Magainin 2
| |||||||||||
3D structures of magainin 2
Updated on 06-January-2016
2mag, 2lsa – Mag2 – frog - NMR
1dum – Mag2 (mutant) - NMR
4mgp, 5cgn, 5cgo – Mag2 (mutant)
1d9j, 1d9l, 1d9o, 1d9m, 1d9p, 1f0d, 1f0e, 1f0f, 1f0g, 1f0h – Mag2/cecropin A - NMR
References
1-J. Gesella., M. Zasloffb and S. J. Opellaa., Two-dimensional H NMR experiments show that the 23-residue magainin antibiotic peptide is an α-helix in dodecylphosphocholine micelles, sodium dodecylsulfate micelles, and trifluoroethanol/water solution. Journal of Biomolecular NMR, 1997. 9: 127–135.
2-Z. Hayouka., D. E. Mortenson., D. F. Kreitler., B. Weisblum., K. T. Forest, and S. H. Gellman., Evidence for Phenylalanine Zipper-Mediated Dimerization in the X‑ray Crystal Structure of a Magainin 2 Analogue. J. Am. Chem. Soc, 2013. 135: 15738−15741.
3- Y. Tamba & M. Yamazaki.,Magainin 2-Induced Pore Formation in the Lipid Membranes Depends on Its Concentration in the Membrane Interface. J. Phys. Chem. B, 2009. 113: 4846–4852.
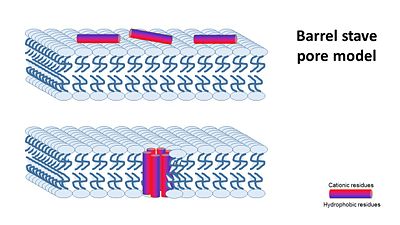
4- W. C. Wimley., Describing the Mechanism of Antimicrobial Peptide Action with the Interfacial Activity Model. ACS CHEMICAL BIOLOGY, 2010. 10: 905-917.