Helicase
From Proteopedia
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
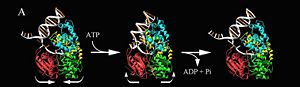
'''Helicase''' (Hel) is a motor protein which separates nucleic acid strands like DNA double helix or self-annealed RNA. They use ATP hydrolysis for energy. Hel falls into 5 superfamilies (SF1-SF5). Some Hel contain a Helicase and RNase D C terminal | '''Helicase''' (Hel) is a motor protein which separates nucleic acid strands like DNA double helix or self-annealed RNA. They use ATP hydrolysis for energy. Hel falls into 5 superfamilies (SF1-SF5). Some Hel contain a Helicase and RNase D C terminal | ||
| - | Domain (HRDC). The α-thalassemia and mental retardation X-linked syndrome helicase (ATRX ), contains an ATRX-Dnmt3-Dnmt3L (ADD) domain in which many disease-related mutations are found. | + | Domain (HRDC). The α-thalassemia and mental retardation X-linked syndrome helicase (ATRX ), contains an ATRX-Dnmt3-Dnmt3L (ADD) domain in which many disease-related mutations are found. '''ATP-dependent helicase Rho''' is a protein involved in termination of transcription in prokaryotes. Rho binds to the transcription terminator site on single-stranded RNA. Rho forms a ring-shaped hexamer and advances along the mRNA until it reaches the RNA polymerase and causing it to dissociate from the DNA and end transcription. |
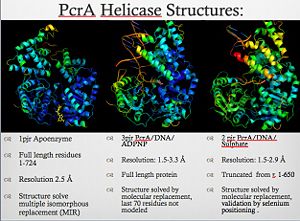
For details of PcrA helicase see<br /> | For details of PcrA helicase see<br /> | ||
| Line 102: | Line 102: | ||
**[[3ice]] – EcRho + ADP + BeF3 + RNA<BR /> | **[[3ice]] – EcRho + ADP + BeF3 + RNA<BR /> | ||
**[[2ht1]] - EcRho + RNA<BR /> | **[[2ht1]] - EcRho + RNA<BR /> | ||
| - | **[[1a8v]] – EcRho RNA-binding domain<br /> | + | **[[1a8v]], [[1a62]] – EcRho RNA-binding domain<br /> |
| + | **[[1a63]] - EcRho RNA-binding domain – NMR<br /> | ||
**[[2a8v]] – EcRho RNA-binding domain + RNA<br /> | **[[2a8v]] – EcRho RNA-binding domain + RNA<br /> | ||
**[[1pv4]] – EcRho + DNA<br /> | **[[1pv4]] – EcRho + DNA<br /> | ||
**[[1pvo]] – EcRho + ssRNA + ANPPNP<br /> | **[[1pvo]] – EcRho + ssRNA + ANPPNP<br /> | ||
| - | **[[1xpr]], [[1xpu]] - EcRho + ssRNA + antibiotic | + | **[[1xpr]], [[1xpu]], [[1xpo]] - EcRho + ssRNA + antibiotic |
*ATP-dependent helicase MFD | *ATP-dependent helicase MFD | ||
Revision as of 07:25, 16 July 2015
| |||||||||||
3D structures of helicase
Updated on 16-July-2015
References
Crystal structure of a DExx box DNA helicase., Subramanya HS, Bird LE, Brannigan JA, Wigley DB, Nature. 1996 Nov 28;384(6607):379-83. PMID:8934527
^ Johnson DS, Bai L, Smith BY, Patel SS, Wang MD (2007). "Single-molecule studies reveal dynamics of DNA unwinding by the ring-shaped t7 helicase". Cell 129 (7): 1299–309. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.04.038. PMID 17604719.
^ a b "Researchers solve mystery of how DNA strands separate" (2007-07-03). Retrieved on 2007-07-05.
^ Dumont S, Cheng W, Serebrov V, Beran RK, Tinoco Jr I, Pylr AM, Bustamante C, "RNA Translocation and Unwinding Mechanism of HCV NS3 Helicase and its Coordination by ATP", Nature. 2006 Jan 5; 439: 105-108.
Anand SP, Zheng H, Bianco PR, Leuba SH, Khan SA. DNA helicase activity of PcrA is not required for displacement of RecA protein from DNA or inhibition of RecA-mediated DNA strand exchange. Journal of Bacteriology (2007) 189 (12):4502-4509.
Bird L, Subramanya HS, Wigley DB, "Helicases: a unifying structural theme?", Current Opinion in Structural Biology. 1998 Feb; 8 (1): 14-18.
Betterton MD, Julicher F, "Opening of nucleic-acid double strands by helicases: active versus passive opening.", Physical Review E. 2005 Jan; 71 (1): 011904.
- Sengoku T, Nureki O, Nakamura A, Kobayashi S, Yokoyama S. Structural basis for RNA unwinding by the DEAD-box protein Drosophila Vasa. Cell. 2006 Apr 21;125(2):287-300. PMID:16630817 doi:10.1016/j.cell.2006.01.054
- Sengoku T, Nureki O, Dohmae N, Nakamura A, Yokoyama S. Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of the helicase domains of Vasa complexed with RNA and an ATP analogue. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2004 Feb;60(Pt 2):320-2. Epub 2004, Jan 23. PMID:14747711 doi:10.1107/S0907444903025897
Content Donators
Created with the participation of Luis E Ramirez-Tapia, Wayne Decatur.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Alexander Berchansky, Wayne Decatur, Joel L. Sussman