This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1086
From Proteopedia
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
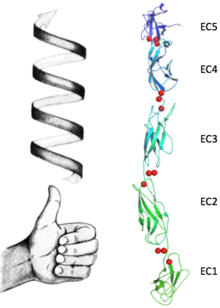
Cadherins are transmembrane,calcium binding proteins that mediate adhesion between cells in the solid tissues of animals. These proteins form huge membrane complexes called Desmosomes of which the architecture is still unclear as well as the molecular mechanism(s) through which the adhesion takes place. | Cadherins are transmembrane,calcium binding proteins that mediate adhesion between cells in the solid tissues of animals. These proteins form huge membrane complexes called Desmosomes of which the architecture is still unclear as well as the molecular mechanism(s) through which the adhesion takes place. | ||
| - | Their expression is a complex and highly regulated process which plays a pivotal role in many biological landscapes from development to invasiveness of some type of tumors. As the most of transmembrane proteins, cadherins have different structural and functional features addressed to their extracellular and intracellular domains (N terminus and C terminus respectively). The outside portion of the protein consists in five ectodomains ''Ig'' like connected by unstructured regions which give a certain flexibility to the structure. The cell-cell adhesion (also called ''trans'' adhesion) occurs, upon the binding of calcium, between cadherins belonging to opposite cells via interaction of these ectodomains. Interaction between neighbours molecules ("Cis" interactions) happens as well as it tightens the desmosomal plaque and prevents its disassembly. The inner domain has a more globular fold and connects the protein to the cytoskeleton forming an high electron density region called ''inner plaque''. The C-cadherin's structure here presented, suggests a molecular mechanism for adhesion between cells by classical cadherins such as [[1q5b]],[[1q5c]], and [[1q55]]. It provides a new framework for understanding both cis and trans cadherin interactions. | + | Their expression is a complex and highly regulated process which plays a pivotal role in many biological landscapes from development to invasiveness of some type of tumors. As the most of transmembrane proteins, cadherins have different structural and functional features addressed to their extracellular and intracellular domains (N terminus and C terminus respectively). The outside portion of the protein consists in five ectodomains ''Ig'' like connected by unstructured regions which give a certain flexibility to the structure. The cell-cell adhesion (also called ''trans'' adhesion) occurs, upon the binding of calcium, between cadherins belonging to opposite cells via interaction of these ectodomains. Interaction between neighbours molecules ("Cis" interactions) happens as well as it tightens the desmosomal plaque and prevents its disassembly. The inner domain has a more globular fold and connects the protein to the cytoskeleton forming an high electron density region called ''inner plaque''. The C-cadherin's structure here presented, suggests a molecular mechanism for adhesion between cells by classical cadherins such as [[1q5b]],[[1q5c]], and [[1q55]]. It provides a new framework for understanding both cis and trans cadherin interactions. <scene name='69/699999/E1/1'>TextToBeDisplayed</scene> |
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 13:34, 21 April 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/04/2015, through 15/06/2015 for use in the course "Protein structure, function and folding" taught by Taru Meri at the University of Helsinki. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1081 through Sandbox Reserved 1090. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Contents |
C-cadherin
| |||||||||||
Exploring the Structure
The extracellular domain of C-cadherin is composed of five ectodomains repeated in tandem and linked by short peptide linkers. Each ectodomain (EC) shares the same greek key fold characteristic of immunoglobulin. The interfaces between the EC are calcium binding sites coordinating three ions each through the highly conserved motif Asp-X-Asp, Leu-Asp-Arg-Glu and Asp-X-Asn-Asp-Asn. The binding of calcium it thought to confer rigidity as well as the classical curved shape to the structure and this is why it´s very suggested to be a triggering if not even compulsory step to the adhesion process.
Upon the calcium binding the ectodomains tilt from e
GFP is a beta barrel protein with 11 beta sheets. It is a 26.9kDa protein made up of 238 amino acids. The chromophore, responsible for the fluorescent properties of the protein, is buried inside the beta barrel as part of the central alpha helix passing through the barrel. The forms via spontaneous cyclization and oxidation of three residues in the central alpha helix: -Thr65 (or Ser65)-Tyr66-Gly67. This cyclization and oxidation creates the chromophore's five-membered ring via a new bond between the threonine and the glycine residues [1].
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
Structural highlights
| 1q5a is a 2 chain structure with sequence from Mus musculus. The March 2008 RCSB PDB Molecule of the Month feature on Cadherin by David S. Goodsell is 10.2210/rcsb_pdb/mom_2008_3. Full crystallographic information is available from OCA. For a guided tour on the structure components use FirstGlance. | |
| Ligands: | , , |
| Related: | 1l3w, 1q55, 1q5b, 1q5c |
| Resources: | FirstGlance, OCA, RCSB, PDBsum |