We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1083
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
=='''AcrA'''== | =='''AcrA'''== | ||
<StructureSection load='2f1m' size='340' side='right' caption='AcrA tetramer' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='2f1m' size='340' side='right' caption='AcrA tetramer' scene=''> | ||
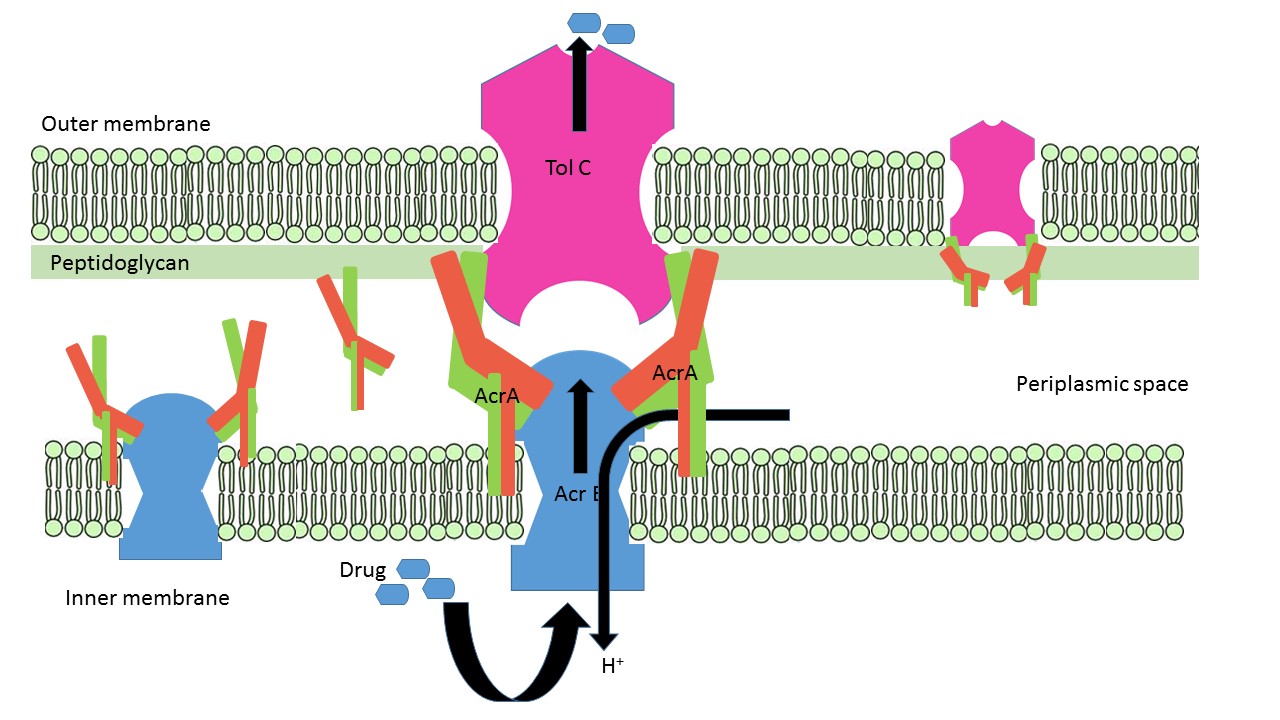
| - | AcrA is a Multidrug efflux system protein. It belongs to resistance nodulation cell division (RND) family protein, which utilize electrochemical gradient to energize efflux of antibiotics and other compounds out of the bacterial cells | + | AcrA is a Multidrug efflux system protein. It belongs to resistance nodulation cell division (RND) family protein, which utilize electrochemical gradient to energize efflux of antibiotics and other compounds out of the bacterial cells <ref>PMCID:PMC99009</ref>. RND system consists of large complexes of three essential proteins and work together as a multiprotein [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Efflux_%28microbiology%29 efflux system]. Two most studied RND systems are E. coli AcrA-AcrB-TolC and P. aeruginosa MexA-MexB-OprM, which are known to efflux antibiotics, heavy metals, dyes, detergents, solvents, plus many other substrates (Ayush Kumar, Herbert P. Schweizer 2005). |
== Stable core of AcrA == | == Stable core of AcrA == | ||
Revision as of 06:44, 23 April 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/04/2015, through 15/06/2015 for use in the course "Protein structure, function and folding" taught by Taru Meri at the University of Helsinki. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1081 through Sandbox Reserved 1090. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
AcrA
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ PMCID:PMC99009