We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1083
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Stable core of AcrA == | == Stable core of AcrA == | ||
| - | Four molecules of AcrA (45-312 residues) in asymmetric unit of the crystal pack as an apparent <scene name='69/699996/Acra-dimer_of_dimers/1'>dimer of dimers</scene>. Each monomers are labeled as A (in cyan), B (in orange), C (in green) and D (in yellow). A, B / C, D are related to one another by approximate <scene name='69/699996/Dyad_symmetry/3'>dyad symmetry</scene>. Each set of dimers are related to one another by approximate <scene name='69/699996/2_fold_symmetry/2'>2 fold axis</scene> | + | Four molecules of AcrA (45-312 residues) in asymmetric unit of the crystal pack as an apparent <scene name='69/699996/Acra-dimer_of_dimers/1'>dimer of dimers</scene>. Each monomers are labeled as A (in cyan), B (in orange), C (in green) and D (in yellow). A, B / C, D are related to one another by approximate <scene name='69/699996/Dyad_symmetry/3'>dyad symmetry</scene>. Each set of dimers are related to one another by approximate <scene name='69/699996/2_fold_symmetry/2'>2 fold axis</scene> <ref>PMID:16531241</ref>. |
Each <scene name='69/699996/Monomer/1'>monomer</scene> is a sickle shaped molecule comprising three domains viz. <scene name='69/699996/Beta_barrel/1'>β-barrel domain</scene>, <scene name='69/699996/Lipoyl_domain/2'>lipoyl domain</scene>, and coiled coil <scene name='69/699996/Hairpin_domain/1'>α-helical hairpin domain</scene>. β-barrel domain comprises six anti-parallel β-sheets and a short α-helix. Lipoyl domain is present in the central part of the AcrA monomer made up of two half motifs interrupted by an α-helical hairpin. Each half of the lipoyl motif is homologous to each other and consist of four β-strands in the form of a β-sandwich. A conserved <scene name='69/699996/Lysine_residue/1'>lysine residue</scene> on the connecting loop of two half motifs serve as carrier of lipoyl or biotinyl co-factors. The coiled coil domain consists of five [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heptad_repeat heptad repeats] per helix. Two α-helices are packed together as a canonical [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Knobs_into_holes_packing knobs-into-holes] by hydrophobic side chains in the <scene name='69/699996/Knob_in_hole/2'>a and d positions</scene> of the heptad repeats (Johnson and Church 1999, Akama et al 2004). Crystal structure provide evidence for the flexibility of the hinge region between α-helical hairpin and lipoyl domain. The difference in hinge angle in case of B and C chain varies approximately by 15° overall and 21 Å at the loop located at the top of the hairpin. | Each <scene name='69/699996/Monomer/1'>monomer</scene> is a sickle shaped molecule comprising three domains viz. <scene name='69/699996/Beta_barrel/1'>β-barrel domain</scene>, <scene name='69/699996/Lipoyl_domain/2'>lipoyl domain</scene>, and coiled coil <scene name='69/699996/Hairpin_domain/1'>α-helical hairpin domain</scene>. β-barrel domain comprises six anti-parallel β-sheets and a short α-helix. Lipoyl domain is present in the central part of the AcrA monomer made up of two half motifs interrupted by an α-helical hairpin. Each half of the lipoyl motif is homologous to each other and consist of four β-strands in the form of a β-sandwich. A conserved <scene name='69/699996/Lysine_residue/1'>lysine residue</scene> on the connecting loop of two half motifs serve as carrier of lipoyl or biotinyl co-factors. The coiled coil domain consists of five [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heptad_repeat heptad repeats] per helix. Two α-helices are packed together as a canonical [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Knobs_into_holes_packing knobs-into-holes] by hydrophobic side chains in the <scene name='69/699996/Knob_in_hole/2'>a and d positions</scene> of the heptad repeats (Johnson and Church 1999, Akama et al 2004). Crystal structure provide evidence for the flexibility of the hinge region between α-helical hairpin and lipoyl domain. The difference in hinge angle in case of B and C chain varies approximately by 15° overall and 21 Å at the loop located at the top of the hairpin. | ||
Revision as of 06:49, 23 April 2015
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/04/2015, through 15/06/2015 for use in the course "Protein structure, function and folding" taught by Taru Meri at the University of Helsinki. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1081 through Sandbox Reserved 1090. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
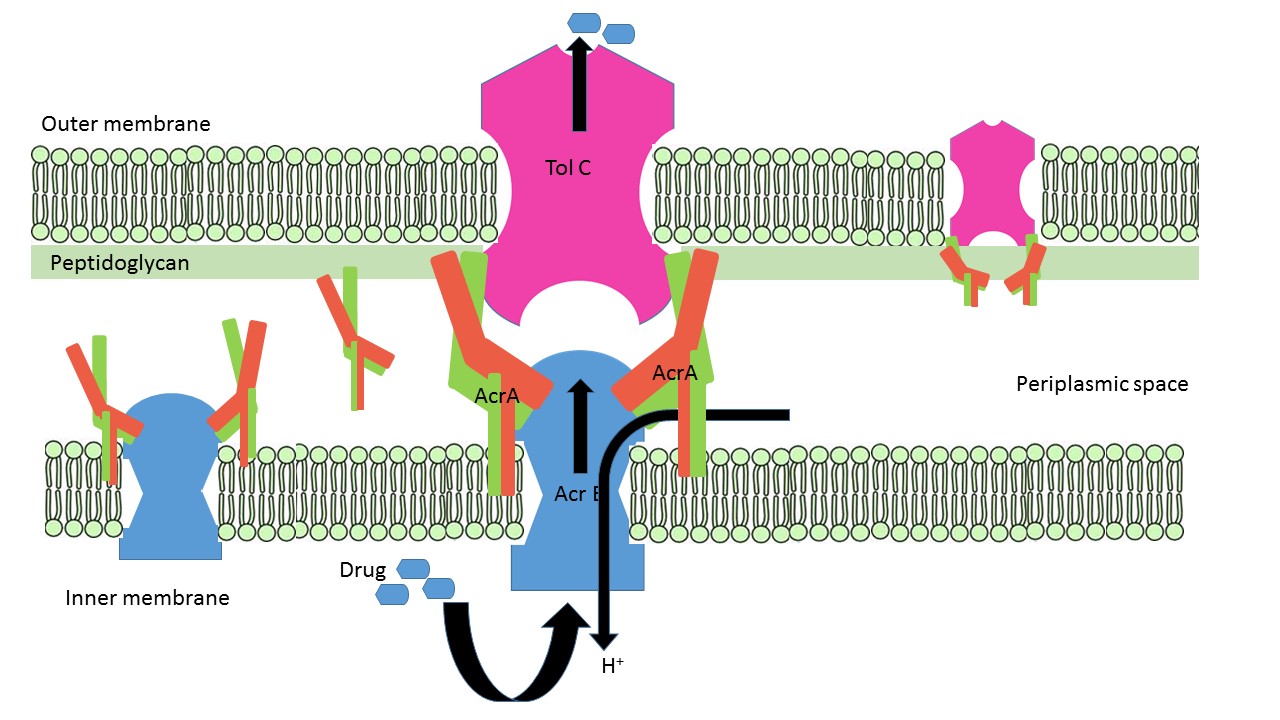
AcrA
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Putman M, van Veen HW, Konings WN. Molecular properties of bacterial multidrug transporters. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2000 Dec;64(4):672-93. PMID:11104814
- ↑ Kumar A, Schweizer HP. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics: active efflux and reduced uptake. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2005 Jul 29;57(10):1486-513. PMID:15939505 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.addr.2005.04.004
- ↑ Mikolosko J, Bobyk K, Zgurskaya HI, Ghosh P. Conformational flexibility in the multidrug efflux system protein AcrA. Structure. 2006 Mar;14(3):577-87. PMID:16531241 doi:10.1016/j.str.2005.11.015