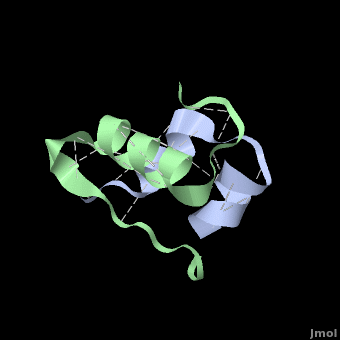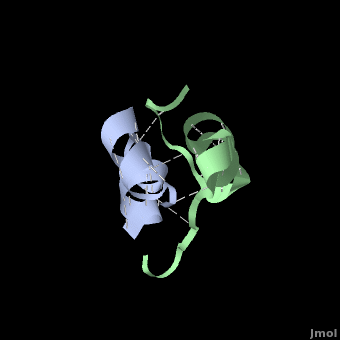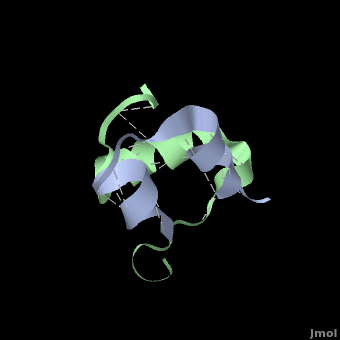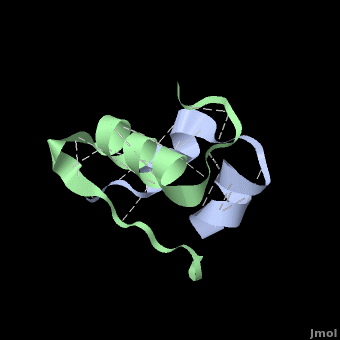Molecular Playground/Insulin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
Insulin is able to pair-up with itself and form a dimer by forming hydrogen bonds between the ends of two B-chains. These <scene name='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Insulin_dimer/2'>hydrogen bonds</scene> are shown above in white. Then, 3 dimers can come together in the presence of zinc ions and form a hexamer. Insulin is stored in the <scene name='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Insulin_hexamer/4'>hexameric form</scene> in the body. This <scene name='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Insulin_ph7/2'>scene highlights</scene> the hydrophobic (gray) and polar (purple) parts of an insulin monomer at a pH of 7. It is believed that the hydrophobic sections on the B-chain cause insulin aggregation which initially caused problems in the manufacture and storage of insulin for [[Pharmaceutical_Drugs#Treatments|pharmaceutical use]]. | Insulin is able to pair-up with itself and form a dimer by forming hydrogen bonds between the ends of two B-chains. These <scene name='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Insulin_dimer/2'>hydrogen bonds</scene> are shown above in white. Then, 3 dimers can come together in the presence of zinc ions and form a hexamer. Insulin is stored in the <scene name='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Insulin_hexamer/4'>hexameric form</scene> in the body. This <scene name='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Insulin_ph7/2'>scene highlights</scene> the hydrophobic (gray) and polar (purple) parts of an insulin monomer at a pH of 7. It is believed that the hydrophobic sections on the B-chain cause insulin aggregation which initially caused problems in the manufacture and storage of insulin for [[Pharmaceutical_Drugs#Treatments|pharmaceutical use]]. | ||
| - | </StructureSection> For additional details see [[Insulin Structure & Function]]. | + | </StructureSection> For additional details see<br /> |
| + | [[Insulin Structure & Function]]<br /> | ||
| + | [[Diabetes & Hypoglycemia]]. | ||
Revision as of 11:48, 1 February 2016
One of the CBI Molecules being studied in the University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program at UMass Amherst in the Roberts Research Group and on display at the Molecular Playground.
| |||||||||||
Insulin Structure & Function
Diabetes & Hypoglycemia.
3D structures of Insulin (Updated on 01-February-2016)
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Diabetes & Hypoglycemia
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Shelly Livne, Karsten Theis, David Canner, Whitney Stoppel, Alexander Berchansky, Yael Shwartz, Lynmarie K Thompson, Jaime Prilusky