Sandbox 4465
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
== Structural Highlights == | == Structural Highlights == | ||
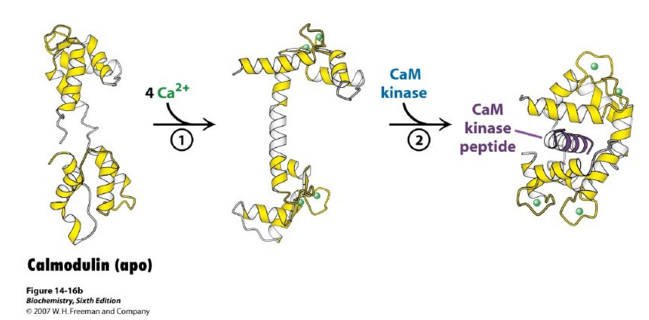
| - | Calmodulin has a molecular mass of 16 kilodaltons (kD) and it functions along with ryanodine receptor (RyR)<ref>doi: 10.1242/jcs.133454</ref>. CaM consists of 148 amino acid residues that is characterized by a helix-loop-helix binding motif, also known as the EF hand <ref>doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77876-2</ref>. Calmodulin has one subunit with a distinct dumbbell shape in which a linker region joins two globular domains<ref>doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004063</ref>. Calmodulin is known to undergo a conformational change upon binding with a calcium ion in which each lobe transitions from a closed conformation to an open conformation<ref>doi:10.1002/elps.1150110104</ref>. Calmodulin typically wraps around its target, with the two globular domains gripping either side of it. NMR studies clearly show that the connector between the two calcium binding globular domains is flexible even when it is not bound to its target proteins. However, the full range of flexibility can be seen in calmodulin interactions with its target proteins. | + | Calmodulin has a molecular mass of 16 kilodaltons (kD) and it functions along with ryanodine receptor (RyR)<ref>doi: 10.1242/jcs.133454</ref>. CaM consists of 148 amino acid residues that is characterized by a helix-loop-helix binding motif, also known as the EF hand <ref>doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77876-2</ref>. Calmodulin has one subunit with a distinct dumbbell shape in which a linker region joins two globular domains<ref>doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004063</ref>. Calmodulin is known to undergo a conformational change upon binding with a calcium ion in which each lobe transitions from a closed conformation to an open conformation<ref>doi:10.1002/elps.1150110104</ref>. This protein has four major, high-affinity binding sites, as shown by figure 1. The calmodulin binding region has been shown to be a series of hydrophobic amino acids (such as Trp or Leu), hydrophilic amino acids (such as Glu or Asp), and basic amino acids (such as Arg or Lys)<ref>PMID:1737757</ref>. Calmodulin typically wraps around its target, with the two globular domains gripping either side of it. NMR studies clearly show that the connector between the two calcium binding globular domains is flexible even when it is not bound to its target proteins. However, the full range of flexibility can be seen in calmodulin interactions with its target proteins. |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
Revision as of 21:43, 5 December 2015
Calmodulin
| |||||||||||
Bibliography
- ↑ Eldik, L., & Watterson, D. (1998). Calmodulin and signal transduction
- ↑ Wolfe, D. M. D. M. (2006). Channeling studies in yeast: Yeast as a model for channelopathies?
- ↑
- ↑ Berridge MJ, Lipp P, Bootman MD. The versatility and universality of calcium signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2000 Oct;1(1):11-21. PMID:11413485 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/35036035
- ↑ Huang X, Liu Y, Wang R, Zhong X, Liu Y, Koop A, Chen SR, Wagenknecht T, Liu Z. Two potential calmodulin-binding sequences in the ryanodine receptor contribute to a mobile, intra-subunit calmodulin-binding domain. J Cell Sci. 2013 Oct 1;126(Pt 19):4527-35. doi: 10.1242/jcs.133454. Epub 2013 Jul, 18. PMID:23868982 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1242/jcs.133454
- ↑ Wriggers W, Mehler E, Pitici F, Weinstein H, Schulten K. Structure and dynamics of calmodulin in solution. Biophys J. 1998 Apr;74(4):1622-39. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77876-2. PMID:9545028 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77876-2
- ↑ Lai M, Brun D, Edelstein SJ, Le Novere N. Modulation of calmodulin lobes by different targets: an allosteric model with hemiconcerted conformational transitions. PLoS Comput Biol. 2015 Jan 22;11(1):e1004063. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004063. , eCollection 2015 Jan. PMID:25611683 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004063
- ↑ Chan KF, Chen WH. High performance capillary electrophoresis of calmodulin. Electrophoresis. 1990 Jan;11(1):15-8. PMID:2108018 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/elps.1150110104
- ↑ Bagchi IC, Huang QH, Means AR. Identification of amino acids essential for calmodulin binding and activation of smooth muscle myosin light chain kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Feb 15;267(5):3024-9. PMID:1737757