Sandbox Reserved 1123
From Proteopedia
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Structural image : By Thomas Splettstoesser (www.scistyle.com) (Own work) [CC BY-SA 4.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)], via Wikimedia Commons | Structural image : By Thomas Splettstoesser (www.scistyle.com) (Own work) [CC BY-SA 4.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)], via Wikimedia Commons | ||
| + | |||
Cytoskeleton interactions : | Cytoskeleton interactions : | ||
| + | |||
- Fernandez J, Gärtner K, Becker A, et al. HIV-1 capsid interacts with cytoskeletal-associated proteins for intracytoplasmic routing to the nucleus. Retrovirology. 2013;10(Suppl 1):P34. doi:10.1186/1742-4690-10-S1-P34. | - Fernandez J, Gärtner K, Becker A, et al. HIV-1 capsid interacts with cytoskeletal-associated proteins for intracytoplasmic routing to the nucleus. Retrovirology. 2013;10(Suppl 1):P34. doi:10.1186/1742-4690-10-S1-P34. | ||
| + | |||
- Fernandez J, Portilho DM, Danckaert A, Munier S, Becker A, Roux P, Zambo A, Shorte S, Jacob Y, Vidalain PO, Charneau P, Clavel F, Arhel NJ. Microtubule-associated proteins 1 (MAP1) promote human immunodeficiency virus type I (HIV-1) intracytoplasmic routing to the nucleus. J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 20;290(8):4631-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.613133. Epub 2014 Dec 11. | - Fernandez J, Portilho DM, Danckaert A, Munier S, Becker A, Roux P, Zambo A, Shorte S, Jacob Y, Vidalain PO, Charneau P, Clavel F, Arhel NJ. Microtubule-associated proteins 1 (MAP1) promote human immunodeficiency virus type I (HIV-1) intracytoplasmic routing to the nucleus. J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 20;290(8):4631-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.613133. Epub 2014 Dec 11. | ||
Revision as of 22:42, 25 January 2016
|
Contents |
Introduction
Function
Structural highlights
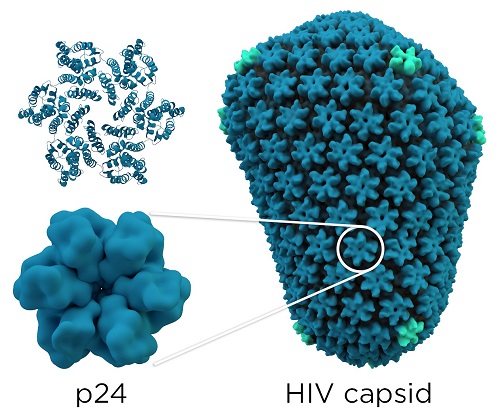
As you can see on the figure bellow, each monomer of capsid is linked to five others to form a hexamer. These hexamers (approximately 330 per virus) associates themselves to form a non-symetrical protein complex.
Interactions with others partners
Even if p24 is classified as a structural protein, it is also involved in many cellular infection processes.
You can find bellow in a non exhaustive list of p24 partners :
- Cytoskeleton (MAP1A, MAP1S, CKAP1, WIRE) - -
The HIV-1 capsid acts like a kind of "nuclear localisation signal" because it targets directly the virus toward the nucleus, where the integation takes place.
References
Structural image : By Thomas Splettstoesser (www.scistyle.com) (Own work) [CC BY-SA 4.0 (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)], via Wikimedia Commons
Cytoskeleton interactions :
- Fernandez J, Gärtner K, Becker A, et al. HIV-1 capsid interacts with cytoskeletal-associated proteins for intracytoplasmic routing to the nucleus. Retrovirology. 2013;10(Suppl 1):P34. doi:10.1186/1742-4690-10-S1-P34.
- Fernandez J, Portilho DM, Danckaert A, Munier S, Becker A, Roux P, Zambo A, Shorte S, Jacob Y, Vidalain PO, Charneau P, Clavel F, Arhel NJ. Microtubule-associated proteins 1 (MAP1) promote human immunodeficiency virus type I (HIV-1) intracytoplasmic routing to the nucleus. J Biol Chem. 2015 Feb 20;290(8):4631-46. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.613133. Epub 2014 Dec 11.