We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1120
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
<table> | <table> | ||
| - | <tr><td colspan='2'>The SRY protein is a 204 residues-long monomeric polypeptide. It is encoded by the SRY gene and is involved in the sex determination in mammals by being responsible for the gonadogenesis and so the male sexual development. It is the HMG-box that gives to the protein its ability to bind DNA by its minor groove | + | <tr><td colspan='2'>The SRY protein is a 204 residues-long monomeric polypeptide. It is encoded by the SRY gene and is involved in the sex determination in mammals by being responsible for the gonadogenesis and so the male sexual development. It is the HMG-box that gives to the protein its ability to bind DNA by its minor groove<ref name ="Tang">PMID: 9626701</ref>.</td></tr> |
<tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[1hrz|1hrz]]</td></tr> | <tr id='related'><td class="sblockLbl"><b>[[Related_structure|Related:]]</b></td><td class="sblockDat">[[1hrz|1hrz]]</td></tr> | ||
| Line 63: | Line 63: | ||
===Regulation of the expression of the SRY gene=== | ===Regulation of the expression of the SRY gene=== | ||
| - | In humans, the SRY promoter is located between −408 and −95 bp. Moreover, the SRY gene has enhancers at -727 pb. The linkage between regulatory proteins and these enhancers has the property to increase the production of SRY proteins. These regulatory proteins could be: SF1 (steroidogenic factor 1), SP1 and WT 1 (Wilms tumor) | + | In humans, the SRY promoter is located between −408 and −95 bp. Moreover, the SRY gene has enhancers at -727 pb. The linkage between regulatory proteins and these enhancers has the property to increase the production of SRY proteins. These regulatory proteins could be: SF1 (steroidogenic factor 1), SP1 and WT 1 (Wilms tumor)<ref name="Harley">Harley VR, Clarkson MJ, Argentaro A. The Molecular Action and Regulation of the Testis-Determining Factors, SRY (Sex-Determining Region on the Y Chromosome) and SOX9 [SRY-Related High-Mobility Group (HMG) Box 9]. Endocr Rev. 2003 Aug 1;24(4):466–87. [http://press.endocrine.org/doi/10.1210/er.2002-0025?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori%3Arid%3Acrossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%3Dpubmed&]</ref>. |
*'''SF1''': this transcriptional factor belongs to the family of nuclear hormone receptors and contains a zinc finger. The activation of this protein requires a ligand (hormone). | *'''SF1''': this transcriptional factor belongs to the family of nuclear hormone receptors and contains a zinc finger. The activation of this protein requires a ligand (hormone). | ||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
*'''SP1''': this transcriptional factor is an ubiquitous protein which binds rich GC-sites and is implicated in the transcription of many genes. Moreover, this protein contains a zinc finger. | *'''SP1''': this transcriptional factor is an ubiquitous protein which binds rich GC-sites and is implicated in the transcription of many genes. Moreover, this protein contains a zinc finger. | ||
| - | *'''WT1''' :this transcriptional factor transactivates the SRY gene. It contains a zinc finger | + | *'''WT1''' :this transcriptional factor transactivates the SRY gene. It contains a zinc finger<ref>Larney C, Bailey TL, Koopman P. Switching on sex: transcriptional regulation of the testis-determining gene Sry. Dev Camb Engl. 2014 Jun;141(11):2195–205</ref>. |
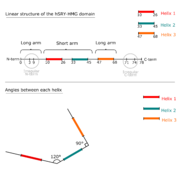
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
Revision as of 13:58, 30 January 2016
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 15/12/2015, through 15/06/2016 for use in the course "Structural Biology" taught by Bruno Kieffer at the University of Strasbourg, ESBS. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1120 through Sandbox Reserved 1159. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
SRY protein (AKA TDF protein)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Tang Y, Nilsson L. Interaction of human SRY protein with DNA: a molecular dynamics study. Proteins. 1998 Jun 1;31(4):417-33. PMID:9626701
- ↑ Sumner, A. T. Sex Chromosomes and Sex Determination. Chromosomes: Organization and Function, 97-108. [1]
- ↑ Bridges CB. TRIPLOID INTERSEXES IN DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. Science. 1921 Sep 16;54(1394):252-4. PMID:17769897 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.54.1394.252
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Goodfellow PN, Darling SM. Genetics of sex determination in man and mouse. Development. 1988 Feb;102(2):251-8. PMID:3046910
- ↑ Jost A. Becoming a male. Adv Biosci. 1973;10:3-13. PMID:4805859
- ↑ Gubbay J, Collignon J, Koopman P, Capel B, Economou A, Munsterberg A, Vivian N, Goodfellow P, Lovell-Badge R. A gene mapping to the sex-determining region of the mouse Y chromosome is a member of a novel family of embryonically expressed genes. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):245-50. PMID:2374589 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/346245a0
- ↑ Sinclair AH, Berta P, Palmer MS, Hawkins JR, Griffiths BL, Smith MJ, Foster JW, Frischauf AM, Lovell-Badge R, Goodfellow PN. A gene from the human sex-determining region encodes a protein with homology to a conserved DNA-binding motif. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):240-4. PMID:1695712 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/346240a0
- ↑ Werner MH, Huth JR, Gronenborn AM, Clore GM. Molecular basis of human 46X,Y sex reversal revealed from the three-dimensional solution structure of the human SRY-DNA complex. Cell. 1995 Jun 2;81(5):705-14. PMID:7774012
- ↑ NCBI gene
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 McElreavey K, Barbaux S, Ion A, Fellous M. The genetic basis of murine and human sex determination: a review. Heredity. 1995 Dec;75 ( Pt 6):599–611. [2]
- ↑ Sekido R, Lovell-Badge R. Genetic control of testis development. Sex Dev Genet Mol Biol Evol Endocrinol Embryol Pathol Sex Determ Differ. 2013;7(1-3):21–32
- ↑ NCBI nucleotide
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 Harley VR, Clarkson MJ, Argentaro A. The Molecular Action and Regulation of the Testis-Determining Factors, SRY (Sex-Determining Region on the Y Chromosome) and SOX9 [SRY-Related High-Mobility Group (HMG) Box 9]. Endocr Rev. 2003 Aug 1;24(4):466–87. [3]
- ↑ Larney C, Bailey TL, Koopman P. Switching on sex: transcriptional regulation of the testis-determining gene Sry. Dev Camb Engl. 2014 Jun;141(11):2195–205
- ↑ Murphy EC, Zhurkin VB, Louis JM, Cornilescu G, Clore GM. Structural basis for SRY-dependent 46-X,Y sex reversal: modulation of DNA bending by a naturally occurring point mutation. J Mol Biol. 2001 Sep 21;312(3):481-99. PMID:11563911 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2001.4977
- ↑ NCBI NCBI gene: SOX9 SRY-BOX9 Homo sapiens
- ↑ EBI-Interpro: Anti-Mullerian-Hormon, N-term
- ↑ 18.0 18.1 Veitia RA. Of adrenaline and SRY in males (comment on DOI 10.1002/bies.201100159). Bioessays. 2014 May;36(5):438. doi: 10.1002/bies.201400026. Epub 2014 Mar 7. PMID:24604382 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/bies.201400026
- ↑ Cohen, Tamara. The 'macho' gene that makes men behave aggressively has been found. The Daily Mail (2012). [4]
- ↑ Prokop JW, Watanabe IK, Turner ME, Underwood AC, Martins AS, Milsted A. From rat to human: regulation of Renin-Angiotensin system genes by sry. Int J Hypertens. 2012;2012:724240. doi: 10.1155/2012/724240. Epub 2012 Jan 22. PMID:22315667 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2012/724240
- ↑ de la Chapelle A. Analytic review: nature and origin of males with XX sex chromosomes. Am J Hum Genet. 1972 Jan;24(1):71-105. PMID:4622299
- ↑ Xue TC, Zhang L, Ren ZG, Chen RX, Cui JF, Ge NL, Ye SL. Sex-determination gene SRY potentially associates with poor prognosis but not sex bias in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig Dis Sci. 2015 Feb;60(2):427-35. doi: 10.1007/s10620-014-3377-y. Epub 2014 Oct, 2. PMID:25274159 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10620-014-3377-y