This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Gluten
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
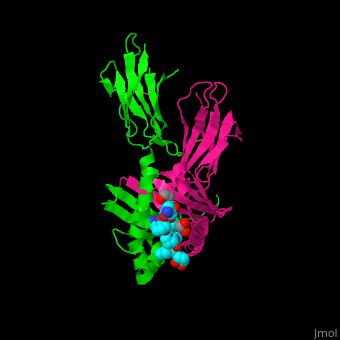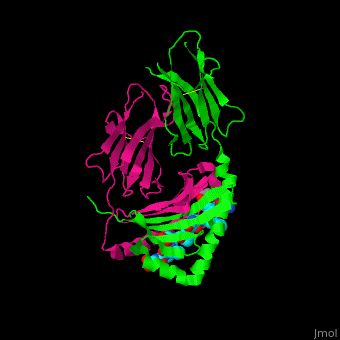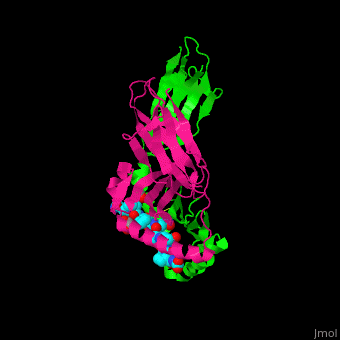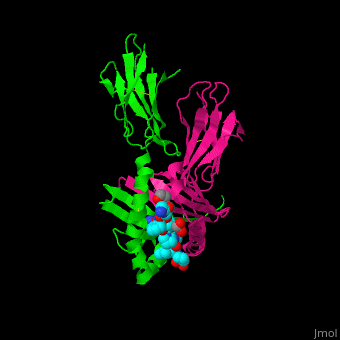
| + | <StructureSection load='1s9v' size='450' side='right' scene ='71/716500/The_best_scene_ever_premal/1' caption = 'Synthetic gliadin peptide complex with antibody (PDB code [[1s9v]])> | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
| Line 5: | Line 6: | ||
'''Gluten''' is a protein complex comprised of 2 components: '''gliadin''' (the water-soluble component) and '''glutenin''' (the water-isoluble component). Gliadins, for those with celiac disease, are the principle toxic component of gluten and are composed of proline and glutamine-rich peptide sequences. The peptides enter the circulatory system and come into contact with [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lymphocyte lymphocytes] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T_cell T-cells], resulting in the release of cytokines. The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cytokine cytokines] interact with the villi of the small intestine and damage them, disabling the body from nutrient absorption. The symptoms can include abdominal pain, weight loss, fatigue, and many other symptoms associated with malnutrition. As of now, the only treatment for celiac disease is the total exclusion of gluten from the person’s diet.<ref>Celiac Disease: MedlinePlus. Retrieved October 27, 2015, from https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/celiacdisease.html</ref><ref>Celiac Disease. Retrieved October 27, 2015, from http://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-topics/digestive-diseases/celiac-disease/Pages/facts.aspx</ref><ref>Go to Science. Retrieved October 27, 2015, from http://www.sciencemag.org/content/297/5590/2275.full</ref> | '''Gluten''' is a protein complex comprised of 2 components: '''gliadin''' (the water-soluble component) and '''glutenin''' (the water-isoluble component). Gliadins, for those with celiac disease, are the principle toxic component of gluten and are composed of proline and glutamine-rich peptide sequences. The peptides enter the circulatory system and come into contact with [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Lymphocyte lymphocytes] and [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/T_cell T-cells], resulting in the release of cytokines. The [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cytokine cytokines] interact with the villi of the small intestine and damage them, disabling the body from nutrient absorption. The symptoms can include abdominal pain, weight loss, fatigue, and many other symptoms associated with malnutrition. As of now, the only treatment for celiac disease is the total exclusion of gluten from the person’s diet.<ref>Celiac Disease: MedlinePlus. Retrieved October 27, 2015, from https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/celiacdisease.html</ref><ref>Celiac Disease. Retrieved October 27, 2015, from http://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-topics/digestive-diseases/celiac-disease/Pages/facts.aspx</ref><ref>Go to Science. Retrieved October 27, 2015, from http://www.sciencemag.org/content/297/5590/2275.full</ref> | ||
| - | |||
| - | <StructureSection load='1s9v' size='450' side='right' scene ='71/716500/The_best_scene_ever_premal/1' caption = 'Synthetic gliadin peptide complex with antibody (PDB code [[1s9v]])> | ||
== Gluten Protein Complex == | == Gluten Protein Complex == | ||
Revision as of 11:55, 10 March 2016
| |||||||||||
3D structures of gliadin
Updated on 10-March-2016
4gg6 – wGLI alpha/beta peptide + antibody + T-cell receptor – wheat
4z7u, 4z7v, 4z7w – wGLI alpha-1 peptide + antibody + T-cell receptor
4ozf, 4ozg, 4ozh, 4ozi – wGLI alpha-2 peptide + antibody + T-cell receptor
1s9v, 2nna – GLI alpha-1 peptide + antibody - synthetic
4d8p – wGLI gamma peptide + antibody
References
- ↑ Celiac Disease: MedlinePlus. Retrieved October 27, 2015, from https://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/celiacdisease.html
- ↑ Celiac Disease. Retrieved October 27, 2015, from http://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/health-topics/digestive-diseases/celiac-disease/Pages/facts.aspx
- ↑ Go to Science. Retrieved October 27, 2015, from http://www.sciencemag.org/content/297/5590/2275.full
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Maiuri, L., Ciacci, C., Ricciardelli, I., Vacca, L., Raia, V., Auricchio, S., . . . Londei, M. (2003). Association between innate response to gliadin and activation of pathogenic T cells in coeliac disease. Lancet, 362(9377), 30-37. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13803-2
- ↑ Mellins, E., & Stern, L. (n.d.). HLA-DM and HLA-DO, key regulators of MHC-ll processing and presentation. Current Opinion in Immunology, 26, 115-122. February 2014. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S095279151300215X
- ↑ Kim, C., Quartsen, H., Bergsen, E., Khosla, C., & Sollid, L.. (n.d.). Structural basis for HLA-DQ2-mediated presentation of gluten epitopes in celiac disease. Cross Mark, 101(12), 4175-4179. March 2004 http://www.pnas.org/content/101/12/4175.figures-only
- ↑ Henderson, K. N., Tye-Din, J. A., Reid, H. H., Chen, Z., Borg, N. A., Beissbarth, T., . . . Anderson, R. P. (2007). A structural and immunological basis for the role of human leukocyte antigen DQ8 in celiac disease. Immunity,27(1), 23-34. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2007.05.015
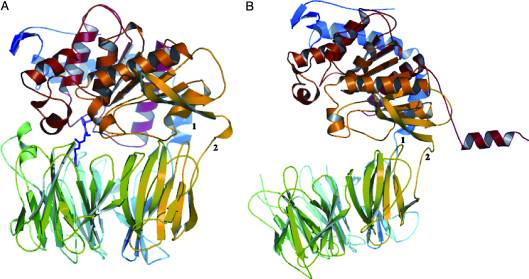
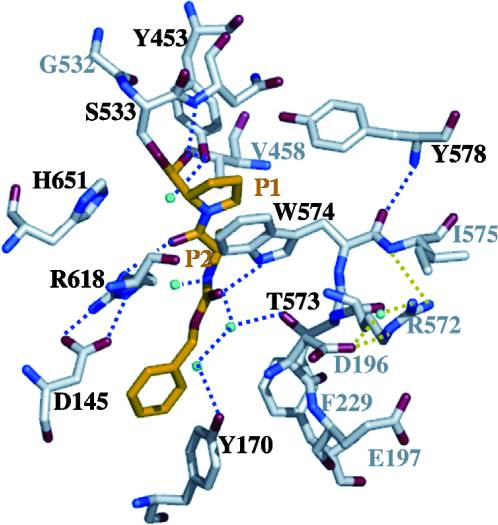
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 8.3 8.4 Shan, L., I. I. Mathews, and C. Khosla. "Structural and Mechanistic Analysis of Two Prolyl nEndopeptidases: Role of Interdomain Dynamics in Catalysis and Specificity." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 102.10 (2005): 3599-604. Web.
- ↑ Matysiak-Budnik, T., Candalh, C., Cellier, C., Dugave, C., Namane, A., Vidal-Martinez, T., . . . Heyman, M. (2005). Limited efficiency of prolyl-endopeptidase in the detoxification of gliadin peptides in celiac disease. Gastroenterology,129(3), 786-796. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2005.06.016
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Premal Patel, Eric Martz, Alexander Berchansky, Devin Joseph, Ben Horansky, Gunnar Reiske, Katlin Cannon, Joel L. Sussman, Jaime Prilusky