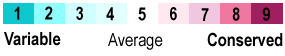Introduction to Evolutionary Conservation
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
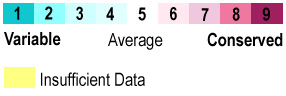
Mutations occur spontaneously in each generation, randomly changing an amino acid here and there in a protein. Individuals with mutations that impair critical functions of proteins may have resulting problems that make them less able to reproduce. Harmful mutations are lost from the gene pool because the individuals carrying them reproduce less effectively. Since the harmful mutations are lost, the amino acids critical for the function of a protein are '''conserved''' in the gene pool. In contrast, harmless (or very rare beneficial) mutations are kept in the gene pool, producing '''variability''' in non-critical amino acids. | Mutations occur spontaneously in each generation, randomly changing an amino acid here and there in a protein. Individuals with mutations that impair critical functions of proteins may have resulting problems that make them less able to reproduce. Harmful mutations are lost from the gene pool because the individuals carrying them reproduce less effectively. Since the harmful mutations are lost, the amino acids critical for the function of a protein are '''conserved''' in the gene pool. In contrast, harmless (or very rare beneficial) mutations are kept in the gene pool, producing '''variability''' in non-critical amino acids. | ||
| - | == | + | ==Example== |
| + | |||
| + | ===Rett Syndrome=== | ||
Consider the protein methyl CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2; [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P51608 UniProt MECP2_HUMAN]). Although its function is still unclear, it is expressed throughout the body, and disruption of its function causes problems with brain development and function<ref name="ghr">[http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/gene/MECP2 MECP2 article] in the ''National Library of Medicine's Genetic Home Reference''</ref>. Some mutations in MeCP2 cause [http://workshops.molviz.org/slides/rett/rett.htm Rett Syndrome], a severely debilitating congential condition affecting mostly women. These women are unlikely to have children; hence, the mutations in their MeCP2 genes are lost from the human gene pool. Because the mutations are lost, the amino acids at the mutated positions remain unchanged (identical) in the vast majority of people. That is, they are conserved. | Consider the protein methyl CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2; [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P51608 UniProt MECP2_HUMAN]). Although its function is still unclear, it is expressed throughout the body, and disruption of its function causes problems with brain development and function<ref name="ghr">[http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/gene/MECP2 MECP2 article] in the ''National Library of Medicine's Genetic Home Reference''</ref>. Some mutations in MeCP2 cause [http://workshops.molviz.org/slides/rett/rett.htm Rett Syndrome], a severely debilitating congential condition affecting mostly women. These women are unlikely to have children; hence, the mutations in their MeCP2 genes are lost from the human gene pool. Because the mutations are lost, the amino acids at the mutated positions remain unchanged (identical) in the vast majority of people. That is, they are conserved. | ||
Revision as of 21:26, 4 August 2018
| |||||||||||
See Also
Notes and References
- ↑ MECP2 article in the National Library of Medicine's Genetic Home Reference
- ↑ Advantageous variability will be seen in these cases: 5hmg, 2vaa, 3hi6.