This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Rhomboid protease
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
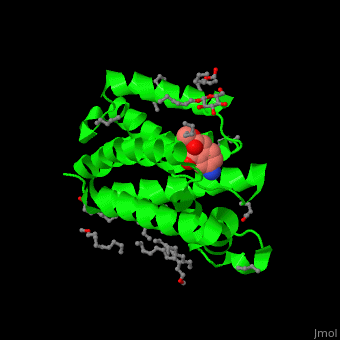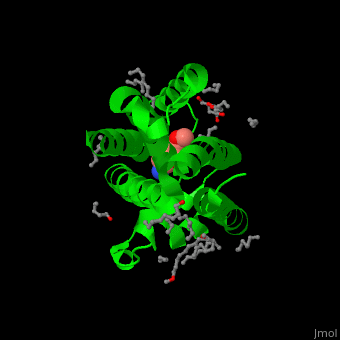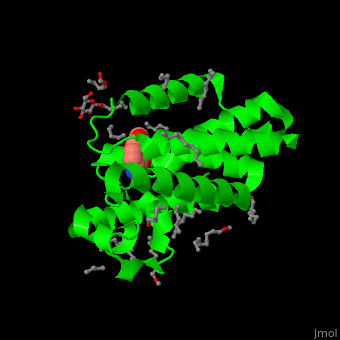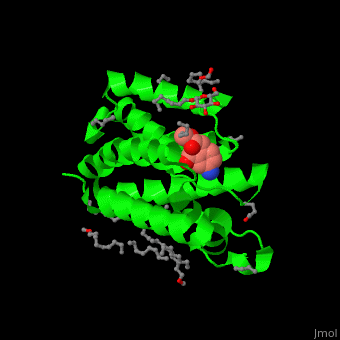
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='' size='450' side='right' caption='Structure of rhomboid protease complex with inhibitor isocoumarin and nonyglucoside detergent molecules (PDB entry [[2xow]])' scene='55/551211/Cv/1'> |
== Function == | == Function == | ||
'''Rhomboid protease''' (GlpG) is a transmembranal serine protease. The active site is buried in the lipid bilayer of cell membrane. It cleaves proteins within their transmembrane domain<ref>PMID:18605900</ref>. Rhomboids regulate many cellular processes and are involved in many human diseases. The catalytic site of rhomboids contains a hydrophilic pocket protected from the lipid bilayer. Rhomboids are specific for a single transmembranal helix proteins. | '''Rhomboid protease''' (GlpG) is a transmembranal serine protease. The active site is buried in the lipid bilayer of cell membrane. It cleaves proteins within their transmembrane domain<ref>PMID:18605900</ref>. Rhomboids regulate many cellular processes and are involved in many human diseases. The catalytic site of rhomboids contains a hydrophilic pocket protected from the lipid bilayer. Rhomboids are specific for a single transmembranal helix proteins. | ||
Revision as of 05:57, 22 October 2017
| |||||||||||
3D Structures of rhomboid protease
Updated on 22-October-2017
References
- ↑ Freeman M. Rhomboid proteases and their biological functions. Annu Rev Genet. 2008;42:191-210. doi: 10.1146/annurev.genet.42.110807.091628. PMID:18605900 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1146/annurev.genet.42.110807.091628
- ↑ Vinothkumar KR, Strisovsky K, Andreeva A, Christova Y, Verhelst S, Freeman M. The structural basis for catalysis and substrate specificity of a rhomboid protease. EMBO J. 2010 Oct 1. PMID:20890268 doi:10.1038/emboj.2010.243