We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Aromatase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
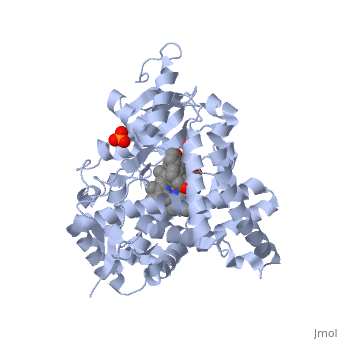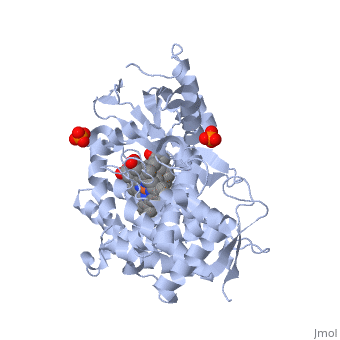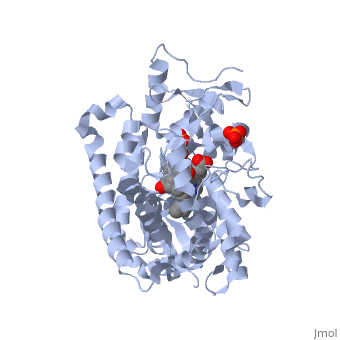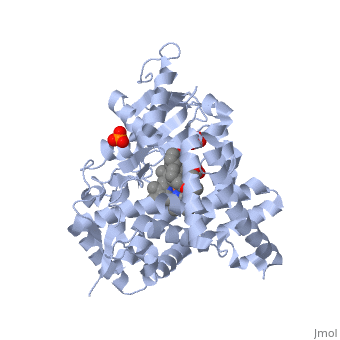
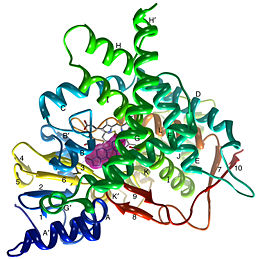
[[Image:Aromatase_Structure.jpg|thumb|260px|left| Ribbon diagram displaying the overall structure of human placental aromatase. <ref name="structure"/>]] | [[Image:Aromatase_Structure.jpg|thumb|260px|left| Ribbon diagram displaying the overall structure of human placental aromatase. <ref name="structure"/>]] | ||
| - | + | {{Clear}} | |
== Structure== | == Structure== | ||
Due to the membrane-bound nature of mammalian CYP enzymes, the structural characterization is extremely difficult. Aromatase is a monomeric enzyme composed of a heme-prosthetic group and a single polypeptide chain consisting of 503 amino acid residues.<ref name="structure" /> One important feature of CYPs is the iron-containing <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_382/Porphyrin/1'>porphyrin</scene> group at the enzyme active site.<ref> PMID: 16395678 </ref> The <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_382/Heme_iron/3'>heme iron</scene> is within the porphyrin and is considered the reaction center of the enzyme. The <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_382/Ligand/3'>ligand</scene> docks in a region adjacent to the porphyrin. Aromatase is anchored to the endoplasmic reticulum by the amino terminal transmembrane domain. The tertiary structure of aromatase includes twelve major α-helices and ten β-strands.<ref name="structure" /> An androstenedione molecule is bound in the active site of the enzyme. The active site of the enzyme can be found in the distal cavity of the heme-binding pocket. '''A ribbon diagram displaying the overall structure of the human placental aromatase is shown to the left.''' The amino terminus starts at residue 45 and is shown in dark blue. The carboxyl terminus ending at residue 496 is shown in red. The helices are labeled A-L and the sheets are labeled 1-10 accordingly. The heme group and the bound ligand are shown in the center of the protein. <ref name="structure" /> | Due to the membrane-bound nature of mammalian CYP enzymes, the structural characterization is extremely difficult. Aromatase is a monomeric enzyme composed of a heme-prosthetic group and a single polypeptide chain consisting of 503 amino acid residues.<ref name="structure" /> One important feature of CYPs is the iron-containing <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_382/Porphyrin/1'>porphyrin</scene> group at the enzyme active site.<ref> PMID: 16395678 </ref> The <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_382/Heme_iron/3'>heme iron</scene> is within the porphyrin and is considered the reaction center of the enzyme. The <scene name='Sandbox_Reserved_382/Ligand/3'>ligand</scene> docks in a region adjacent to the porphyrin. Aromatase is anchored to the endoplasmic reticulum by the amino terminal transmembrane domain. The tertiary structure of aromatase includes twelve major α-helices and ten β-strands.<ref name="structure" /> An androstenedione molecule is bound in the active site of the enzyme. The active site of the enzyme can be found in the distal cavity of the heme-binding pocket. '''A ribbon diagram displaying the overall structure of the human placental aromatase is shown to the left.''' The amino terminus starts at residue 45 and is shown in dark blue. The carboxyl terminus ending at residue 496 is shown in red. The helices are labeled A-L and the sheets are labeled 1-10 accordingly. The heme group and the bound ligand are shown in the center of the protein. <ref name="structure" /> | ||
Current revision
| |||||||||||
3D structures of aromatase
See human P450 19 family in Cytochrome P450
References
- ↑ Kagawa N. Efficient expression of human aromatase (CYP19) in E. coli. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;705:109-22. PMID:21125383 doi:10.1007/978-1-61737-967-3_7
- ↑ Conley A, Hinshelwood M. Mammalian aromatases. Reproduction. 2001 May;121(5):685-95. PMID:11427156
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 Ghosh, D., Griswold, J., Erman, M., Pangborn, W. " X-ray Structure of Human Aromatase Reveals An Androgen-Specific Active Site" Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. [Online] 2010,Vol. 118, Issue 4-5, p197-202. [1]
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 "Aromatase Products" [2]
- ↑ Favia AD, Cavalli A, Masetti M, Carotti A, Recanatini M. Three-dimensional model of the human aromatase enzyme and density functional parameterization of the iron-containing protoporphyrin IX for a molecular dynamics study of heme-cysteinato cytochromes. Proteins. 2006 Mar 1;62(4):1074-87. PMID:16395678 doi:10.1002/prot.20829
- ↑ "Aromatase Inhibitors" [3]
- ↑ Jones ME, Boon WC, McInnes K, Maffei L, Carani C, Simpson ER. Recognizing rare disorders: aromatase deficiency. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab. 2007 May;3(5):414-21. PMID:17452968 doi:10.1038/ncpendmet0477
- ↑ Stratakis CA, Vottero A, Brodie A, Kirschner LS, DeAtkine D, Lu Q, Yue W, Mitsiades CS, Flor AW, Chrousos GP. The aromatase excess syndrome is associated with feminization of both sexes and autosomal dominant transmission of aberrant P450 aromatase gene transcription. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1998 Apr;83(4):1348-57. PMID:9543166
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, David Canner, Joel L. Sussman, Whitney Smith, Alexander Berchansky