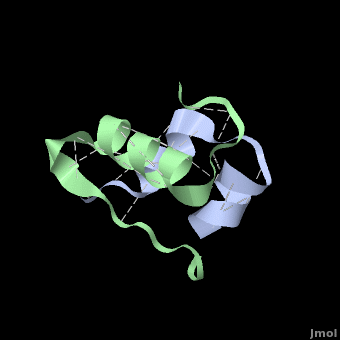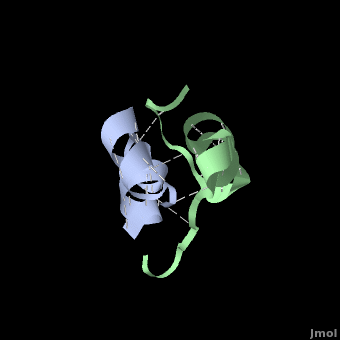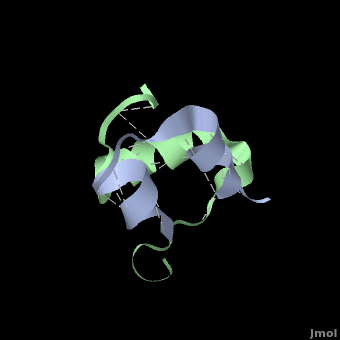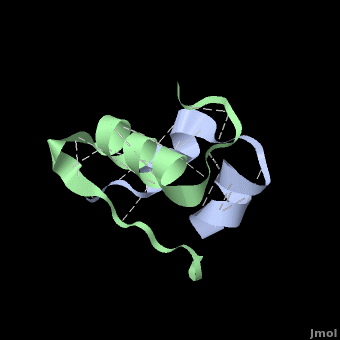Molecular Playground/Insulin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Human_insulin2/1' caption='Human insulin chain A (grey) and chain B (green), [[3i40]]'> | <StructureSection load='' size='350' side='right' scene='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Human_insulin2/1' caption='Human insulin chain A (grey) and chain B (green), [[3i40]]'> | ||
[[Image:InsulinHexamer.jpg|200px|left]] | [[Image:InsulinHexamer.jpg|200px|left]] | ||
| - | '''איסולין''' הוא הורמון המפקח על המטבוליזם של פחמימות | + | ''',איסולין''' הוא הורמון המפקח על [[Carbohydrate Metabolism|המטבוליזם של פחמימות ]] ומאגרי הסוכר בגוף האדם. הגוף מסוגל לחוש את ריכוז הסוכר בדם ומגיב בהפרשת איסולין |
| - | המיוצר בתאי בטא שבלבלב | + | המיוצר בתאי בטא שבלבלב. |
| - | סינטזה של אינסולין הומני בחיידק E. coli הוא חשוב לייצור אינסולין לצורך טיפול בסוכרת שלב 1. '''פרואינסולין''' מעובד | + | סינטזה של אינסולין הומני בחיידק E. coli הוא חשוב לייצור אינסולין לצורך טיפול בסוכרת שלב 1. '''פרואינסולין''' (Pins) מעובד בעזרת מספר פרוטאזות במערכת הגולג'י וממנו נוצר האינסולין, הקצר ב-35 חומצות אמינו מהפרואינסולין. |
| - | + | אינסולין מורכב משני חלקים הנקראים שרשרות A ו-B הנראות בצבעים אפור וירוק בהתאמה. שתי השרשרות קשורות בקשרי די-סולפיד הנראים בצהוב. | |
| - | + | המודל הנראה בצבעים ירוק-אפור הוא מונומר של אינסולין והוא ההורמון הפעיל. בצורתו זו הוא נקשר אל הרצפטור לאינסולין הנמצא בתאי שומן או השריר בגוף. וע"י כך מסמן לרצפטור | |
| + | לקשור גלוקוז, או סוכר, מהדם ולשמור אותו בתא. | ||
| - | | + | אינסולין מסוגר להתקשר לעצמו וליצור דימר ע"י יצירת קשרי מימן בין הקצוות של שרשרות ה-B. <scene name='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Insulin_dimer/2'>קשרי מימן אלה</scene> נראים במודל בצבע לבן. |
| - | + | בנוסף לכך, 3 דימרים כאלה, בנוכחות יוני אבץ, יכולים להיקשר יחד ליצירת | |
| - | + | <scene name='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Insulin_hexamer/4'>הקסמר</scene>. | |
| + | אינסולין נאגר בגוף בצורת ההקסמר. | ||
| + | Insulin is able to pair-up with itself and form a dimer by forming hydrogen bonds between the ends of two B-chains. These are shown above in white. Then, 3 dimers can come together in the presence of zinc ions and form a hexamer. Insulin is stored in the <scene name='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Insulin_hexamer/4'>hexameric form</scene> in the body. This <scene name='User:Whitney_Stoppel/sandbox1/Insulin_ph7/2'>scene highlights</scene> the hydrophobic (gray) and polar (purple) parts of an insulin monomer at a pH of 7. It is believed that the hydrophobic sections on the B-chain cause insulin aggregation which initially caused problems in the manufacture and storage of insulin for [[Pharmaceutical_Drugs#Treatments|pharmaceutical use]]. | ||
</StructureSection> For additional details see<br /> | </StructureSection> For additional details see<br /> | ||
[[Insulin Structure & Function]]<br /> | [[Insulin Structure & Function]]<br /> | ||
Revision as of 12:50, 3 July 2017
One of the CBI Molecules being studied in the University of Massachusetts Amherst Chemistry-Biology Interface Program at UMass Amherst in the Roberts Research Group and on display at the Molecular Playground.
| |||||||||||
Insulin Structure & Function
Diabetes & Hypoglycemia
Insulin (Hebrew)
Insulin mo-or-sl (Hebrew).
3D structures of Insulin
(Updated on 03-July-2017)
References
Additional Resources
For additional information, see: Diabetes & Hypoglycemia
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Joel L. Sussman, Shelly Livne, Karsten Theis, David Canner, Whitney Stoppel, Alexander Berchansky, Yael Shwartz, Lynmarie K Thompson, Jaime Prilusky