Beta-glucosidase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
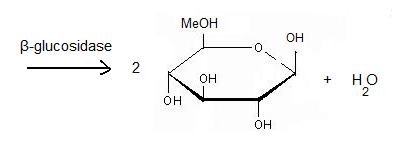
'''β-glucosidase''' is an enzyme which catalyses the hydrolysis of terminal non-reducing residues in β-glucosides (EC number : 3.2.1.21). In the case of 2VRJ, it comes from ''Thermotoga maritima'' which is a rod-shaped bacterium belonging to the order of Thermotogates. This bacterium was originally isolated from geothermal heated marine sediments. | '''β-glucosidase''' is an enzyme which catalyses the hydrolysis of terminal non-reducing residues in β-glucosides (EC number : 3.2.1.21). In the case of 2VRJ, it comes from ''Thermotoga maritima'' which is a rod-shaped bacterium belonging to the order of Thermotogates. This bacterium was originally isolated from geothermal heated marine sediments. | ||
| - | 2VRJ is here is in complex with an inhibitor called N-octyl-5-deoxy66-oxa-N-carbamoylcalystegine <ref>PMID: 18833549</ref>. Raucaffricine β-glucosidase (RGB) catalyzes the conversion of raucaffricine to glucose and vomilenine. Some more details in<br /> | + | 2VRJ is here is in complex with an inhibitor called N-octyl-5-deoxy66-oxa-N-carbamoylcalystegine <ref>PMID: 18833549</ref>. '''Raucaffricine β-glucosidase''' (RGB) catalyzes the conversion of raucaffricine to glucose and vomilenine. Some more details in<br /> |
* [[Molecular Playground/Beta-galactosidase]]<br /> | * [[Molecular Playground/Beta-galactosidase]]<br /> | ||
* [[Partially deglycosylated acid-beta-glucosidase]]<br /> | * [[Partially deglycosylated acid-beta-glucosidase]]<br /> | ||
| Line 130: | Line 130: | ||
**[[5dt7]], [[5dt5]] – GB – ''Exiguobacterium antarcticum''<br /> | **[[5dt7]], [[5dt5]] – GB – ''Exiguobacterium antarcticum''<br /> | ||
**[[5cg0]] – GB – fall armyworm<br /> | **[[5cg0]] – GB – fall armyworm<br /> | ||
| - | **[[5bwf]] – GB – ''Trichoderma harzianum''<br /> | + | **[[5bwf]], [[5jbk]], [[5jbo]] – GB – ''Trichoderma harzianum''<br /> |
**[[5bvu]] – TxGB – ''Thermoanaerobacterium xylanolyticum''<br /> | **[[5bvu]] – TxGB – ''Thermoanaerobacterium xylanolyticum''<br /> | ||
**[[3w53]] – GB – ''Micrococcus antarcticus''<br /> | **[[3w53]] – GB – ''Micrococcus antarcticus''<br /> | ||
**[[4mdo]] – HgGB – ''Humicola grisea''<br /> | **[[4mdo]] – HgGB – ''Humicola grisea''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[3wh5]], [[3u48]], [[3u4a]] – MeGB – ''Metagenome''<br /> | + | **[[3wh5]], [[3u48]], [[3u4a]], [[5gnx]], [[5gny]], [[5gnz]], [[5wka]] – MeGB – ''Metagenome''<br /> |
**[[5ayi]], [[5ayb]] – MeGB (mutant)<br /> | **[[5ayi]], [[5ayb]] – MeGB (mutant)<br /> | ||
**[[5ju6]] – GB – ''Talaromyces emersonii''<br /> | **[[5ju6]] – GB – ''Talaromyces emersonii''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5wug]], [[5wvp]] – GB – ''Paenibacillus barengoltzii''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5xxl]] – BtGB – ''Bacterioides thetaiotaomicron''<br /> | ||
*Beta-glucosidase complex with sugar | *Beta-glucosidase complex with sugar | ||
| Line 162: | Line 164: | ||
**[[1e4i]] - BpGB (mutant) + glucoside<br /> | **[[1e4i]] - BpGB (mutant) + glucoside<br /> | ||
**[[2e40]] – PcGB + gluconolactone<br /> | **[[2e40]] – PcGB + gluconolactone<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5xxm]] - BtGB + gluconolactone<br /> | ||
**[[3vif]] - NkGB + gluconolactone – ''Neotermes koshunensis''<br /> | **[[3vif]] - NkGB + gluconolactone – ''Neotermes koshunensis''<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5xxn]], [[5xxo]] - BtGB + sophorose derivative<br /> | ||
**[[3vig]], [[3vii]] - NkGB + saccharide<br /> | **[[3vig]], [[3vii]] - NkGB + saccharide<br /> | ||
**[[3vih]] – NkGB + glycerol<br /> | **[[3vih]] – NkGB + glycerol<br /> | ||
| Line 183: | Line 187: | ||
**[[4mdp]] – HgGB + glucose<br /> | **[[4mdp]] – HgGB + glucose<br /> | ||
**[[3wh6]] – MeGB + glucose<br /> | **[[3wh6]] – MeGB + glucose<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5z9s]] – EcGB + glucose – ''Escherichia coli''<br /> | ||
**[[3wh7]] – MeGB + fucose<br /> | **[[3wh7]] – MeGB + fucose<br /> | ||
**[[3wh8]] – MeGB + isofagomine<br /> | **[[3wh8]] – MeGB + isofagomine<br /> | ||
| + | **[[5nbs]] – GB + mannose – ''Neurospora crassa''<br /> | ||
*Beta-glucosidase complex with inhibitor | *Beta-glucosidase complex with inhibitor | ||
| Line 201: | Line 207: | ||
**[[1up6]], [[1up7]] – TmPGB + NAD + G6P<br /> | **[[1up6]], [[1up7]] – TmPGB + NAD + G6P<br /> | ||
**[[3qom]], [[4gze]] – PGB – ''Lactobacillus plantarum''<br /> | **[[3qom]], [[4gze]] – PGB – ''Lactobacillus plantarum''<br /> | ||
| - | **[[2xhy]] – | + | **[[2xhy]] – EcPGB <br /> |
**[[1h4p]] – PGB I/II – yeast<br /> | **[[1h4p]] – PGB I/II – yeast<br /> | ||
**[[3eqn]] – WfPGB – White-rot fungus<br /> | **[[3eqn]] – WfPGB – White-rot fungus<br /> | ||
| Line 217: | Line 223: | ||
**[[4gzi]] – poGGB (mutant)<br /> | **[[4gzi]] – poGGB (mutant)<br /> | ||
**[[4gzj]] - poGGB (mutant) + saccharide | **[[4gzj]] - poGGB (mutant) + saccharide | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Glucan 1,4-β-glucosidase | ||
| + | |||
| + | **[[5m6g]] – CaGGB + sorbitol – ''Saccharopolyspora erythraea''<br /> | ||
*Raucaffricine-β-glucosidase | *Raucaffricine-β-glucosidase | ||
Revision as of 09:36, 28 March 2018
| |||||||||||
3D structures of Beta-glucosidase
Updated on 28-March-2018
References
- ↑ Aguilar M, Gloster TM, Garcia-Moreno MI, Ortiz Mellet C, Davies GJ, Llebaria A, Casas J, Egido-Gabas M, Garcia Fernandez JM. Molecular basis for beta-glucosidase inhibition by ring-modified calystegine analogues. Chembiochem. 2008 Nov 3;9(16):2612-8. PMID:18833549 doi:10.1002/cbic.200800451
- ↑ http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/B-glucosidase
- ↑ Davies G, Henrissat B. Structures and mechanisms of glycosyl hydrolases. Structure. 1995 Sep 15;3(9):853-9. PMID:8535779
- ↑ http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/IEntry?ac=IPR018120#PUB00002205
- ↑ http://www.ebi.ac.uk/thornton-srv/databases/cgi-bin/CSA/CSA_Site_Wrapper.pl?pdb=2vrj
- ↑ Davies G, Henrissat B. Structures and mechanisms of glycosyl hydrolases. Structure. 1995 Sep 15;3(9):853-9. PMID:8535779
- ↑ http://www.cazy.org/fam/ghf_INV_RET.html#3
- ↑ Dvir H, Harel M, McCarthy AA, Toker L, Silman I, Futerman AH, Sussman JL. X-ray structure of human acid-beta-glucosidase, the defective enzyme in Gaucher disease. EMBO Rep. 2003 Jul;4(7):704-9. PMID:12792654 doi:10.1038/sj.embor.embor873
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 9.2 Premkumar L, Sawkar AR, Boldin-Adamsky S, Toker L, Silman I, Kelly JW, Futerman AH, Sussman JL. X-ray structure of human acid-beta-glucosidase covalently bound to conduritol-B-epoxide. Implications for Gaucher disease. J Biol Chem. 2005 Jun 24;280(25):23815-9. Epub 2005 Apr 6. PMID:15817452 doi:M502799200
- ↑ Hrmova M, Varghese JN, De Gori R, Smith BJ, Driguez H, Fincher GB. Catalytic mechanisms and reaction intermediates along the hydrolytic pathway of a plant beta-D-glucan glucohydrolase. Structure. 2001 Nov;9(11):1005-16. PMID:11709165
- ↑ Zeev-Ben-Mordehai T, Silman I, Sussman JL. Acetylcholinesterase in motion: visualizing conformational changes in crystal structures by a morphing procedure. Biopolymers. 2003 Mar;68(3):395-406. PMID:12601798 doi:10.1002/bip.10287
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 Shaaltiel Y, Bartfeld D, Hashmueli S, Baum G, Brill-Almon E, Galili G, Dym O, Boldin-Adamsky SA, Silman I, Sussman JL, Futerman AH, Aviezer D. Production of glucocerebrosidase with terminal mannose glycans for enzyme replacement therapy of Gaucher's disease using a plant cell system. Plant Biotechnol J. 2007 Sep;5(5):579-90. Epub 2007 May 24. PMID:17524049 doi:10.1111/j.1467-7652.2007.00263.x
- ↑ Brumshtein B, Greenblatt HM, Butters TD, Shaaltiel Y, Aviezer D, Silman I, Futerman AH, Sussman JL. Crystal structures of complexes of N-butyl- and N-nonyl-deoxynojirimycin bound to acid beta-glucosidase: insights into the mechanism of chemical chaperone action in Gaucher disease. J Biol Chem. 2007 Sep 28;282(39):29052-8. Epub 2007 Jul 31. PMID:17666401 doi:10.1074/jbc.M705005200
- ↑ Lieberman RL, Wustman BA, Huertas P, Powe AC Jr, Pine CW, Khanna R, Schlossmacher MG, Ringe D, Petsko GA. Structure of acid beta-glucosidase with pharmacological chaperone provides insight into Gaucher disease. Nat Chem Biol. 2007 Feb;3(2):101-7. Epub 2006 Dec 24. PMID:17187079 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nchembio850
- ↑ Brumshtein B, Wormald MR, Silman I, Futerman AH, Sussman JL. Structural comparison of differently glycosylated forms of acid-beta-glucosidase, the defective enzyme in Gaucher disease. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr. 2006 Dec;62(Pt 12):1458-65. Epub 2006, Nov 23. PMID:17139081 doi:S0907444906038303
- ↑ 16.0 16.1 Brumshtein B, Salinas P, Peterson B, Chan V, Silman I, Sussman JL, Savickas PJ, Robinson GS, Futerman AH. Characterization of gene-activated human acid-beta-glucosidase: crystal structure, glycan composition, and internalization into macrophages. Glycobiology. 2010 Jan;20(1):24-32. Epub 2009 Sep 9. PMID:19741058 doi:10.1093/glycob/cwp138
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Michal Harel, Muriel Breteau, Alexander Berchansky, Joel L. Sussman, David Canner