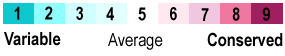Mutations occur spontaneously in each generation, randomly changing an amino acid here and there in a protein. Individuals with mutations that impair critical functions of proteins may have resulting problems that make them less able to reproduce. Harmful mutations are lost from the gene pool because the individuals carrying them reproduce less effectively. Since the harmful mutations are lost, the amino acids critical for the function of a protein are conserved in the gene pool. In contrast, harmless (or very rare beneficial) mutations are kept in the gene pool, producing variability in non-critical amino acids.
Example
Rett Syndrome
Consider the protein methyl CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2; UniProt MECP2_HUMAN). Although its function is still unclear, it is expressed throughout the body, and disruption of its function causes problems with brain development and function[1]. Some mutations in MeCP2 cause Rett Syndrome, a severely debilitating congential condition affecting mostly women. These women are unlikely to have children; hence, the mutations in their MeCP2 genes are lost from the human gene pool. Because the mutations are lost, the amino acids at the mutated positions remain unchanged (identical) in the vast majority of people. That is, they are conserved.
|
Example
|
Effect of mutation on protein function
|
Genetic consequence
|
|
R133C*
|
Function LOST**
|
Mutation is LOST from gene pool, so
R133 is CONSERVED.
|
|
E143?*
|
None
|
Mutation remains in gene pool, so
E143 is NOT conserved.
|
|
* in methyl CpG binding protein 2 (MeCP2),
3c2i. Amino acid sequence in 1 letter code:
ASASPKQRRS IIRDRGPMYD
DPTLPEGWTR KLKQRKSGRS AGKYDVYLIN
PQGKAFRSKV
ELIMYFEKVG DTSLDPNDFD
FTVTGRGSPS RHHHHHH
|
|
133
143
** Mutation R133C causes
Rett syndrome,
a severe neurological disorder.
E143 is highly variable, so mutations here are harmless and remain in the gene pool.
Gray: disordered in crystal, absent in model 3c2i.
|
Locations of Mutations in 3D Model
The positions of conserved Arg133 and variable Glu143 are highlighted with yellow halos (). You can see that conserved Arg133 is in intimate contact with the DNA, while variable Glu143 is on the surface, and remote from the contact with the DNA.
Finding Conservation
Simplistic Analysis of Conservation
Evolutionary conservation in proteins is identified by aligning the amino acid sequences of proteins with the same function from different taxa (orthologs). As an example, we'll use the glycolytic enzyme enolase, present in a wide range of taxa. Take a quick look to get an impression of a multiple sequence alignment for ~400 amino acids in enolase for taxa ranging from eubacteria and archaebacteria through yeast, insects, and humans. In the full multiple sequence alignment is one segment highlighted in pink . This segment is enlarged below.

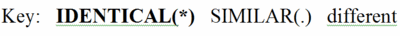
By comparing the amino acids in each column, you will find that some positions are 100% identical (conserved) between taxa. These amino acids are in BOLD UPPER CASE and indicated by an asterisk (*) at the bottom of the column.
Other columns are similar but not identical. That is, the general properties of the amino acids in these columns are similar. Hence they are not highly conserved, but there is some evolutionary pressure to keep similar amino acids in these positions, which are marked with UPPER CASE and a period (.) below the column. (The definitions of similar are given at the bottom of the full multiple sequence alignment page.)
Finally, there are columns in which at least two of the amino acids are not only different, but also not members of a group of amino acids with similar properties. These are given in lower case, and there is no mark at the bottom of the column.
Sophisticated Analysis of Conservation: ConSurf
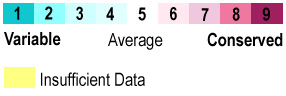
The above analysis assigns each amino acid in enolase to one of three categories: conserved, similar, or different. This is very simplistic, and sensitive to the addition or removal of one or a few sequences from the alignment which can have a large effect on the results. In contrast, the analysis used in Proteopedia (and in the molecular view at right) is sophisticated, using many more sequences, and weighting the impact of each sequence in the multiple sequence alignment according to the phylogenetic tree calculated from the alignment. This sophisticated determination of conservation and variability is done by the ConSurf Servers (see also summaries of their mechanism: short version, or longer version). ConSurf's analysis is robust: addition or removal of a few sequences has little effect. ConSurf divides conservation into 9 levels, and colors them as follows:
Sequence Colored by Conservation
When ConSurf's colors are applied to the 436 amino acids in the sequence of enolase (based on a multiple sequence alignment containing 150 sequences), this is the result:
Notice that the conserved residues are scattered around the sequence with no obvious pattern.
3D Structure Colored by Conservation
However, when the same , they form a conserved patch around the catalytic site (marked with a zinc ion colored green .
Conserved surface patches identify functional regions of proteins. Less commonly, patches of high variability may also be functional. (Can you think of situations where high variability would be advantageous?[2])
For instructions on how to identify conserved regions of a molecule of interest, and how to show them in Proteopedia (for example with green links), please see How to see conserved regions.
Expected vs. Unexpected Conservation
Conservation is expected for those amino acids that support the 3D structure and functions of a protein. Common examples are listed in the table below. When there is no known structural or functional explanation for conservation of an amino acid, or a cluster of amino acids, their conservation is unexpected. Unexpected conservation may provide clues for discovering new functions or structural features, e.g. through functional analysis of mutants.
|
Expected Evolutionary Conservation
|
|
Amino Acids
|
Reason for Conservation
|
|---|
|
Gly, Pro in turns between helices or beta strands
|
Required for protein domain folding
|
|
Charged amino acid (Lys, Arg, Asp, Glu) in a salt bridge
|
Required for protein stability
|
|
Cys in a disulfide bond
|
Required for protein stability
|
|
N-terminal Met
|
Start codon for protein synthesis
|
|
Amino acids in a large cluster of highly-conserved residues
|
Required for protein function, e.g. catalytic or binding site
|
FirstGlance in Jmol makes it easy to locate turns, salt bridges, disulfide bonds, or the N-teminus. In FirstGlance:
- Touch the conserved residue of interest to get its name and sequence number, e.g. Gly236 (in enolase 4enl).
- Use Find to put yellow halos around the residue of interest, e.g. enter Gly236 in the Find slot.
- Turns: Views tab, Secondary Structure.
- Salt bridges: Tools tab, Salt Bridges.
- Disulfide bonds: Tools tab, Disulfide Bonds.
- N terminus: Views tab, N->C Rainbow. You may also wish to check Sequence Numbers and/or Residue Names near the bottom of the control panel (upper left panel).