Aspartate carbamoyltransferase
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
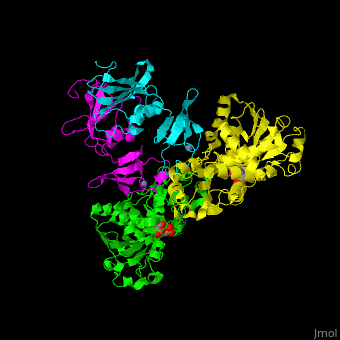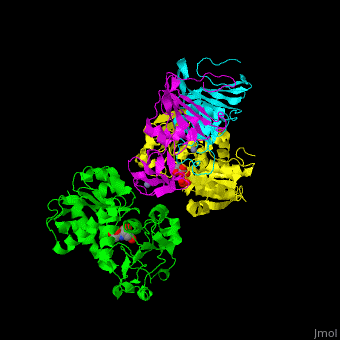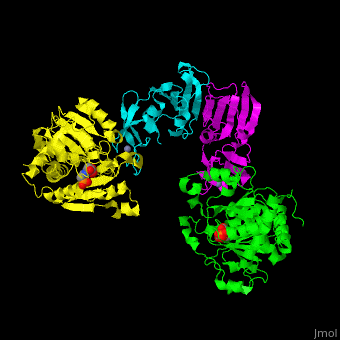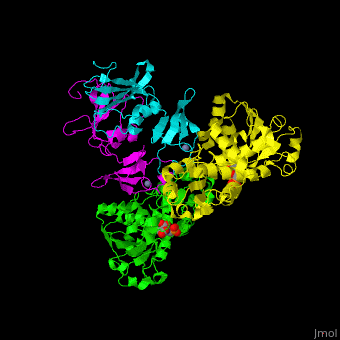
ATC is composed of <scene name='59/592660/Cv/10'>2 trimers of catalytic subunits (C) and 3 dimers of regulatory subunits (R)</scene>. Click to see <scene name='59/592660/Cv/11'>two catalytic trimers</scene> and <scene name='59/592660/Cv/12'>three regulatory dimers</scene>. The <scene name='59/592660/Cv/13'>catalytic subunit</scene> contains an <scene name='59/592660/Cv/14'>aspartate-binding domain</scene> and a carbamoyl-phosphate-binding domain. The regulatory subunit contains a nucleotide effectors-binding domain and a zinc domain. <ref>PMID:10651286</ref> | ATC is composed of <scene name='59/592660/Cv/10'>2 trimers of catalytic subunits (C) and 3 dimers of regulatory subunits (R)</scene>. Click to see <scene name='59/592660/Cv/11'>two catalytic trimers</scene> and <scene name='59/592660/Cv/12'>three regulatory dimers</scene>. The <scene name='59/592660/Cv/13'>catalytic subunit</scene> contains an <scene name='59/592660/Cv/14'>aspartate-binding domain</scene> and a carbamoyl-phosphate-binding domain. The regulatory subunit contains a nucleotide effectors-binding domain and a zinc domain. <ref>PMID:10651286</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==3D structures of aspartate carbamoyltransferase== | ||
| + | [[Aspartate carbamoyltransferase 3D structures]] | ||
</StructureSection> | </StructureSection> | ||
Revision as of 11:14, 21 March 2019
| |||||||||||
3D structures of aspartate carbamoyltransferase
Updated on 21-March-2019
References
- ↑ Jin L, Stec B, Lipscomb WN, Kantrowitz ER. Insights into the mechanisms of catalysis and heterotropic regulation of Escherichia coli aspartate transcarbamoylase based upon a structure of the enzyme complexed with the bisubstrate analogue N-phosphonacetyl-L-aspartate at 2.1 A. Proteins. 1999 Dec 1;37(4):729-42. PMID:10651286