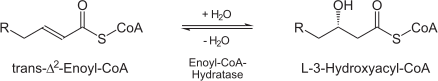We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1547
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
[2] of the b-oxidation pathway of fatty acid metabolism. Straight-chain enoyl-CoA thioesters from C4 up to at least C16 are processed, although with decreasing catalytic rate. The chains homologous to 2DUB: 1DUB, 1EY3. | [2] of the b-oxidation pathway of fatty acid metabolism. Straight-chain enoyl-CoA thioesters from C4 up to at least C16 are processed, although with decreasing catalytic rate. The chains homologous to 2DUB: 1DUB, 1EY3. | ||
(3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA = trans-2(or 3)-enoyl-CoA + H(2)O | (3S)-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA = trans-2(or 3)-enoyl-CoA + H(2)O | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Enoly_CoA_Hyratase.png ]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
== Disease == | == Disease == | ||
Mutation of any type like deletion,and or insertion on the HADHA will result in a rare autosomal recessive complete mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency, in which all three enzymatic processes do not function properly; more common is LCHAD deficiency, due to a less-encompassing HADHA missense mutation. This deficiency is rare satistics show that in the united States it rages from 1/75,00 to 1/250,000. more most common incidence is recorded in Finland. Clinically, LCHAD deficiency manifests early, typically in the first year of life, with episodes of hypoketotic hypoglycemia accompanied by variable other manifestations, including poor feeding, vomiting, lethargy, hypotonia, hepatic failure, skeletal myopathy and possibly rhabdomyolysis, early-onset cardiomyopathy, sensory polyneuropathy, and sudden death in infancy. | Mutation of any type like deletion,and or insertion on the HADHA will result in a rare autosomal recessive complete mitochondrial trifunctional protein deficiency, in which all three enzymatic processes do not function properly; more common is LCHAD deficiency, due to a less-encompassing HADHA missense mutation. This deficiency is rare satistics show that in the united States it rages from 1/75,00 to 1/250,000. more most common incidence is recorded in Finland. Clinically, LCHAD deficiency manifests early, typically in the first year of life, with episodes of hypoketotic hypoglycemia accompanied by variable other manifestations, including poor feeding, vomiting, lethargy, hypotonia, hepatic failure, skeletal myopathy and possibly rhabdomyolysis, early-onset cardiomyopathy, sensory polyneuropathy, and sudden death in infancy. | ||
Current revision
| This Sandbox is Reserved from May 28 through July 01, 2019 for use in the course Advanced Biochemistry BCHM 4100 taught by Tom Gluick at the Georgia Gwinnett College. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1544 through Sandbox Reserved 1555. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Enoyl-coa hydratase complexed with octanoyl-coa
Alternative names: Crotonase, Enoyl hydrase, Unsaturated acyl-CoA hydratase.Cocrystallized with octanoyl-CoA.The structure of the hexameric rat mitochondrial enoyl-Coenzyme A (CoA) hydratase, co-crystallised with the inhibitor octanoyl-CoA.
The source of the sample from organism: is from mitochondrial Cell of iver of Norway rat, Rattus norvegicus. Organism_taxid: 10116.
| |||||||||||