Journal:Acta Cryst D:S2059798319004169
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
<scene name='81/817979/Cv/4'>Zinc is bound by His99, Glu134, His255 and a water molecule in a tetrahedral coordination</scene>. Mutation in any of these residues interferes with zinc binding, which in turn leads to a non-functional enzyme. Isothermal calorimetric experiments with mutants showed that loss of zinc binding is associated with lack of substrate binding as well. Hence zinc plays an important role in anchoring the substrate in the active site. | <scene name='81/817979/Cv/4'>Zinc is bound by His99, Glu134, His255 and a water molecule in a tetrahedral coordination</scene>. Mutation in any of these residues interferes with zinc binding, which in turn leads to a non-functional enzyme. Isothermal calorimetric experiments with mutants showed that loss of zinc binding is associated with lack of substrate binding as well. Hence zinc plays an important role in anchoring the substrate in the active site. | ||
| + | |||
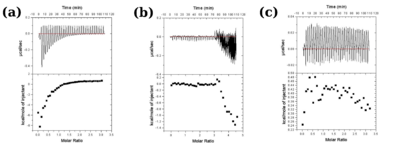
| + | [[Image:Figure3_proteopedia.png|left|400px|thumb|'''Figure 3''': Isothermal titration calorimetric measurements for wild type protein (a), H99Q (b) and E134H (c) mutants. The characteristic profile observed for wild type protein indicative of binding of substrate is lost in the mutants.]] | ||
| + | {{Clear}} | ||
Active site and catalytic base | Active site and catalytic base | ||
Revision as of 13:39, 10 June 2019
| |||||||||||
This page complements a publication in scientific journals and is one of the Proteopedia's Interactive 3D Complement pages. For aditional details please see I3DC.