Journal:Acta Cryst D:S205979832000501X
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)

| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
<scene name='84/842878/Cv/3'>GBA monomer comprising of three domains</scene>. Domain I (residues 1-27 and 383-414) in red, domain II (residues 30-75 and 431-497) in blue and domain III (residues 76-381 and 416-430) in gold. <scene name='84/842878/Cv/5'>Active site</scene> structure of bound bis-tris-propane which forms hydrogen bonds with Trp179, Asn234, Glu235, Glu340, Trp381 and an ethylene glycol (EDO) cryoprotectant molecules. | <scene name='84/842878/Cv/3'>GBA monomer comprising of three domains</scene>. Domain I (residues 1-27 and 383-414) in red, domain II (residues 30-75 and 431-497) in blue and domain III (residues 76-381 and 416-430) in gold. <scene name='84/842878/Cv/5'>Active site</scene> structure of bound bis-tris-propane which forms hydrogen bonds with Trp179, Asn234, Glu235, Glu340, Trp381 and an ethylene glycol (EDO) cryoprotectant molecules. | ||
| - | <scene name='84/842878/Cv/6'>Overlay of recombinant GBA (gold) obtained at pH 7.0 and Cerezyme (cyan) obtained at pH 4.6 | + | <scene name='84/842878/Cv/6'>Overlay of recombinant GBA (gold) obtained at pH 7.0 and Cerezyme (cyan) obtained at pH 4.6</scene> (PDB [[6tjj]]). |
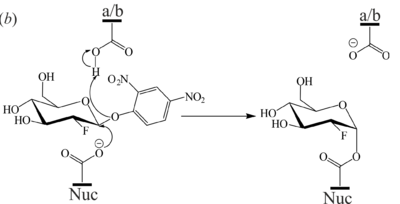
| + | <scene name='84/842878/Cv/8'>Active site structure of the 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-β-D-glucopyranoside-GBA covalent intermediate</scene> (PDB [[6tjq]]). The 2F-Glc moiety is covalently bound to the catalytic nucleophile (Glu340) which occupies two conformations. a/b = catalytic acid-base, Nuc = catalytic nucleophile, EDO = ethylene glycol. | ||
[[Image:Fig7b.png|left|400px|thumb|'''Figure 7''' (b) Mechanism of 2F-DNPGlc hydrolysis by GBA to generate the covalent glycosyl-enzyme intermediate.]] | [[Image:Fig7b.png|left|400px|thumb|'''Figure 7''' (b) Mechanism of 2F-DNPGlc hydrolysis by GBA to generate the covalent glycosyl-enzyme intermediate.]] | ||
Revision as of 14:24, 26 April 2020
| |||||||||||
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
This page complements a publication in scientific journals and is one of the Proteopedia's Interactive 3D Complement pages. For aditional details please see I3DC.