This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Sandbox Reserved 1647
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | {{Sandbox_Reserved_ESBS20_}}<!-- PLEASE ADD YOUR CONTENT BELOW HERE --> | ||
<Structure load='5t1j' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Insert caption here' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | <Structure load='5t1j' size='350' frame='true' align='right' caption='Insert caption here' scene='Insert optional scene name here' /> | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| Line 13: | Line 12: | ||
== Some roles of TBX21 == | == Some roles of TBX21 == | ||
| + | === Regulation of Th cells differentiation by TBX21 === | ||
| + | The transcription factor T-bet directs Th1 cell differentiation. The molecular mechanisms that underlie this lineage-specific gene regulation are not completely understood but several hypotheses have already been made of the mechanism of action of T-bet. | ||
| + | We know that T-bet initiates Th1 lineage development from naive Thp cells by activating Th1 genetics and repressing the opposing Th2 programs. Th1 cells stimulate cellular immune response while Th2 stimulates humoral immune response and induces antibody production. | ||
| + | [[Image:TBET.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here, we show that T-bet acts through enhancers to allow the recruitment of Mediator and P-TEFb in the formation of the super elongation complex (SEC). Th1 genes are occupied by RNA polymerase II in Thp cells, while T-bet-mediated recruitment of P-TEFb and mediator and activates transcriptional elongation giving place to an increased differentiation of Thp into Th1. | ||
| + | |||
| + | T-bet can also regulates Th1 cell differentiation by directly initiating gamma interferon (IFN-γ) transcription and by suppressing Th2-specific transcription factor GATA-3. The T-bet induced expression of IFN-γ derives Th precursor cells to differentiate into Th1 effector cells. | ||
| + | This stimulation of IFN-γ can takes place thanks to the action of a nuclear tyrosine kinase, c-Abl. C-Abl induces phosphorylation of T-bet at tyrosine residues 219, 265, and 304. C-Abl phosphorylates the tyrosine residues within the T-box domain, which is the DNA-binding domain of T-bet. This phosphorylation leads to conformational changes of the T-box domain to facilitate the DNA-binding activity of T-bet and appears to play a crucial role in the IFN-γ promoter-binding activity of T-bet. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Recently, many studies have reported that T-bet also modulates other Th cell lineages, including Th17, Treg, and follicular Th (TFH) cells, in coordination with many transcription factors, such as the retinoic acid-related orphan receptor-𝛾t (ROR𝛾t), runt-related transcription factor 3 (RUNX3), and B-cell lymphoma-6 (BCL6).These findings suggest that T-bet is a transcription factor that is critical for fine-tuning Th cell development. | ||
| + | |||
Revision as of 15:13, 14 January 2021
|
Contents |
Introduction
TBX21 or T-bet is a transcription factor, more precisely a T-box proteins. The DNA binding domain of T-bet has a dimer structure composes of two identical chains ( / ) with a total molecular weight of 76,37 kDA. This binding domain allows it to bind itself to the DNA on promotor or regulator area. The particularity of this T-box protein is that is able to link two DNA molecules or two areas of the same DNA molecules which are far from each other.
Structure and structural interactions
Secondary structure and interactions
The secondary structure of the protein allows it to bind with the DNA : The T-box domain consists of several repeats of β-strands and α-helices and is involved in both dimerization and DNA binding. The crystal structure of the α-helices of the T-box domain bound to DNA strongly suggests that the amino group of K313 is associated with the phosphate of a DNA base via hydrogen-bond interaction. Thanks to some post-translational modifications of the protein’s residues, the transcription factor TBX21 can bind with DNA and some proteins. Firstly, the ubiquitination of the residue K313 allows TBX21 to bind with the DNA sequence. Secondly, the phosphorylation of some residues allows TBX21 to interact with several proteins : the phosphorylation of T302 allows TBX21 to interact with NFAT, the one of Y304 allows TBX21 to interact with RUNX1, the one of S508 allows the interaction with NF-кB p65 and finally the one of Y525 allows the interaction with GATA-3.
Some roles of TBX21
Regulation of Th cells differentiation by TBX21
The transcription factor T-bet directs Th1 cell differentiation. The molecular mechanisms that underlie this lineage-specific gene regulation are not completely understood but several hypotheses have already been made of the mechanism of action of T-bet.
We know that T-bet initiates Th1 lineage development from naive Thp cells by activating Th1 genetics and repressing the opposing Th2 programs. Th1 cells stimulate cellular immune response while Th2 stimulates humoral immune response and induces antibody production.
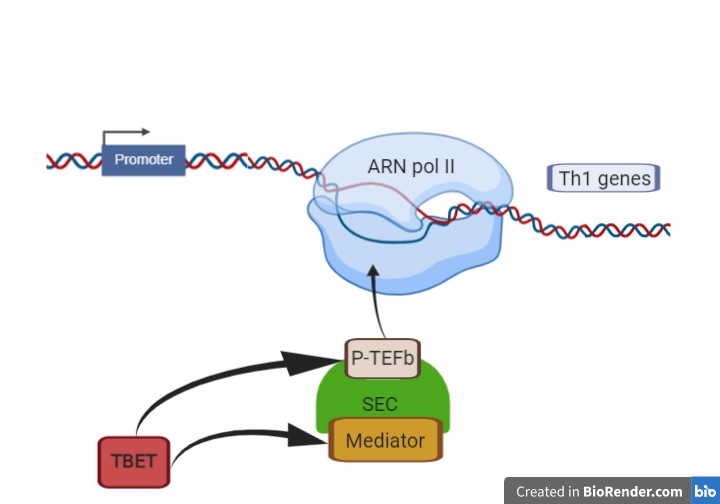
Here, we show that T-bet acts through enhancers to allow the recruitment of Mediator and P-TEFb in the formation of the super elongation complex (SEC). Th1 genes are occupied by RNA polymerase II in Thp cells, while T-bet-mediated recruitment of P-TEFb and mediator and activates transcriptional elongation giving place to an increased differentiation of Thp into Th1.
T-bet can also regulates Th1 cell differentiation by directly initiating gamma interferon (IFN-γ) transcription and by suppressing Th2-specific transcription factor GATA-3. The T-bet induced expression of IFN-γ derives Th precursor cells to differentiate into Th1 effector cells. This stimulation of IFN-γ can takes place thanks to the action of a nuclear tyrosine kinase, c-Abl. C-Abl induces phosphorylation of T-bet at tyrosine residues 219, 265, and 304. C-Abl phosphorylates the tyrosine residues within the T-box domain, which is the DNA-binding domain of T-bet. This phosphorylation leads to conformational changes of the T-box domain to facilitate the DNA-binding activity of T-bet and appears to play a crucial role in the IFN-γ promoter-binding activity of T-bet.
Recently, many studies have reported that T-bet also modulates other Th cell lineages, including Th17, Treg, and follicular Th (TFH) cells, in coordination with many transcription factors, such as the retinoic acid-related orphan receptor-𝛾t (ROR𝛾t), runt-related transcription factor 3 (RUNX3), and B-cell lymphoma-6 (BCL6).These findings suggest that T-bet is a transcription factor that is critical for fine-tuning Th cell development.
Structural highlights
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
</StructureSection>
