Introduction
Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase is an enzyme essential for the biosynthesis of monosaturated fatty acids from saturated fatty acids.SCD catalyzes the rate-limiting step in the conversion of Stearoyl-CoA to oleic acid, an essential substrate in the biosynthesis of phospholipids, triacyclglycerols, and cholesterol. SCD is highly conserved in eukaryotes and has different gene isoforms. Mice have four isoforms: SCD1, SCD2, SCD3, and SCD4. Humans have two different isoforms: SCD1 and SCD5. The SCD discussed in this page is Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1 (SCD1) found in mice. SCD is believed to have once been an anaerobic pathway found in cartilaginous fish about 450 million years ago[1]. The enzyme’s mechanism is now aerobic and this aerobic pathway is favored. The structure of SCD1 was found using X-ray crystallography.
Structure
Overall Structure
SCD1 is an integral membrane protein embedded within the endoplasmic reticulum and consists of 4 transmembrane alpha helices, arranged in a cone-like shape. The cytosolic domain of the enzyme consists of 11 alpha helices and contains the carboxy and amino termini. Its substrate, Stearoyl-CoA, binds to the cytosolic region which contains a "kink" that properly orients Stearoyl-CoA to undergo a dehydrogenation reaction between the of Stearoyl-CoA.
Binding of Substrate
Stearoyl-CoA is the substrate that binds to the enzyme, SCD1. The binding of the substrate is stabilized by specific residues on the exterior and interior of the protein. Stearoyl-CoA is a long-chain fatty acyl-CoA. The head group of the substrate is composed of an adenine, ribose, phosphate groups, and polar atoms such as of nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur. The fatty acid tail is a 17-carbon chain which reaches into the interior of the protein. The head of stearoyl-CoA is attached to the exterior of the protein by polar residues. The adenine, ribose, and phosphate are attached by the residues . The rest of the exterior of the substrate is attached by the residues . The fatty acid chain dives into the interior of the enzyme. The acyl chain is enclosed in a tunnel (24 ang) buried in the cytosolic domain. The geometry of the tunnel and formation of bound acyl chain are the structural basis for the stereospecificity of the desaturation reaction [2].
Kink of Chain
The chain is kinked at where the double bond is generated. The Kink is induced through the interactions of four conserved residues. Three out of four of these residues are not bound to the chain, but are hydrogen bonded to each other: . T257 is hydrogen bonded to Q143, and Q143 is hydrogen bonded to W149. These residues are directly below the kink and will be hydrolyzed when the substrate is ready to be released. The residue that is directly hydrogen bonded to the chain is . This residue is highly conserved and stabilizes the chain so it will be in the correct orientation in the active site.
Active Site
Two structures of SCD known. One structure shows the substrate, water molecule, and zinc (4YMK). The second structure shows the product and iron (6WF2). For the pictures below, the structure is shown with two zinc ions in order to demonstrate how is coordination with the ions. Water is used in the mechanism, which is why we chose to use the structure with zinc to explain the active site.
The two ions are 6.4 Angstroms apart. The ions sit above the kink in the active site. They are stabilized by the . The ion closest to C9 is 5.2 angstroms from it. This ion interacts with 4 histidines, H156, H265, H294, H298, and one water molecule. The ion closest to C10 is 4.7 angstroms away from it. This ion interacts with 5 histidines, H116, H121, H153, H157, and H297. These 9 total Histidine residues form a .The his box is used to stabilize the ions into the active site, forming a prosthetic group. The his box is highly conserved among the other isoforms of SCD. Other residues around the his box are used to hydrogen bond to the histidines to stabilize them. These residues include:
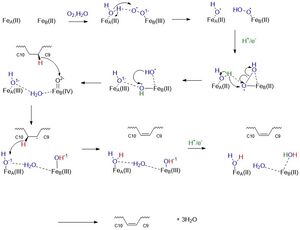
Mechanism
Disease
One common mutation that leads to the loss of function SCD1 is a mutation at any of the histidine residues within the A mutation at any of these 9 histidine residues interrupts the active site. This knockout of SCD1 has been known to combat obesity and lead to liver disease.
Another common mutation with SCD is the insertion of a proline at position This is due to an insertion of a 'CCC' codon at position 835 in exon 5 of the SCD1 gene. This mutation results in a loss of function of SCD1. This study was done using a mouse model. In mice with this mutation, hair loss, similar to alopecia, occurs. The mice were also found to be lean throughout their lifespan due to reduced triglyceride synthesis due to loss of SCD1 function.