We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
User:Abbey Wells/Sandbox 1
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
==Introduction== | ==Introduction== | ||
| - | Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase is an enzyme essential for the biosynthesis of monosaturated fatty acids from saturated fatty acids.SCD catalyzes the rate-limiting step in the conversion of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stearoyl-CoA Stearoyl-CoA] to [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oleic_acid oleic acid], an essential substrate in the biosynthesis of phospholipids, triacyclglycerols, and cholesterol. SCD is highly conserved in eukaryotes and has different gene isoforms. Mice have four isoforms: SCD1, SCD2, SCD3, and SCD4. Humans have two different isoforms: SCD1 and SCD5. The SCD discussed in this page is [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stearoyl-CoA_desaturase-1 Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1 (SCD1)] found in mice. SCD is believed to have once been an anaerobic pathway found in cartilaginous fish about 450 million years ago<ref name="Filipe">doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-11-132</ref>. The enzyme’s mechanism is now aerobic and this aerobic pathway is favored. The structure of SCD1 was found using X-ray crystallography. | + | Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase is an enzyme essential for the biosynthesis of monosaturated fatty acids from saturated fatty acids.SCD catalyzes the rate-limiting step in the conversion of [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stearoyl-CoA Stearoyl-CoA] to [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Oleic_acid oleic acid], an essential substrate in the biosynthesis of phospholipids, triacyclglycerols, and cholesterol <ref name="Bai">PMID:26098370</ref>. SCD is highly conserved in eukaryotes and has different gene isoforms. Mice have four isoforms: SCD1, SCD2, SCD3, and SCD4. Humans have two different isoforms: SCD1 and SCD5. The SCD discussed in this page is [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stearoyl-CoA_desaturase-1 Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1 (SCD1)] found in mice. SCD is believed to have once been an anaerobic pathway found in cartilaginous fish about 450 million years ago<ref name="Filipe">doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-11-132</ref>. The enzyme’s mechanism is now aerobic and this aerobic pathway is favored. The structure of SCD1 was found using X-ray crystallography. |
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
=== Overall Structure === | === Overall Structure === | ||
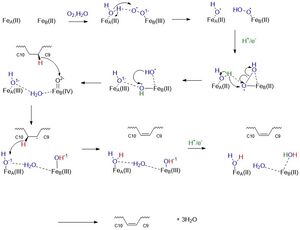
| - | SCD1 is an integral membrane protein embedded within the [http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/endoplasmicreticulum/endoplasmicreticulum.html endoplasmic reticulum] and consists of 4 transmembrane alpha helices, arranged in a cone-like shape. The cytosolic domain of the enzyme consists of 11 alpha helices and contains the carboxy and amino termini. Its substrate, Stearoyl-CoA, binds to the cytosolic region which contains a "kink" that properly orients Stearoyl-CoA to undergo a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dehydrogenation#:~:text=Dehydrogenation%20is%20the%20a%20chemical,reaction%20and%20a%20serious%20problem.&text=Enzymes%20that%20catalyze%20dehydrogenation%20are%20called%20dehydrogenases. dehydrogenation] reaction between the <scene name='87/877602/C9_and_c10/1'>Carbon 9 and Carbon 10</scene> of Stearoyl-CoA. | + | SCD1 is an integral membrane protein embedded within the [http://micro.magnet.fsu.edu/cells/endoplasmicreticulum/endoplasmicreticulum.html endoplasmic reticulum] and consists of 4 transmembrane alpha helices, arranged in a cone-like shape. The cytosolic domain of the enzyme consists of 11 alpha helices and contains the carboxy and amino termini <ref name="Bai">PMID:26098370</ref>. Its substrate, Stearoyl-CoA, binds to the cytosolic region which contains a "kink" that properly orients Stearoyl-CoA to undergo a [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dehydrogenation#:~:text=Dehydrogenation%20is%20the%20a%20chemical,reaction%20and%20a%20serious%20problem.&text=Enzymes%20that%20catalyze%20dehydrogenation%20are%20called%20dehydrogenases. dehydrogenation] reaction between the <scene name='87/877602/C9_and_c10/1'>Carbon 9 and Carbon 10</scene> of Stearoyl-CoA. |
=== Binding of Substrate === | === Binding of Substrate === | ||
Revision as of 16:53, 17 April 2021
Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase 1 from Mus musculus
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Bai Y, McCoy JG, Levin EJ, Sobrado P, Rajashankar KR, Fox BG, Zhou M. X-ray structure of a mammalian stearoyl-CoA desaturase. Nature. 2015 Jun 22. doi: 10.1038/nature14549. PMID:26098370 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nature14549
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Castro LF, Wilson JM, Goncalves O, Galante-Oliveira S, Rocha E, Cunha I. The evolutionary history of the stearoyl-CoA desaturase gene family in vertebrates. BMC Evol Biol. 2011 May 19;11:132. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-11-132. PMID:21595943 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/1471-2148-11-132
- ↑ Shen J, Wu G, Tsai AL, Zhou M. Structure and Mechanism of a Unique Diiron Center in Mammalian Stearoyl-CoA Desaturase. J Mol Biol. 2020 May 27. pii: S0022-2836(20)30367-3. doi:, 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.05.017. PMID:32470559 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2020.05.017
Student Contributors
- Abbey Wells
- Josey McKinley
- Anthony Durand