We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox GGC15
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
== Relevance == | == Relevance == | ||
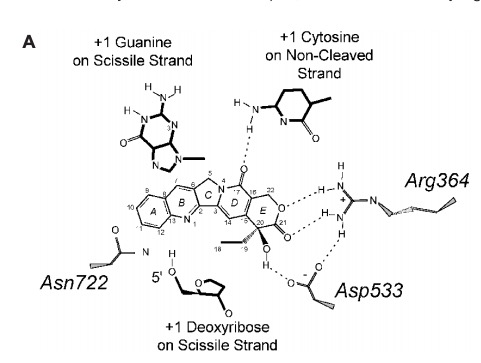
| - | '''Many anticancer drugs target topo 1 enzymes. This enzyme is the target of camptothecin (CPT) family of anticancer drugs<ref name="Redinbo" />. These drugs work by increasing the duration of the nicked intermediate in the <scene name='78/781215/04_28_revelance_cpt_bind/1'>topo I</scene> reaction <ref name="Redinbo" />. The stabilized intermediates prevent transcription and replication to continue in the cancer cells<ref name="Redinbo" />. This eventually leads to DNA damage and cell death<ref name="Redinbo" />.''' | + | '''Many anticancer drugs target topo 1 enzymes. This enzyme is the target of camptothecin (CPT) family of anticancer drugs<ref name="Redinbo" />. These drugs work by increasing the duration of the nicked intermediate in the <scene name='78/781215/04_28_revelance_cpt_bind/1'>topo I</scene> reaction <ref name="Redinbo" />. CPT enhances DNA breakage at sites with a guanine base at the +1 position on the DNA strand that is being cut<ref name="Redinbo" />. This is immediately downstream of the site that is being cleaved<ref name="Redinbo" />. The stabilized intermediates prevent transcription and replication to continue in the cancer cells<ref name="Redinbo" />. This eventually leads to DNA damage and cell death<ref name="Redinbo" />.''' |
[[Image:CPT and Enzyme.jpg]] <ref name="Redinbo" /> | [[Image:CPT and Enzyme.jpg]] <ref name="Redinbo" /> | ||
Revision as of 12:22, 28 April 2021
DNA TOPOISOMERASE I
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 Staker BL, Hjerrild K, Feese MD, Behnke CA, Burgin AB Jr, Stewart L. The mechanism of topoisomerase I poisoning by a camptothecin analog. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002 Nov 26;99(24):15387-92. Epub 2002 Nov 8. PMID:12426403 doi:10.1073/pnas.242259599
- ↑ 2.00 2.01 2.02 2.03 2.04 2.05 2.06 2.07 2.08 2.09 2.10 2.11 2.12 2.13 2.14 2.15 2.16 2.17 Redinbo MR, Stewart L, Kuhn P, Champoux JJ, Hol WG. Crystal structures of human topoisomerase I in covalent and noncovalent complexes with DNA. Science. 1998 Mar 6;279(5356):1504-13. PMID:9488644
- ↑ D'yakonov, V. A., Dzhemileva, L. U., & Dzhemilev, U. M. (2017). Advances in the Chemistry of Natural and Semisynthetic Topoisomerase I/II Inhibitors. Studies in Natural Products Chemistry, 21–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-444-63929-5.00002-4
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Stewart, L. (1998). A Model for the Mechanism of Human Topoisomerase I. Science, 279(5356), 1534–1541. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.279.5356.1534
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Interthal H, Quigley PM, Hol WG, Champoux JJ. The role of lysine 532 in the catalytic mechanism of human topoisomerase I. J Biol Chem. 2004 Jan 23;279(4):2984-92. Epub 2003 Oct 31. PMID:14594810 doi:10.1074/jbc.M309959200