We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1692
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
== Important amino acids== | == Important amino acids== | ||
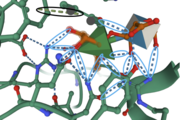
Amino Acids <scene name='89/892735/Amino_acids2/2'>His85, Asp106, Tyr150, Ser170, Tyr202, Arg220, Pro223, Ala225, and Arg331</scene> provide important interactions for binding in the active site. The amino acid residue <scene name='89/892735/His85interactions/1'>His85</scene> is located near the C-5 atom of Rha, suggesting it has a catalytic role as a proton acceptor within the active site. The <scene name='89/892735/His85_and_his105/1'>His105 side chain forms a hydrogen bond with His85</scene> side chain, providing further stabilizing assistance. Amino Acid Residues <scene name='89/892735/Tyr150_and_his85/1'>Tyr150 and His85</scene> form a hydrogen bond with the O-1 atom of Rha, suggesting these residues play a catalytic role for the elimination reaction. <scene name='89/892735/O2o3hbonds/1'>Tyr26, Asn275, Gln276, and Arg331</scene> form hydrogen bonds with O-2 and O-3 atoms of Rha, providing further stabilization within the active site <ref name="Kondo">PMID:34303708</ref>.[[Image:IntermolforcesBIOCHEM.png|thumb]] | Amino Acids <scene name='89/892735/Amino_acids2/2'>His85, Asp106, Tyr150, Ser170, Tyr202, Arg220, Pro223, Ala225, and Arg331</scene> provide important interactions for binding in the active site. The amino acid residue <scene name='89/892735/His85interactions/1'>His85</scene> is located near the C-5 atom of Rha, suggesting it has a catalytic role as a proton acceptor within the active site. The <scene name='89/892735/His85_and_his105/1'>His105 side chain forms a hydrogen bond with His85</scene> side chain, providing further stabilizing assistance. Amino Acid Residues <scene name='89/892735/Tyr150_and_his85/1'>Tyr150 and His85</scene> form a hydrogen bond with the O-1 atom of Rha, suggesting these residues play a catalytic role for the elimination reaction. <scene name='89/892735/O2o3hbonds/1'>Tyr26, Asn275, Gln276, and Arg331</scene> form hydrogen bonds with O-2 and O-3 atoms of Rha, providing further stabilization within the active site <ref name="Kondo">PMID:34303708</ref>.[[Image:IntermolforcesBIOCHEM.png|thumb]] | ||
| - | The image to the right shows important amino acids in the active site. Hydrogen bonding and pi-stacking interactions are indicated by the blue and black circles, respectively. | + | The image to the right shows important interactions between the enzyme and amino acids in the active site. Hydrogen bonding and pi-stacking interactions are indicated by the blue and black circles, respectively. |
== Structural highlights == | == Structural highlights == | ||
Secondary Structure: In this enzyme, there are around <scene name='89/892735/Beta_sheets/3'>30 anti-parallel beta sheets</scene> and three small <scene name='89/892735/Helices/1'>alpha helices</scene>. Compared to parallel beta sheets, anti-parallel beta sheets provide stronger hydrogen bonding between side chains of amino acids. The alpha helices provide structure for the formation of the active site, allowing the substrate (Rha) to bind in the active site. | Secondary Structure: In this enzyme, there are around <scene name='89/892735/Beta_sheets/3'>30 anti-parallel beta sheets</scene> and three small <scene name='89/892735/Helices/1'>alpha helices</scene>. Compared to parallel beta sheets, anti-parallel beta sheets provide stronger hydrogen bonding between side chains of amino acids. The alpha helices provide structure for the formation of the active site, allowing the substrate (Rha) to bind in the active site. | ||
Revision as of 21:59, 8 December 2021
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 10/01/2021 through 01/01//2022 for use in Biochemistry taught by Bonnie Hall at Grand View University, Des Moines, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1690 through Sandbox Reserved 1699. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Structure and Function of FoRham1
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Kondo T, Kichijo M, Maruta A, Nakaya M, Takenaka S, Arakawa T, Fushinobu S, Sakamoto T. Structural and functional analysis of gum arabic l-rhamnose-alpha-1,4-d-glucuronate lyase establishes a novel polysaccharide lyase family. J Biol Chem. 2021 Jul 22:101001. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101001. PMID:34303708 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101001