We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1659
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
[[Image:pymol1.jpg]] | [[Image:pymol1.jpg]] | ||
| + | |||
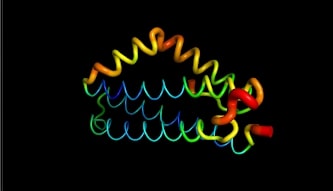
The flexibility of <scene name='86/868192/Helix_h4ter/1'>H4</scene> and <scene name='86/868192/Helix_h5/4'>H5</scene> may have a role in the binding to BADH1. Indeed, the positioning of this "elbow" relatively to the "trunk" formed by the less mobile regions <scene name='86/868192/Helix_h1/1'>H1</scene>, <scene name='86/868192/Helix_h2/1'>H2</scene> and <scene name='86/868192/Helix_h3/1'>H3</scene> is determining in the ligands recognition. Many amino acids may be involved in the interaction of LntA with its ligand, such as BAHD1. A <scene name='86/868192/Dilysine/1'>dilysine motif located in the elbow region of lntA at position 180/181 on the H5 helix</scene> has proven to be essential for the interaction with the transcription factor BAHD1 thanks to a conformational change <scene name='86/868192/The_lysine_180_and_181/1'>(global overview of this dilysine motif)</scene>. Indeed, when this motif is substituted by two aspartic acid amino acids (K180D/K181D by mutation of LntA), a local redistribution of the charges is observed and lntA is not able anymore to interact with BAHD1. <ref> Lebreton A, Job V, Ragon M, Le Monnier A, Dessen A, Cossart P, Bierne H. 2014. Structural basis for the inhibition of the chromatin repressor BAHD1 by the bacterial nucleomodulin LntA </ref> | The flexibility of <scene name='86/868192/Helix_h4ter/1'>H4</scene> and <scene name='86/868192/Helix_h5/4'>H5</scene> may have a role in the binding to BADH1. Indeed, the positioning of this "elbow" relatively to the "trunk" formed by the less mobile regions <scene name='86/868192/Helix_h1/1'>H1</scene>, <scene name='86/868192/Helix_h2/1'>H2</scene> and <scene name='86/868192/Helix_h3/1'>H3</scene> is determining in the ligands recognition. Many amino acids may be involved in the interaction of LntA with its ligand, such as BAHD1. A <scene name='86/868192/Dilysine/1'>dilysine motif located in the elbow region of lntA at position 180/181 on the H5 helix</scene> has proven to be essential for the interaction with the transcription factor BAHD1 thanks to a conformational change <scene name='86/868192/The_lysine_180_and_181/1'>(global overview of this dilysine motif)</scene>. Indeed, when this motif is substituted by two aspartic acid amino acids (K180D/K181D by mutation of LntA), a local redistribution of the charges is observed and lntA is not able anymore to interact with BAHD1. <ref> Lebreton A, Job V, Ragon M, Le Monnier A, Dessen A, Cossart P, Bierne H. 2014. Structural basis for the inhibition of the chromatin repressor BAHD1 by the bacterial nucleomodulin LntA </ref> | ||
Revision as of 16:14, 20 January 2022
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ ROHDE JOHN R. Listeria unwinds host’s DNA. SCIENCE, 2011 : 1271-1272
- ↑ Winter SE, Thiennimitr P et al. Gut inflammation provides a respiratory electron acceptor for Salmonella. Nature. 2010
- ↑ Dewoody, R., Merritt, P.M., Houppert, A.S. and Marketon, M.M. (2011), YopK regulates the Yersinia pestis type III secretion system from within host cells. Molecular Microbiology, 79: 1445-1461. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07534.x
- ↑ Lebreton A, Job V, Ragon M, Le Monnier A, Dessen A, Cossart P, Bierne H. 2014. Structural basis for the inhibition of the chromatin repressor BAHD1 by the bacterial nucleomodulin LntA
- ↑ Alice Lebreton. Régulations post-transcriptionnelles de l’expression génique de la cellule hôte en réponse à l’infection bactérienne. Sciences du Vivant, 2015