SARS-CoV-2 virus proteins
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
[[Image:SARS-Cov-2-genome.jpg|900px|left|thumb|SARS-CoV-2 Protein Organization, from Gordon | [[Image:SARS-Cov-2-genome.jpg|900px|left|thumb|SARS-CoV-2 Protein Organization, from Gordon | ||
| - | et al. & Krogan (2020)<ref> | + | et al. & Krogan (2020)<ref>PMID: 34119626</ref> )]] |
[[Image:VirusImage.jpg|right|280px|thumb|Organization of SARS-CoV-2 virus (from Holmes & Enjuanes (2003)<ref>pmid 12775826</ref>)]] | [[Image:VirusImage.jpg|right|280px|thumb|Organization of SARS-CoV-2 virus (from Holmes & Enjuanes (2003)<ref>pmid 12775826</ref>)]] | ||
Revision as of 13:36, 8 February 2022
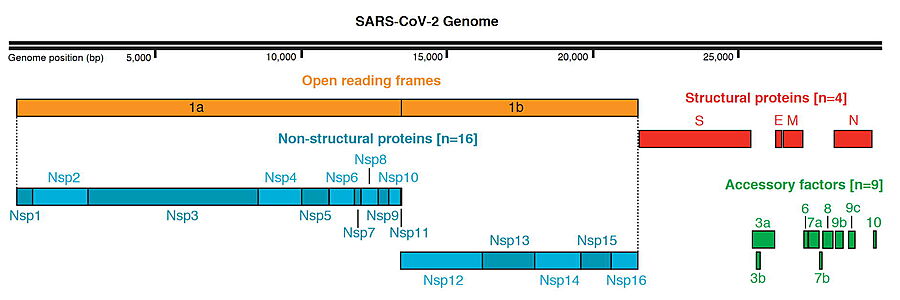
SARS-CoV-2 Protein Organization, from Gordon et al. & Krogan (2020)[1] )
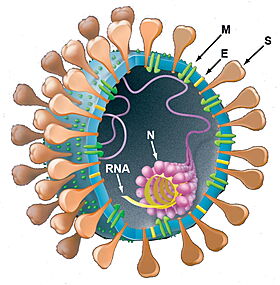
Organization of SARS-CoV-2 virus (from Holmes & Enjuanes (2003)[2])
| The quality of SARS-CoV-2 experimentally determined structures varies widely (Grabowski et al., 2021). Validated and corrected structures can be obtained from COVID19.BioReproducibility.Org. |
The genome of the SARS-CoV-2 virus codes for 28 proteins:
Out of those, 19 have already been characterized structurally. For the rest there are accurate AlphaFold2 predicted structures.
Details of the 3D structure & function of the key proteins & RNA inside the virus can be seen in the NY Times[3].
"The first viral protein created inside the infected cell, ORF1ab, is actually a chain of 16 proteins joined together. Two of these proteins act like scissors, snipping the links between the different proteins and freeing them to do their jobs."[3]
- Main protease: it is a cysteine protease that is essential for the viral life cycle.
- NSP1: Inhibits host translation by interacting with the 40S ribosomal subunit.
- NSP2: May play a role in the modulation of host cell survival signaling pathway by interacting with host PHB and PHB2.
- NSP3: Papain-like proteinase
- NSP4: Participates in the assembly of virally-induced cytoplasmic double-membrane vesicles necessary for viral replication.[1][2]
- NSP5: SARS 3CL-PRO: Main proteinase
- NSP6: AlphaFold2 Theoretical Model - Plays a role in the initial induction of autophagosomes from host reticulum endoplasmic.
- NSP7: NSP7, together with NSP8, aid the virus to make new copies of the RNA genome.
- NSP8: NSP8, together with NSP7, aid the virus to make new copies of the RNA genome.
- NSP9: Non-structural protein 9.
- NSP10: Non-structural protein 10.
- RNA-directed RNA polymerase (RdRp)
- Helicase (Hel): Multi-functional protein with a zinc-binding domain in N-terminus
- Guanine-N7 methyltransferase (ExoN)
- Uridylate-specific endoribonuclease (NendoU)
- 2'-O-methyltransferase (2'-O-MT): Methyltransferase that mediates mRNA cap 2'-O-ribose methylation to the 5'-cap structure of viral mRNAs.
- Surface glycoprotein (S) and SARS-CoV-2 protein S priming by furin
- ORF3a: Forms homotetrameric potassium sensitive ion channels (viroporin) and may modulate virus release.
- Protein E: Plays a central role in virus morphogenesis and assembly.
- Protein M: AlphaFold2 Theoretical Model - Component of the viral envelope.
- Protein N: AlphaFold2 Theoretical Model - Packages the positive strand viral genome RNA into a helical ribonucleocapsid (RNP).
- ORF6: Could be a determinant of virus virulence.
- ORF7a: Non-structural protein which is dispensable for virus replication in cell culture.
- ORF8: Open Reading Frame 8.
- ORF10:AlphaFold2 Theoretical Model - It is currently unclear whether this region translates into a functional protein.
References
- ↑ Gadhave K, Kumar P, Kumar A, Bhardwaj T, Garg N, Giri R. Conformational dynamics of 13 amino acids long NSP11 of SARS-CoV-2 under membrane mimetics and different solvent conditions. Microb Pathog. 2021 Sep;158:105041. doi: 10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105041. Epub 2021, Jun 10. PMID:34119626 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2021.105041
- ↑ Holmes KV, Enjuanes L. Virology. The SARS coronavirus: a postgenomic era. Science. 2003 May 30;300(5624):1377-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1086418. PMID:12775826 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1126/science.1086418
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 NY Times (3-Apr-2020) Bad News Wrapped in Protein: Inside the Coronavirus Genome
