Sandbox Reserved 1700
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
== GPCR Structure == | == GPCR Structure == | ||
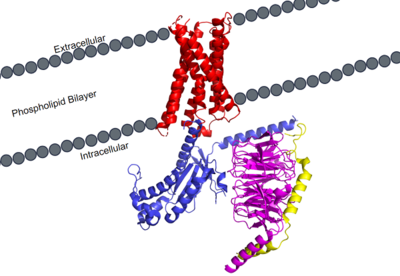
| - | Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) was used to image the MRGPRX2 receptor to analyze its structure. <ref name= "Cao" /> <ref name= "Yang" /> which helped to classify it into the A family of GPCR's. MRGPRX2 therefore shares the same general structural domains of all GPCR's. This includes a <scene name='90/904305/Structure_overview_red/1'>transmembrane domain</scene> and a <scene name='90/904305/Structure_overview_gprotein/1'>G-protein</scene> domain. The G-protein domain consists of <scene name='90/904305/Structure_overview_alpha/1'>alpha</scene>, <scene name='90/904305/Structure_overview_beta/1'>beta</scene>, and <scene name='90/904305/Structure_overview_gamma/1'>gamma</scene> subunits. In preparing the protein sample, MRGPRX2 was prepared with the antibody scFv16 in order to stabilize the membrane for proper imaging. For simplicity and to focus on the specific MRGPRX2 receptor, the antibody has been removed. | + | Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) was used to image the MRGPRX2 receptor to analyze its structure. <ref name= "Cao" /> <ref name= "Yang" /> which helped to classify it into the A family of GPCR's. MRGPRX2 therefore shares the same general structural domains of all GPCR's. This includes a <scene name='90/904305/Structure_overview_red/1'>transmembrane domain</scene> and a <scene name='90/904305/Structure_overview_gprotein/1'>G-protein</scene> domain. The G-protein domain consists of <scene name='90/904305/Structure_overview_alpha/1'>alpha</scene>, <scene name='90/904305/Structure_overview_beta/1'>beta</scene>, and <scene name='90/904305/Structure_overview_gamma/1'>gamma</scene> subunits. In preparing the protein sample, MRGPRX2 was prepared with the <scene name='90/904305/Antibody_representation/1'>antibody scFv16</scene> in order to stabilize the membrane for proper imaging. For simplicity and to focus on the specific MRGPRX2 receptor, the antibody has been removed. |
=== Transmembrane Domain === | === Transmembrane Domain === | ||
Revision as of 19:57, 27 March 2022
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 28 through September 1, 2022 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1700 through Sandbox Reserved 1729. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
MRGPRX2 Human Itch G-Protein Coupled Receptor (GPCR)
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Hauser AS, Attwood MM, Rask-Andersen M, Schioth HB, Gloriam DE. Trends in GPCR drug discovery: new agents, targets and indications. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017 Dec;16(12):829-842. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2017.178. Epub, 2017 Oct 27. PMID:29075003 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrd.2017.178
- ↑ Basith S, Cui M, Macalino SJY, Park J, Clavio NAB, Kang S, Choi S. Exploring G Protein-Coupled Receptors (GPCRs) Ligand Space via Cheminformatics Approaches: Impact on Rational Drug Design. Front Pharmacol. 2018 Mar 9;9:128. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00128. eCollection, 2018. PMID:29593527 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00128
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Cao C, Kang HJ, Singh I, Chen H, Zhang C, Ye W, Hayes BW, Liu J, Gumpper RH, Bender BJ, Slocum ST, Krumm BE, Lansu K, McCorvy JD, Kroeze WK, English JG, DiBerto JF, Olsen RHJ, Huang XP, Zhang S, Liu Y, Kim K, Karpiak J, Jan LY, Abraham SN, Jin J, Shoichet BK, Fay JF, Roth BL. Structure, function and pharmacology of human itch GPCRs. Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7887):170-175. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04126-6. Epub 2021, Nov 17. PMID:34789874 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04126-6
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Yang F, Guo L, Li Y, Wang G, Wang J, Zhang C, Fang GX, Chen X, Liu L, Yan X, Liu Q, Qu C, Xu Y, Xiao P, Zhu Z, Li Z, Zhou J, Yu X, Gao N, Sun JP. Structure, function and pharmacology of human itch receptor complexes. Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7887):164-169. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04077-y. Epub 2021, Nov 17. PMID:34789875 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04077-y