Background
Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) is a transmembrane receptor and a member of the family of Receptor Tyrosine Kinases (RTKs), a family of biomolecules that are primarily responsible for biosignaling pathways such as the insulin signaling pathway. It was discovered as a novel tyrosine phosphoprotein in 1994 in an analysis of Anaplastic Large-Cell Lymphoma, the protein's namesake. A full analysis and characterization of ALK was completed in 1997, properly identifying it as a RTK, and linking it closely to Leukocyte Tyrosine Kinase (LTK).
Structure
As previously mentioned, ALK is a close homolog of LTK, and together these two homologous proteins create a subgroup within the superfamily of insulin receptors (IR). ALK is composed of 1620 amino acids in total, with three primary domains. ALK is described as showing the "classic structural features of RTKs, with an extracellular ligand-binding domain, a transmembrane-spanning region, and an intracellular kinase domain." As displayed in (insert line figure here), the intracellular tyrosine kinase domain ranges from residues 1116-1392, and features the C-terminal end. The transmembrane helical domain (TMH) bridges the gap between the intracellular and extracellular regions from residues 1039-1116. The final section of ALK is the extracellular region, which spans from residues 1025 to 1, and contains 8 domains. Of these 8 domains, two regions of the extracellular region can be found; one containing the ligand-binding site of the protein, and another lesser-known subregion. This lesser-known subregion contains 4 domains from residues 1-626; an N-terminal Region (NTR), two meprin–A-5 protein–receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase μ (MAM), and a low-density lipoprotein receptor class A (LDL) domain sandwiched between the two MAM domains. The presence of an LDL domain sandwiched by two MAM domains is a unique feature that ALK does not share with other RTKs. The purpose behind this unique difference is still unclear. The ligand-binding extracellular subregion is the most well-characterized of the two subregions, containing 4 distinct domains from residues 673-1025; a triple helix bundle (THB) domain, a glycine-rich domain (GlyR) that is also referred to as the poly-Glycine domain, a tumor necrosis factor-like (TNF-like), and an epidermal growth factor-like domain (EGF-like). All four domains of this subregion of the extracellular region contribute to ligand-binding, (more info here).
Domains
Three Helix Bundle-like Domain
The mainly has a structural function overall as it interacts with the tumor necrosis factor-like domain upon ligand binding.
Poly-Glycine Domain
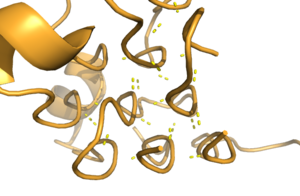
Figure 1. Rare Glycine helices on Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase
Located between the three helix bundle-like domain and the tumor necrosis factor-like domain, the has an important structural role. The poly-Glycine domain also has a rare and unique structure with hexagonal hydrogen bonding shown in Figure 1.
Tumor Necrosis Factor-like Domain
The interacts with the three helix bundle-like domain to begin the conformational changes associated with ligand binding. The three helix bundle-like domain's α-helix interacts with the helix α-1' and β strand A-1'. This domain also assists in mediating ligand binding with the epidermal growth factor-like domain.
Epidermal Growth Factor-like Domain
The is very malleable and repositioning of this domain is essential for activation of the protein. This domain is able to undergo conformational changes with the ligand bound and when in contact with the tumor necrosis factor-like domain.
Binding Site
This site doesn't start out surrounding the ligand, instead the proximity of the ligand allows conformational changes across the protein.
Ligands
ALKAL1
ALKAL2
Dimerization of Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase
After binding to one of its ligands, Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase undergoes ligand-induced dimerization [1]. The dimerization causes trans-phosphorylation of specific tyrosine residues which in turn amplifies the signal. It has been presumed that the phosphorylation cascade activates ALK kinase activity [1].
Function
Disease
Relevance
Structural highlights
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.

