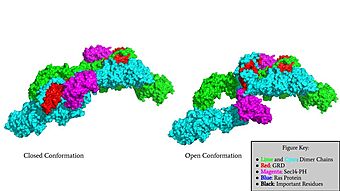
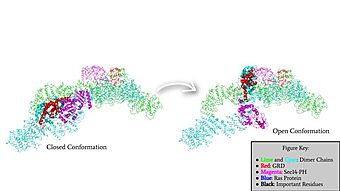
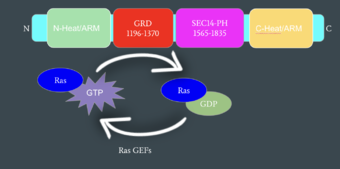
We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1710
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
== Disease and Medical Relevance == | == Disease and Medical Relevance == | ||
| - | Currently, there are over 1485 mutations of Neurofibromin that have been identified. Mutations in Neurofibromin can lead to life-threatening illnesses or conditions such as Neurofibromatosis Type I due to the inability of Neurofibromin to interact with Ras.<ref name="Lupton">PMID: 34887559 </ref> The role of Neurofibromin is to inhibit cellular proliferation via its guanine triphosphatase-activating protein (GAP) activity, therefore when there are mutations to the NF1 gene that prevents the interaction of Neufibromin with Ras, there is nothing stopping Ras from promoting cell growth. Uncontrolled cell growth can lead to tumors and a higher risk of cancer.<ref name="Ratner">PMID:25877329</ref> [https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/neurofibromatosis-type-1/ Neurofibromatosis Type 1], the most well-known disease resulting from mutations in Neurofibromin, is characterized by cognitive impairment, soft, non-cancerous tumors on or under the skin known as neurofibromas, birthmarks, clusters of freckles in unusual places, and problems with the bones, eyes and nervous system. | + | Currently, there are over 1485 mutations of Neurofibromin that have been identified. Mutations in Neurofibromin can lead to life-threatening illnesses or conditions such as Neurofibromatosis Type I due to the inability of Neurofibromin to interact with Ras.<ref name="Lupton">PMID: 34887559 </ref> The role of Neurofibromin is to inhibit cellular proliferation via its guanine triphosphatase-activating protein (GAP) activity, therefore when there are mutations to the NF1 gene that prevents the interaction of Neufibromin with Ras, there is nothing stopping Ras from promoting cell growth. Uncontrolled cell growth can lead to tumors and a higher risk of cancer.<ref name="Ratner">PMID:25877329</ref> [https://medlineplus.gov/genetics/condition/neurofibromatosis-type-1/ Neurofibromatosis Type 1], the most well-known disease resulting from mutations in Neurofibromin, is characterized by cognitive impairment, soft, non-cancerous tumors on or under the skin known as neurofibromas, birthmarks called cafe au lait macules, clusters of freckles in unusual places, and problems with the bones, eyes and nervous system. |
Neurofibromin is an essential protein and is involved mainly in the differentiation of neural crest derived cells, mesenchymal cells, neural cells, melanocytes, and bone cells. As Neurofibromin is essential for embryonic development, mutations to the NF1 gene can result in psychological retardation resulting from Type I neurofibromatosis. Most of the 1485 mutations identified lead to a synthesis of truncated, non-functional protein and are a result of point mutations. Type I Neurofibromatosis is inherited in autosomal dominant manner but about 50% of cases de novo ones. <ref name="Abramowicz">PMID:25182393</ref> | Neurofibromin is an essential protein and is involved mainly in the differentiation of neural crest derived cells, mesenchymal cells, neural cells, melanocytes, and bone cells. As Neurofibromin is essential for embryonic development, mutations to the NF1 gene can result in psychological retardation resulting from Type I neurofibromatosis. Most of the 1485 mutations identified lead to a synthesis of truncated, non-functional protein and are a result of point mutations. Type I Neurofibromatosis is inherited in autosomal dominant manner but about 50% of cases de novo ones. <ref name="Abramowicz">PMID:25182393</ref> | ||
Revision as of 00:57, 29 March 2022
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 28 through September 1, 2022 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1700 through Sandbox Reserved 1729. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Human Neurofibromin - The Tumor Suppressor Gene
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Naschberger A, Baradaran R, Rupp B, Carroni M. The structure of neurofibromin isoform 2 reveals different functional states. Nature. 2021 Nov;599(7884):315-319. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04024-x. Epub 2021, Oct 27. PMID:34707296 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04024-x
- ↑ Trovo-Marqui AB, Tajara EH. Neurofibromin: a general outlook. Clin Genet. 2006 Jul;70(1):1-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2006.00639.x. PMID:16813595 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-0004.2006.00639.x
- ↑ Lupton CJ, Bayly-Jones C, D'Andrea L, Huang C, Schittenhelm RB, Venugopal H, Whisstock JC, Halls ML, Ellisdon AM. The cryo-EM structure of the human neurofibromin dimer reveals the molecular basis for neurofibromatosis type 1. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2021 Dec;28(12):982-988. doi: 10.1038/s41594-021-00687-2., Epub 2021 Dec 9. PMID:34887559 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41594-021-00687-2
- ↑ Ratner N, Miller SJ. A RASopathy gene commonly mutated in cancer: the neurofibromatosis type 1 tumour suppressor. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015 May;15(5):290-301. doi: 10.1038/nrc3911. Epub 2015 Apr 16. PMID:25877329 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrc3911
- ↑ Abramowicz A, Gos M. Neurofibromin in neurofibromatosis type 1 - mutations in NF1gene as a cause of disease. Dev Period Med. 2014 Jul-Sep;18(3):297-306. PMID:25182393