We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1710
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
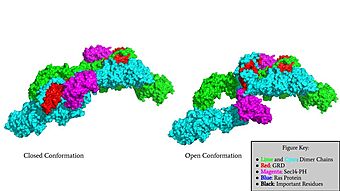
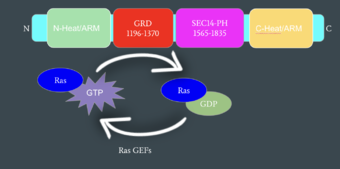
Neurofibromin is a <scene name='90/904315/Homodimer/4'>homodimer</scene> made up of two identical chains. Neurofibromin has two conformations, open and closed. Shifting between these controls neurofibromins ability to associate with [hhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ras_GTPase Ras](6ob3) and perform its function of Ras regulation. The transformation between the overall closed and open conformations transitions it from an active to inactive state. There are two important domains involved in the transition between the open and closed conformations, the <scene name='90/904316/Grd_domains/2'>GRD</scene> domain and the <scene name='90/904315/Sec14ph_domain/3'>Sec14-PH</scene> domain. Although neurofibromin is a homodimer with two identical protomers, only one protomer has its GRD and Sec14-PH domains rotated into the open conformation. | Neurofibromin is a <scene name='90/904315/Homodimer/4'>homodimer</scene> made up of two identical chains. Neurofibromin has two conformations, open and closed. Shifting between these controls neurofibromins ability to associate with [hhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ras_GTPase Ras](6ob3) and perform its function of Ras regulation. The transformation between the overall closed and open conformations transitions it from an active to inactive state. There are two important domains involved in the transition between the open and closed conformations, the <scene name='90/904316/Grd_domains/2'>GRD</scene> domain and the <scene name='90/904315/Sec14ph_domain/3'>Sec14-PH</scene> domain. Although neurofibromin is a homodimer with two identical protomers, only one protomer has its GRD and Sec14-PH domains rotated into the open conformation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | == Conformational States == | ||
=== Closed Conformation (7PGR) === | === Closed Conformation (7PGR) === | ||
| - | In the | + | In the <scene name='90/904315/Closed/2'>closed, inactive conformation</scene>, the GRD and Sec14-PH domains are rotated so Ras cannot bind. In this conformation, the GRD and Sec14-PH are inaccessible and inactive. Neurofibromin is held in the inactive state by a <scene name='90/904315/Catalytic_triade/2'>triad</scene> consisting of residues Cys 1032, His 1558, and His 1576 that form a transition metal-binding site with zinc. The rigid organization of the <scene name='90/904316/Closed_triade/3'>triad in closed conformation</scene> keeps the GRD domain packed tightly on top of the Heat Arms in the Neurofibromin core. This tight compaction sterically occludes Neurofibromin from associating with Ras. In its active form, Ras and Neurofibromin will associate via an <scene name='90/904316/Arg_finger/2'>Arginine finger</scene> (Arg 1276). However, the steric hindrance from the Neurofibromin core in the closed conformation inhibits this association. Therefore, in the closed conformation, neurofibromin cannot catalyze GTP hydrolysis by Ras and Ras continues to signal for cell growth and proliferation. |
=== Open Conformation (7PGT) === | === Open Conformation (7PGT) === | ||
| - | + | In the <scene name='90/904315/Open_conformation/3'>open, active conformation</scene>, (REWRITE ABOUT RAS REGULATION) | |
| + | |||
| + | This transition is initiated by movement of the transition metal-binding site. The Cys 1032, His 1558, and His 1576 Residues become separated and zinc is not able to bond. | ||
| + | |||
| + | because the transition metal-binding site with zinc no longer is able to form due to an increase in distance between the C1032, H1558 and H1576 residues that form the <scene name='90/904315/Open_conformation_triade/4'>Open Triade</scene>. One protomer in Neurofibromin has its GRD and Sec14-PH domains oriented in way that is almost reversed in position compared to the closed conformation. The GRD rotates -130° and the Sec14-PH domain rotates -90° in the transition between the closed and the open conformation. Due to this rotation, C1032 is now located too far away, approximately 30 Angstroms, from H1558 and H1576 which results in the loss of the metal-binding site. The lack of the transition metal-binding site allows the GRD to orient itself in such a way that it can associate with <scene name='90/904315/Ras_open_conformation/2'>Ras in the Open Conformation</scene>. The reason that Neurofibromin is only able to associate with Ras in the open conformation is due to one critical residue, the <scene name='90/904315/Open_conformation_arginine_fin/2'>Arginine Finger</scene> located at position 1276 in Neurofibromin. When Neurofibromin is in the open conformation, R1276 is able to <scene name='90/904315/Ras_open_conformation_with_arg/2'>bind to Ras</scene> because there is no steric hindrance from the Neurofibromin core. | ||
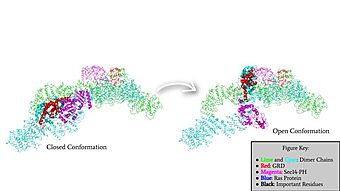
[[Image:GRDandSec14PHRotation.jpg|340 px|left|thumb|Rotation of the GRD and Sec14-PH domains from the closed conformation of neurofibromin to the open conformation of neurofibromin to allow Ras binding. The GRD rotates -130° and the Sec14-PH domain rotates -90°]] | [[Image:GRDandSec14PHRotation.jpg|340 px|left|thumb|Rotation of the GRD and Sec14-PH domains from the closed conformation of neurofibromin to the open conformation of neurofibromin to allow Ras binding. The GRD rotates -130° and the Sec14-PH domain rotates -90°]] | ||
Revision as of 19:21, 5 April 2022
| This Sandbox is Reserved from February 28 through September 1, 2022 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1700 through Sandbox Reserved 1729. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Human Neurofibromin - The Tumor Suppressor Gene
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ Naschberger A, Baradaran R, Rupp B, Carroni M. The structure of neurofibromin isoform 2 reveals different functional states. Nature. 2021 Nov;599(7884):315-319. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04024-x. Epub 2021, Oct 27. PMID:34707296 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04024-x
- ↑ Trovo-Marqui AB, Tajara EH. Neurofibromin: a general outlook. Clin Genet. 2006 Jul;70(1):1-13. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2006.00639.x. PMID:16813595 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-0004.2006.00639.x
- ↑ Lupton CJ, Bayly-Jones C, D'Andrea L, Huang C, Schittenhelm RB, Venugopal H, Whisstock JC, Halls ML, Ellisdon AM. The cryo-EM structure of the human neurofibromin dimer reveals the molecular basis for neurofibromatosis type 1. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2021 Dec;28(12):982-988. doi: 10.1038/s41594-021-00687-2., Epub 2021 Dec 9. PMID:34887559 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41594-021-00687-2
- ↑ Abramowicz A, Gos M. Neurofibromin in neurofibromatosis type 1 - mutations in NF1gene as a cause of disease. Dev Period Med. 2014 Jul-Sep;18(3):297-306. PMID:25182393
- ↑ Ratner N, Miller SJ. A RASopathy gene commonly mutated in cancer: the neurofibromatosis type 1 tumour suppressor. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015 May;15(5):290-301. doi: 10.1038/nrc3911. Epub 2015 Apr 16. PMID:25877329 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nrc3911