We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1719
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
==== Sub-pocket 1 ==== | ==== Sub-pocket 1 ==== | ||
| - | <scene name='90/904324/Active_site_residues/9'>Sub-pocket 1</scene> is a small, shallow pocket formed by TM3, TM6, and ECL2.<ref name="Can"/> Ligand binding is mediated by two key residues on the MRGPRX2 protein within the binding site: Glu164 and Asp184.<ref name="Can"/> The strong charge interactions of these two residues create a highly | + | <scene name='90/904324/Active_site_residues/9'>Sub-pocket 1</scene> is a small, shallow pocket formed by TM3, TM6, and ECL2.<ref name="Can"/> Ligand binding is mediated by two key residues on the MRGPRX2 protein within the binding site: Glu164 and Asp184.<ref name="Can"/> The strong charge interactions of these two residues create a highly negative electrostatic interaction crucial for binding cationic ligands, namely those containing arginine or lysine as shown in '''Figure 3A'''.<ref name="Can"/>. |
==== Sub-pocket 2 ==== | ==== Sub-pocket 2 ==== | ||
| - | <scene name='90/904324/Active_site_residues/8'>Sub-pocket 2</scene> is formed by TM1, TM2, TM6, and TM7.<ref name="Can"/> This binding sub-pocket is much broader and allows for the binding of larger structures ('''Figure 3B''').<ref name="Can"/> The key residues involved are Trp243 and Phe170 | + | <scene name='90/904324/Active_site_residues/8'>Sub-pocket 2</scene> is formed by TM1, TM2, TM6, and TM7.<ref name="Can"/> This binding sub-pocket is much broader and allows for the binding of larger structures ('''Figure 3B''').<ref name="Can"/> The key residues involved are Trp243 and Phe170 which contribute to the high hydrophobicity of the binding pocket.<ref name="Can"/> The hydrophobicity of this binding pocket accounts for the large electrostatic difference observed between the two sub-pockets demonstrated in '''Figure 2'''. |
[[Image:Screen_Shot_2022-04-18_at_3.32.58_PM.png|500px|center|thumb|'''Figure 3.''' (A). Cross-sectional views of electrostatic surface of MRGPRX2 sub-pocket 1 interaction with lysine 3 and (B). sub-pocket 2 interaction with phenylalanine 6 of cortistatin-14.]] | [[Image:Screen_Shot_2022-04-18_at_3.32.58_PM.png|500px|center|thumb|'''Figure 3.''' (A). Cross-sectional views of electrostatic surface of MRGPRX2 sub-pocket 1 interaction with lysine 3 and (B). sub-pocket 2 interaction with phenylalanine 6 of cortistatin-14.]] | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
== Ligand interactions == | == Ligand interactions == | ||
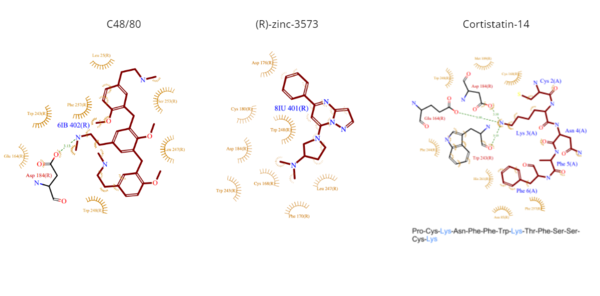
*<scene name='90/904324/C4880/8'>C48/80</scene> | *<scene name='90/904324/C4880/8'>C48/80</scene> | ||
| - | **C48/80 is a peptide limetic agonist that can bind to MRGPRX2 when it is associated with a G<sub>i</sub> or G<sub>q</sub> protein.<ref name= "Yang">DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-04077-y</ref> The structure of the ligand consists of three phenethylamine groups that are arranged in a Y shape with a semicircular arrangement ('''Figure 4''').<ref name="Yang"/> Upon its binding, the Asp184 and Glu164 within sub-pocket 1 interact only with the central phenethylamine ring, forming hydrogen bonds and charge-charge interactions.<ref name="Yang"/> | + | **C48/80 is a peptide limetic agonist that can bind to MRGPRX2 when it is associated with a G<sub>i</sub> or G<sub>q</sub> protein.<ref name= "Yang">DOI: 10.1038/s41586-021-04077-y</ref> The structure of the ligand consists of three phenethylamine groups that are arranged in a Y shape with a semicircular arrangement ('''Figure 4''').<ref name="Yang"/> Upon its binding, the Asp184 and Glu164 residues within sub-pocket 1 interact only with the central phenethylamine ring, forming hydrogen bonds and charge-charge interactions.<ref name="Yang"/> |
*<scene name='90/904324/Rzinc3573/7'>(R)-zinc-3573</scene> | *<scene name='90/904324/Rzinc3573/7'>(R)-zinc-3573</scene> | ||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
== Differences to most class A GPCRs == | == Differences to most class A GPCRs == | ||
| - | The unique characteristics of <scene name='90/904324/Mrgprx2/5'>MRGPRX2</scene> in comparison to class A GPCRs provides an explanation for the differences in ligand interactions. These differences in intermolecular interactions and structural motifs contribute to the surface level ligand binding in MRGPRX2, whereas the typical ligand interaction occurs deep within the helices in class A GPCRs. | + | The unique characteristics of <scene name='90/904324/Mrgprx2/5'>MRGPRX2</scene> in comparison to class A GPCRs provides an explanation for the differences in ligand interactions. These differences in intermolecular interactions and structural motifs contribute to the surface level ligand binding in MRGPRX2, whereas the typical ligand interaction occurs deep within the helices in class A GPCRs.<ref name="Can"/> |
<jmol> | <jmol> | ||
| Line 65: | Line 65: | ||
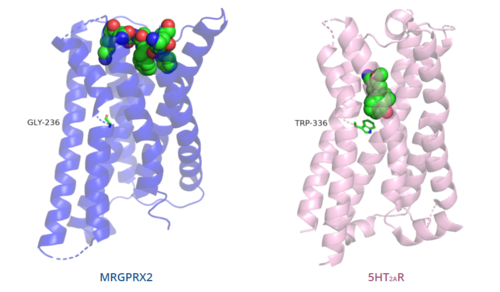
=== Toggle switch === | === Toggle switch === | ||
| - | The conserved <scene name='90/904324/5ht2a_toggle_switch/3'>toggle switch</scene> of class A GPCRs | + | The conserved <scene name='90/904324/5ht2a_toggle_switch/3'>toggle switch</scene> of class A GPCRs functions to activate or inhibit the transduction of the signaling cascade. Typical class A GPCRs contain the conserved ‘toggle switch’ Trp336. In MRGPRX2, this residue is replaced by <scene name='90/904324/Toggle_switch/7'>Gly236</scene>.<ref name="Can"/> By substituting the larger Trp residue with a smaller Gly residue, TM6 is shifted closer to TM3 on the extracellular side of the membrane and contributes to the more tightly packed and shallow binding pocket as compared to other canonical structures. The occluded binding pocket contributes the surface level binding depicted in '''Figure 5''', and allows for a greater variety of ligands interactions with MRGPRX2 as compared to other class A GPCRs, such as [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/5-hydroxytryptamine_receptor 5-HT<sub>2A</sub>R], [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Adrenergic_receptor A<sub>2A</sub>R], and [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Beta-2_Adrenergic_Receptor β<sub>2</sub>AR].<ref name="Can"/> |
=== PIF/LLF motif === | === PIF/LLF motif === | ||
| Line 71: | Line 71: | ||
Canonically, the conserved PIF motif consists of a Pro, Ile, and Phe that transduce the signal produce by ligand binding through the TMD within conserved distances.<ref name="Can"/><ref>DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-02257-x</ref> | Canonically, the conserved PIF motif consists of a Pro, Ile, and Phe that transduce the signal produce by ligand binding through the TMD within conserved distances.<ref name="Can"/><ref>DOI: 10.1038/s41467-017-02257-x</ref> | ||
| - | In MRGPRX2, the PIF motif is changed to a <scene name='90/904324/Pifllf_motif/5'>LLF motif</scene>, in which the residues are shifted down, so that the specific amino acid sequence is not conserved, but instead are conserved at distances that allow them to interact.<ref name="Can"/> Specifically, the residues that make up TM5 have shifted down two residues making Leu194 analogous to the position of | + | In MRGPRX2, the PIF motif is changed to a <scene name='90/904324/Pifllf_motif/5'>LLF motif</scene>, in which the residues are shifted down, so that the specific amino acid sequence is not conserved, but instead residues are conserved at distances that allow them to interact.<ref name="Can"/> Specifically, the residues that make up TM5 have shifted down two residues making Leu194 analogous to the position of Pro in other GPCRs. However, one key difference is that Leu194 is positioned closer (5.48Å) than the conserved distance (5.50Å).<ref name="Can"/> Leu194 is involved in this motif, despite the closer positioning, because the residue that is at the canonical distance is angled away from the TM3-TM6 interface, so it is unable to interact.<ref name="Can"/> Compared with other structures, such as [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/5-hydroxytryptamine_receptor 5-HT<sub>2A</sub>R], [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Adrenergic_receptor A<sub>2A</sub>R], and [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Beta-2_Adrenergic_Receptor β<sub>2</sub>AR], the TM6 helix of MRGPRX2 is closer to the TM3 helix due to the shift in residues, which accounts for the tighter packing of the transmembrane domain helices<ref name="Can"/>, thereby contributing to surface level ligand interactions. |
=== DRY/ERC motif === | === DRY/ERC motif === | ||
The majority of class A GPCRs have a [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/A_Physical_Model_of_the_%CE%B22-Adrenergic_Receptor#conserved%20DRY%20motif conserved E/DRY motif] that is responsible for creating salt bridges that maintain the inactive conformation of the receptor until ligand binding.<ref name="Can"/> | The majority of class A GPCRs have a [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/A_Physical_Model_of_the_%CE%B22-Adrenergic_Receptor#conserved%20DRY%20motif conserved E/DRY motif] that is responsible for creating salt bridges that maintain the inactive conformation of the receptor until ligand binding.<ref name="Can"/> | ||
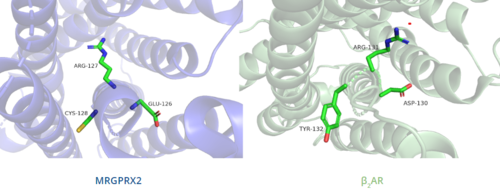
| - | In contrast, '''Figure 6''' shows MRGPRX2 containing an <scene name='90/904324/Erc_motif/3'>ERC motif</scene> in place of the E/DRY motif, which replaces Tyr174 with Cys128.<ref name="Can"/> This replacement alters the spatial organization of the helices due to the replacement of the larger Tyr residue with the smaller Cys residue, thereby condensing the helices.<ref name="Can"/> The condensed spatial organization in MRGPRX2 accounts for the less significant change once a ligand binds to the receptor.<ref name="Can"/> | + | In contrast, '''Figure 6''' shows MRGPRX2 containing an <scene name='90/904324/Erc_motif/3'>ERC motif</scene> in place of the E/DRY motif, which replaces Tyr174 with Cys128.<ref name="Can"/> This replacement alters the spatial organization of the helices due to the replacement of the larger Tyr residue with the smaller Cys residue, thereby condensing the helices.<ref name="Can"/> The condensed spatial organization in MRGPRX2 accounts for the less significant conformational change observed once a ligand binds to the receptor.<ref name="Can"/> |
[[Image:B2AR_motif.png|500px|center|thumb|'''Figure 6.''' Comparison of ERC motif in MRGPRX2 (blue) and conserved DRY motif in β<sub>2</sub>AR (green).]] | [[Image:B2AR_motif.png|500px|center|thumb|'''Figure 6.''' Comparison of ERC motif in MRGPRX2 (blue) and conserved DRY motif in β<sub>2</sub>AR (green).]] | ||
=== Disulfide bonds === | === Disulfide bonds === | ||
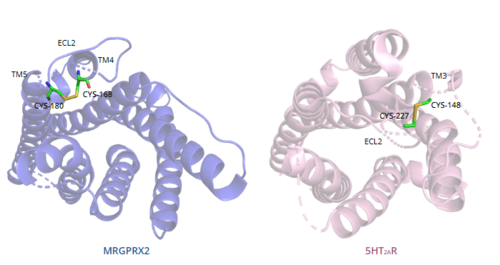
| - | In general, class A GPCRs have a <scene name='90/904324/5ht2a/4'>conserved disulfide bond</scene> between TM3 and ECL2.<ref name="Can"/> In contrast, '''Figure 7''' shows the location MRGPRX2 <scene name='90/904324/Mrgprx2_disulfide_bonds/5'>disulfide bond</scene> between Cys168 of TM4 and Cys180 of TM5, which structurally flips ECL2 to the top of TM4 and TM5.<ref name="Can"/> This creates the wide ligand-binding surface of MRGPRX2 that contributes to surface level binding | + | In general, class A GPCRs have a <scene name='90/904324/5ht2a/4'>conserved disulfide bond</scene> between TM3 and ECL2.<ref name="Can"/> In contrast, '''Figure 7''' shows the location of the MRGPRX2 <scene name='90/904324/Mrgprx2_disulfide_bonds/5'>disulfide bond</scene> between Cys168 of TM4 and Cys180 of TM5, which structurally flips ECL2 to the top of TM4 and TM5.<ref name="Can"/> This creates the wide ligand-binding surface of MRGPRX2 that contributes to surface level binding and allows diverse ligand interactions.<ref name="Can"/> |
[[Image:Disulfide_bond_comparison.png|500px|center|thumb|'''Figure 7.''' Comparison of disulfide bond location in MRGPRX2 (blue) and 5HT2AR (purple).]] | [[Image:Disulfide_bond_comparison.png|500px|center|thumb|'''Figure 7.''' Comparison of disulfide bond location in MRGPRX2 (blue) and 5HT2AR (purple).]] | ||
=== Sodium binding site === | === Sodium binding site === | ||
| - | The [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Neurotensin_receptor#sodium%20binding%20pocket sodium binding site] conserved in class A GPCRs allosterically modulates the stabilization of the GPCR's inactive state. The <scene name='90/904324/Mrgprx2_sodium_site/3'>sodium binding site</scene> of MRGPRX2 contains the conserved Asp75, however, the conserved Ser116 on TM3 seen in class A GPCRs is replaced by Gly116.<ref name="Can"/> The presence of Gly as opposed to the polar Ser contributes to a lack of polar character in addition to decreasing the size of the binding pocket. Both factors thereby limit the binding of sodium ions to the sodium binding site in MRGPRX2.<ref name="Can"/> | + | The [https://proteopedia.org/wiki/index.php/Neurotensin_receptor#sodium%20binding%20pocket sodium binding site] conserved in class A GPCRs allosterically modulates the stabilization of the GPCR's inactive state.<ref name="Can"/> The <scene name='90/904324/Mrgprx2_sodium_site/3'>sodium binding site</scene> of MRGPRX2 contains the conserved Asp75, however, the conserved Ser116 on TM3 seen in class A GPCRs is replaced by Gly116.<ref name="Can"/> The presence of Gly as opposed to the polar Ser contributes to a lack of polar character in addition to decreasing the size of the binding pocket. Both factors thereby limit the binding of sodium ions to the sodium binding site in MRGPRX2.<ref name="Can"/> |
= Mechanism = | = Mechanism = | ||
Revision as of 13:31, 19 April 2022
Human Itch G-Coupled Protein Receptors
| |||||||||||