Introduction

Figure 1. Location of MRGPRX2 in plasma membrane.
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) are the largest class of integral membrane proteins divided into five families; the rhodopsin family (class A), the secretin family (class B), the glutamate family (class C), the frizzled/taste family (class F), and the adhesion family.[1][2][3] GPCRs promote signal transduction activated by a variety of stimuli by undergoing a transmembrane domain conformational change once ligand binding to the N-terminus occurs. This allows for the transduction of a signal to a coupled, heterotrimeric G protein, which then dictates whether an intracellular signaling pathway will be initiated or inhibited.[1][3]
Human Itch G-coupled protein receptors (GPCRs), or Mast cell-related GPCRs (MRGPRX), have been identified as pruritogenic receptors and are found in human sensory neurons, specifically in the connective tissue mast cells and dorsal root ganglia in humans.[4] They are classified as class A GPCRs, however, MRGPRX receptors respond to a diverse number of agonists, antagonists, and inverse agonists some of which are not typical ligands of class A receptors. MRGPRX receptors are involved in host defense, pseudo-allergic reactions, non-histaminergic itch, periodontitis, neurogenic inflammation, and inflammatory pain.[4]
The determination of the first structures of a ligand-activated GPCR was achieved by Robert J. Lefkowitz and Brian K. Kobilka which won them the 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. They also successfully captured images of the first activated GPCR in a complex with a G protein. See Nobel Prizes for 3D Molecular Structure.
Related Enzymes
Among Human Itch GPCRs, is a class A GPCR that regulates mast cell degranulation and itch-related hypersensitivity reactions.[5][6] MRGPRX2 is also a target of morphinan alkaloids, like morphine, codeine, and dextromethorphan.[5][6] MRGPRX2 couples to nearly all G-protein families and subtypes with robust coupling to Gq and Gi families.[5][6]
is another sub-group of the MRGPRX family, which mediates cholestatic itch and is a target of nateglinide drugs.[5][6] MRGPRX4 also couples to Gq and Gi similar to MRGPRX2.
Structure Overview
The receptor [5] Ligand binding occurs at the N-terminus in the extracellular domain and is composed of two binding sub-pockets.[5] The intracellular domain consists of helix VII and a C-terminal sequence, which binds the G-protein and promotes downstream signaling.[5]
Ligand Binding Site

Figure 2. Electrostatic surface of MRGPRX2 ligand binding pocket with cortistatin-14
In , the ligand binding pocket is located in the N-terminus of the transmembrane domain and consists of two sub-pockets that differ in physical and chemical properties (Figure 2) that allows for various ligand interactions.[5][6] Unlike most class A GPCRs, the ligand binding site of MRGPRX2 is closer to the surface of the membrane due to the absence and alterations in conserved class A GPCR motifs and structures.[5][6]
Sub-pocket 1
is a small, shallow pocket formed by TM3, TM6, and ECL2.[5] Ligand binding is mediated by two key residues on the MRGPRX2 protein within the binding site: Glu164 and Asp184.[5] The strong charge interactions of these two residues create a highly negative electrostatic interaction crucial for binding cationic ligands, namely those containing arginine or lysine as shown in Figure 3A.[5].
Sub-pocket 2
is formed by TM1, TM2, TM6, and TM7.[5] This binding sub-pocket is much broader and allows for the binding of larger structures (Figure 3B).[5] The key residues involved are Trp243 and Phe170 which contribute to the high hydrophobicity of the binding pocket.[5] The hydrophobicity of this binding pocket accounts for the large electrostatic difference observed between the two sub-pockets demonstrated in Figure 2.

Figure 3. (A). Cross-sectional views of electrostatic surface of MRGPRX2 sub-pocket 1 interaction with lysine 3 and (B). sub-pocket 2 interaction with phenylalanine 6 of cortistatin-14.
Ligand interactions
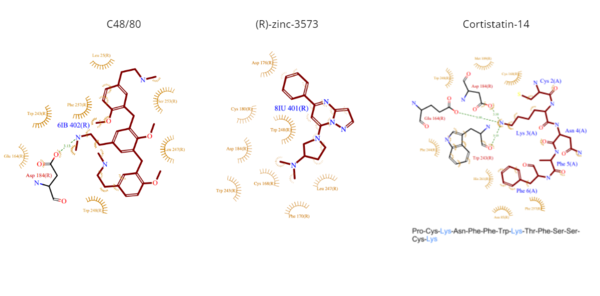
Figure 4. Common MRGPRX2 ligand structures and interactions. Hydrophobic interactions are shown by dashed wheat lines indicating direction. Positive atoms are represented in blue. Negative atoms are represented in red.
-
- C48/80 is a peptide limetic agonist that can bind to MRGPRX2 when it is associated with a Gi or Gq protein.[6] The structure of the ligand consists of three phenethylamine groups that are arranged in a Y shape with a semicircular arrangement (Figure 4).[6] Upon its binding, the Asp184 and Glu164 residues within sub-pocket 1 interact only with the central phenethylamine ring, forming hydrogen bonds and charge-charge interactions.[6]
-
- (R)-zinc-3573 is an agonist that binds to MRGPRX2 when it is associated with a Gi or Gq protein.[5] This agonist is a small cationic molecule that forms largely ionic interactions with the negatively-charged sub-pocket 1 and has no interactions with sub-pocket 2 (Figure 4).[5] (R)-zinc-3573 forms hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions with Asp184 and Glu164 of sub-pocket 1.[5][7]
-
- Cortistatin-14 is an endogenous, cyclic, neuropeptide agonist which interacts with MRGPRX2 in the same way whether it is coupled to Gi or Gq proteins (Figure 4).[5][8] Cortistation-14 is widely available in many systems throughout the body and naturally functions to regulate many physiological and pathological mechanisms. The lysine residue (Lys3) on Cortistatin-14 binds in the negatively-charged sub-pocket 1 and forms strong charge interactions with Asp184 and Glu164.[5] The remaining residues of Cortistatin-14 will extend over to sub-pocket 2 and bind through hydrophobic interactions.[5]
Differences to most class A GPCRs
The unique characteristics of in comparison to class A GPCRs provides an explanation for the differences in ligand interactions. These differences in intermolecular interactions and structural motifs contribute to the surface level ligand binding in MRGPRX2, whereas the typical ligand interaction occurs deep within the helices in class A GPCRs.[5]
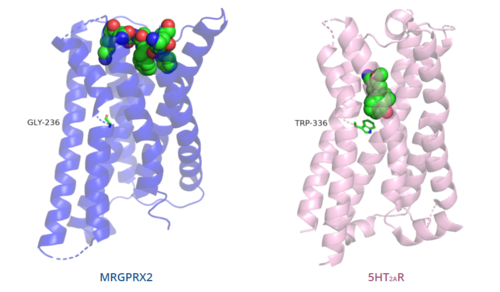
Figure 5. Comparison of ligand binding depth in MRGPRX2 (blue) and 5HT2AR (purple).
Toggle switch
The conserved of class A GPCRs functions to activate or inhibit the transduction of the signaling cascade. Typical class A GPCRs contain the conserved ‘toggle switch’ Trp336. In MRGPRX2, this residue is replaced by .[5] By substituting the larger Trp residue with a smaller Gly residue, TM6 is shifted closer to TM3 on the extracellular side of the membrane and contributes to the more tightly packed and shallow binding pocket as compared to other canonical structures. The occluded binding pocket contributes the surface level binding depicted in Figure 5, and allows for a greater variety of ligands interactions with MRGPRX2 as compared to other class A GPCRs, such as 5-HT2AR, A2AR, and β2AR.[5]
PIF/LLF motif
The majority of class A GPCRs contain a conserved at the TM3-TM6 interface.[5]
Canonically, the conserved PIF motif consists of a Pro, Ile, and Phe that transduce the signal produce by ligand binding through the TMD within conserved distances.[5][9]
In MRGPRX2, the PIF motif is changed to a , in which the residues are shifted down, so that the specific amino acid sequence is not conserved, but instead residues are conserved at distances that allow them to interact.[5] Specifically, the residues that make up TM5 have shifted down two residues making Leu194 analogous to the position of Pro in other GPCRs. However, one key difference is that Leu194 is positioned closer (5.48Å) than the conserved distance (5.50Å).[5] Leu194 is involved in this motif, despite the closer positioning, because the residue that is at the canonical distance is angled away from the TM3-TM6 interface, so it is unable to interact.[5] Compared with other structures, such as 5-HT2AR, A2AR, and β2AR, the TM6 helix of MRGPRX2 is closer to the TM3 helix due to the shift in residues, which accounts for the tighter packing of the transmembrane domain helices[5], thereby contributing to surface level ligand interactions.
DRY/ERC motif
The majority of class A GPCRs have a conserved E/DRY motif that is responsible for creating salt bridges that maintain the inactive conformation of the receptor until ligand binding.[5]
In contrast, Figure 6 shows MRGPRX2 containing an in place of the E/DRY motif, which replaces Tyr174 with Cys128.[5] This replacement alters the spatial organization of the helices due to the replacement of the larger Tyr residue with the smaller Cys residue, thereby condensing the helices.[5] The condensed spatial organization in MRGPRX2 accounts for the less significant conformational change observed once a ligand binds to the receptor.[5]
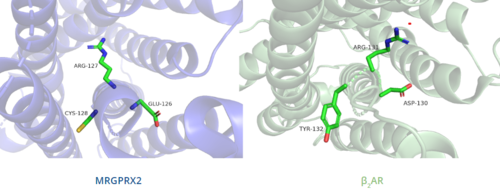
Figure 6. Comparison of ERC motif in MRGPRX2 (blue) and conserved DRY motif in β
2AR (green).
Disulfide bonds
In general, class A GPCRs have a between TM3 and ECL2.[5] In contrast, Figure 7 shows the location of the MRGPRX2 between Cys168 of TM4 and Cys180 of TM5, which structurally flips ECL2 to the top of TM4 and TM5.[5] This creates the wide ligand-binding surface of MRGPRX2 that contributes to surface level binding and allows diverse ligand interactions.[5]
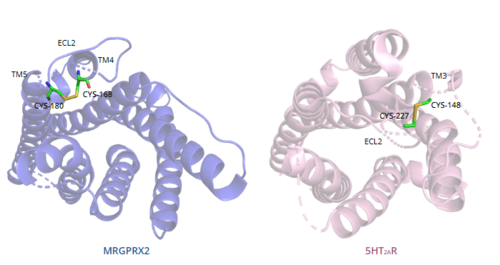
Figure 7. Comparison of disulfide bond location in MRGPRX2 (blue) and 5HT2AR (purple).
Sodium binding site
The sodium binding site conserved in class A GPCRs allosterically modulates the stabilization of the GPCR's inactive state.[5] The of MRGPRX2 contains the conserved Asp75, however, the conserved Ser116 on TM3 seen in class A GPCRs is replaced by Gly116.[5] The presence of Gly as opposed to the polar Ser contributes to a lack of polar character in addition to decreasing the size of the binding pocket. Both factors thereby limit the binding of sodium ions to the sodium binding site in MRGPRX2.[5]
Mechanism
G-proteins, when paired with a GPCR, assist in signal transduction.[10][11] G-proteins are heterotrimeric GTPases composed of three subunits: . The α subunit acts as the main signal mediator and contains a binding site for GDP or GTP, which acts as a biological “switch” to regulate the transmission of a signal from the activated receptor.[10][11] The α subunit will dissociate and can then move in the plane of the membrane from the receptor to bind to downstream effectors to continue signal transmission and ultimately produce a cellular response.[10][11]
Gq and Gi Family α Subunits
The actions that G-proteins induce can be classified based on the sequence homology of α subunit (Gα) present.[10][12] The most well-known are referred to as Gi, Gs, and Gq. The Gs and Gq proteins are stimulatory, while the Gi protein is inhibitory.[10][12] In addition, proteins are classified based on the signaling pathway that they regulate. For example, Gq proteins are seen in a signaling pathway that relies on phospholipase C enzymes, while Gs and Gi proteins are regulators of adenylate cyclase.[12] On this page, we will be focusing solely on the structures of the Gq and Gi proteins and their interactions with mast-cell receptors.
Gαq and Gαi are proteins comprised of 359 amino acid residues, with varying sequences, that both contain a helical domain and a GTPase binding domain.[12] The GTPase binding domain is responsible for the hydrolysis of GTP as well as the binding of the β and γ subunits that form the trimeric protein structure. The helical domain contains six α helices, which are responsible for the binding of the G-protein to the coupled receptor.[12]
The conformations of the G-proteins vary based on their association with a particular membrane receptor due to interactions between the amino acids in the N-terminus of the α subunit and the C-terminus of the receptor.[12]
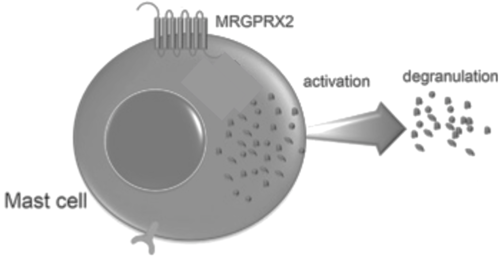
Figure 8. Cellular response of mast cell upon activation of MRGPRX2.
Binding to the extracellular N-terminus domain triggers a transmembrane conformation change of MRGPRX2, which demonstrates a less significant change when compared to other class A GPCRs due to the surface level binding of the ligand to MRGPRX2.[5] Once ligand binding and the conformational change to the active state have taken place, the signal is relayed to the α-subunit of the heterotrimeric G-protein.[11] The α-subunit will then exchange a GDP for GTP to initiate the dissociation of the α, β, and γ subunits.[11] During this dissociation, the α-subunit is able to travel away from the receptor in the plane of the membrane to bind to downstream effectors to produce a cellular response.[11]
Clinical Relevance
The discovery of -mediated allergic reactions has provided additional insight into anaphylactic and allergic-type reactions to medications. The MRGPRX2 mechanism allows for the triggering of mast-cell granulation without immune priming due to the fact that it bypasses the previously known antibody-mediated, or IgE-mediated pathway.[13][14]
The activation of the MRGPRX2-mediated pathway has been labeled as “pseudo-allergic” events, so as to separate them from true allergic reactions.[14] Due to this distinction, there is now the possibility that side effects that were previously attributed to IgE-mediated reactions, may have actually been caused by MRGPRX2-mediated reactions.[14]
In general, MRGPRX2-mediated anaphylactic responses occur more quickly than IgE-mediated responses, but the responses also tended to be more transient.[13][14] Common commercial drugs, like icatibant and cetrorelix, as well as neuromuscular blocking agents activate mast cells through the MRGPRX2 pathway. Furthermore, due to the wide and shallow binding pocket of MRGPRX2, there is a wide range of molecules, and thus medications, that can possibly bind and activate this mechanism.[14] The majority of these medications have a net positive charge and carry cationic groups.
Many mutations also affect the actions of MRGPRX2. For example, a single residue mutation in sub-pocket 1 (Glu164Arg) prevented interactions between the receptor and ligands like C48/80.[13] In addition, single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) have been linked to many variations of MRGPRX2 which predispose patients to hyperactivation of the receptors. Two of the most common SNPs are Asn62Thr which affects the cytoplasmic domain and Asn16His which affects the extracellular domain.[13] These mutations have been theorized to potentially protect patients from drug-induced mast cell degranulation and hypersensitivity reactions.
Interestingly, within the MRGPRX2-mediated pathway, reaction frequencies differ. In the same patients, anaphylactic reactions can occur by both IgE-mediated and MRGPRX2-mediated pathways, however since MRGPRX2-mediated are often dose-dependent it would require an extended period of exposure through plasma drug levels.[14] The presence of both mechanisms within a single patient may be responsible for the cross-reactivity between drugs and the variations in severity of allergic-type reactions.[14][13] This has led to a hypothesis that certain drugs may interact with MRGPRX2 on different active sites within the receptor. In addition, studies have also led to hypotheses that the intracellular signaling pathways triggered by the binding of varying drugs may have different intracellular responses based on the site of binding.[13]
3D Structures
See Also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 Zhang Y, Devries ME, Skolnick J. Structure modeling of all identified G protein-coupled receptors in the human genome. PLoS Comput Biol. 2006 Feb;2(2):e13. Epub 2006 Feb 17. PMID:16485037 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.0020013
- ↑ Millar RP, Newton CL. The year in G protein-coupled receptor research. Mol Endocrinol. 2010 Jan;24(1):261-74. Epub 2009 Dec 17. PMID:20019124 doi:10.1210/me.2009-0473
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Zhang D, Zhao Q, Wu B. Structural Studies of G Protein-Coupled Receptors. Mol Cells. 2015 Oct;38(10):836-42. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2015.0263. Epub 2015, Oct 15. PMID:26467290 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2015.0263
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Davidson S, Giesler GJ. The multiple pathways for itch and their interactions with pain. Trends Neurosci. 2010 Dec;33(12):550-8. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2010.09.002. Epub, 2010 Nov 5. PMID:21056479 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2010.09.002
- ↑ 5.00 5.01 5.02 5.03 5.04 5.05 5.06 5.07 5.08 5.09 5.10 5.11 5.12 5.13 5.14 5.15 5.16 5.17 5.18 5.19 5.20 5.21 5.22 5.23 5.24 5.25 5.26 5.27 5.28 5.29 5.30 5.31 5.32 5.33 5.34 5.35 5.36 5.37 5.38 5.39 5.40 Cao C, Kang HJ, Singh I, Chen H, Zhang C, Ye W, Hayes BW, Liu J, Gumpper RH, Bender BJ, Slocum ST, Krumm BE, Lansu K, McCorvy JD, Kroeze WK, English JG, DiBerto JF, Olsen RHJ, Huang XP, Zhang S, Liu Y, Kim K, Karpiak J, Jan LY, Abraham SN, Jin J, Shoichet BK, Fay JF, Roth BL. Structure, function and pharmacology of human itch GPCRs. Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7887):170-175. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04126-6. Epub 2021, Nov 17. PMID:34789874 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04126-6
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 6.2 6.3 6.4 6.5 6.6 6.7 6.8 Yang F, Guo L, Li Y, Wang G, Wang J, Zhang C, Fang GX, Chen X, Liu L, Yan X, Liu Q, Qu C, Xu Y, Xiao P, Zhu Z, Li Z, Zhou J, Yu X, Gao N, Sun JP. Structure, function and pharmacology of human itch receptor complexes. Nature. 2021 Dec;600(7887):164-169. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04077-y. Epub 2021, Nov 17. PMID:34789875 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41586-021-04077-y
- ↑ Lansu K, Karpiak J, Liu J, Huang XP, McCorvy JD, Kroeze WK, Che T, Nagase H, Carroll FI, Jin J, Shoichet BK, Roth BL. In silico design of novel probes for the atypical opioid receptor MRGPRX2. Nat Chem Biol. 2017 May;13(5):529-536. doi: 10.1038/nchembio.2334. Epub 2017 Mar , 13. PMID:28288109 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2334
- ↑ Jiang J, Peng Y, Liang X, Li S, Chang X, Li L, Chang M. Centrally Administered Cortistation-14 Induces Antidepressant-Like Effects in Mice via Mediating Ghrelin and GABAA Receptor Signaling Pathway. Front Pharmacol. 2018 Jul 19;9:767. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.00767. eCollection, 2018. PMID:30072893 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00767
- ↑ Schonegge AM, Gallion J, Picard LP, Wilkins AD, Le Gouill C, Audet M, Stallaert W, Lohse MJ, Kimmel M, Lichtarge O, Bouvier M. Evolutionary action and structural basis of the allosteric switch controlling beta2AR functional selectivity. Nat Commun. 2017 Dec 18;8(1):2169. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02257-x. PMID:29255305 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02257-x
- ↑ 10.0 10.1 10.2 10.3 10.4 Edward Zhou X, Melcher K, Eric Xu H. Structural biology of G protein-coupled receptor signaling complexes. Protein Sci. 2019 Mar;28(3):487-501. doi: 10.1002/pro.3526. Epub 2018 Dec 13. PMID:30311978 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/pro.3526
- ↑ 11.0 11.1 11.2 11.3 11.4 11.5 Nelson, David L. (David Lee), 1942-. (2005). Lehninger principles of biochemistry. New York :W.H. Freeman
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 Kamato D, Thach L, Bernard R, Chan V, Zheng W, Kaur H, Brimble M, Osman N, Little PJ. Structure, Function, Pharmacology, and Therapeutic Potential of the G Protein, Galpha/q,11. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2015 Mar 24;2:14. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2015.00014. eCollection, 2015. PMID:26664886 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fcvm.2015.00014
- ↑ 13.0 13.1 13.2 13.3 13.4 13.5 Porebski G, Kwiecien K, Pawica M, Kwitniewski M. Mas-Related G Protein-Coupled Receptor-X2 (MRGPRX2) in Drug Hypersensitivity Reactions. Front Immunol. 2018 Dec 20;9:3027. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.03027. eCollection, 2018. PMID:30619367 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.03027
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 14.4 14.5 14.6 McNeil BD. MRGPRX2 and Adverse Drug Reactions. Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 6;12:676354. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.676354. eCollection , 2021. PMID:34421893 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2021.676354
Student contributors
Joey Gareis
Madeline Beck








