Citric Acid Cycle
From Proteopedia
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
'''Step 0 / 10 - Aldol condensation - Citrate synthase''' | '''Step 0 / 10 - Aldol condensation - Citrate synthase''' | ||
| + | *[[Citrate Synthase]] | ||
Articles in Proteopedia concerning [[Citric Acid Cycle]] include: | Articles in Proteopedia concerning [[Citric Acid Cycle]] include: | ||
Revision as of 12:56, 12 September 2022
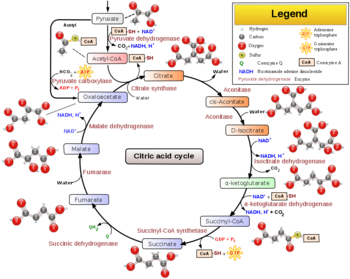
The Citric Acid Cycle is a key metabolic pathway that connects carbohydrate, fat, and protein metabolism.
The Citric Acid Cycle (tricarboxylic acid cycle) is a series of enzyme catalyzed reactions which are critical in cellular respiration. Under oxidative conditions, pyruvate continues to be metabolized through the tricarboxylic acid cycle. In this cycle, Acetyl-CoA, a byproduct of glycolysis, along with various cofactors, are broken down into carbon dioxide, water, and energy in the form of GTP and NADH.
Step 0 / 10 - Aldol condensation - Citrate synthase
Articles in Proteopedia concerning Citric Acid Cycle include:
- Citrate Synthase Structure & Mechanism
- Aconitase
- Isocitrate Dehydrogenase
- 2-Oxoglutarate Dehydrogenase (also known as alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase)
- Succinyl-CoA Synthetase
- Succinate Dehydrogenase
- Fumarase
- Malate Dehydrogenase
- Glutamate Dehydrogenase
To view Citric Acid Cycle related proteins which are Structure Index entries see:
To view automatically seeded indices concerning Citric Acid Cycle See:
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Alexander Berchansky, David Canner, Ann Taylor, Wayne Decatur, Jaime Prilusky