This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
BASIL2022GV3R8E
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
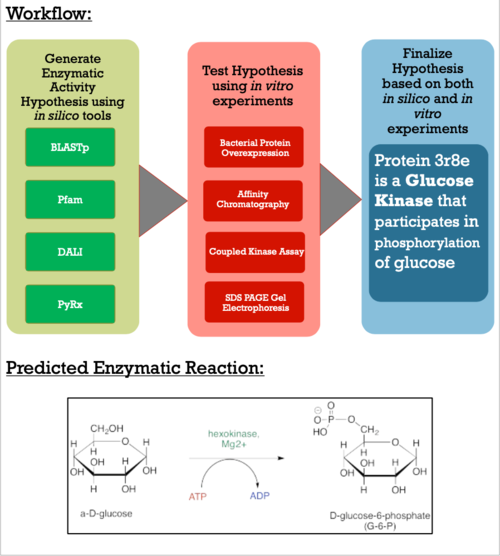
==Characterization of the 3r8e Protein, a Novel Glucose Kinase== | ==Characterization of the 3r8e Protein, a Novel Glucose Kinase== | ||
| - | <StructureSection load=' | + | <StructureSection load='3r8e' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> |
== Abstract == | == Abstract == | ||
The Protein Data Bank (PDB) contains approximately 188 thousand protein structures, 5000 of which have not been assigned a specific function. As a part of the Biochemistry Authentic Scientific Inquiry Laboratory (BASIL) project, we were tasked with analyzing and determining the function of one of these proteins, PDB ID 3r8e. This protein is a putative kinase, which is of interest due to the key roles kinases play in many cellular processes. Utilizing the modules the BASIL consortium provides, a series of in silico and in vitro experiments were conducted. The 3r8e protein was first studied using a variety of in silico tools, including BLASTp, Pfam, and DALI. Based on our in silico results, glucose was determined to be the most likely substrate for 3r8e and was used for further in vitro characterization of the protein. To confirm the in silico function prediction for the 3r8e protein, bacterial protein overexpression, affinity chromatography purification, and coupled kinase activity assays were utilized. Multiple sugar substrates for 3r8e were tested, including glucose. The coupled kinase assay results confirmed that 3r8e likely plays a role in glucose phosphorylation, aligning with our in silico conclusions. Future directions include repeating the above experiments and testing additional hexose substrates to further characterize the enzymatic activity of 3r8e. Overall, we have strong preliminary evidence that the 3r8e protein is a glucose kinase and future work will allow us to confirm this. | The Protein Data Bank (PDB) contains approximately 188 thousand protein structures, 5000 of which have not been assigned a specific function. As a part of the Biochemistry Authentic Scientific Inquiry Laboratory (BASIL) project, we were tasked with analyzing and determining the function of one of these proteins, PDB ID 3r8e. This protein is a putative kinase, which is of interest due to the key roles kinases play in many cellular processes. Utilizing the modules the BASIL consortium provides, a series of in silico and in vitro experiments were conducted. The 3r8e protein was first studied using a variety of in silico tools, including BLASTp, Pfam, and DALI. Based on our in silico results, glucose was determined to be the most likely substrate for 3r8e and was used for further in vitro characterization of the protein. To confirm the in silico function prediction for the 3r8e protein, bacterial protein overexpression, affinity chromatography purification, and coupled kinase activity assays were utilized. Multiple sugar substrates for 3r8e were tested, including glucose. The coupled kinase assay results confirmed that 3r8e likely plays a role in glucose phosphorylation, aligning with our in silico conclusions. Future directions include repeating the above experiments and testing additional hexose substrates to further characterize the enzymatic activity of 3r8e. Overall, we have strong preliminary evidence that the 3r8e protein is a glucose kinase and future work will allow us to confirm this. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
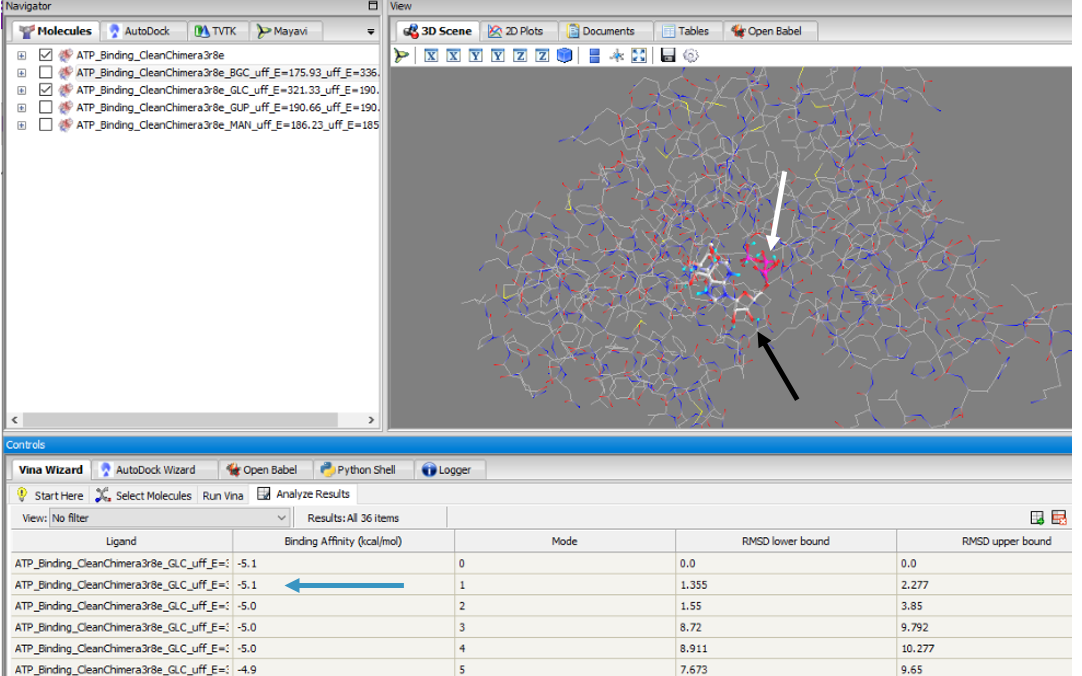
These results along with supporting evidence from the other in silico tools allowed us to then conduct in silico docking experiments to further confirm our hypothesis. Below is a figure with the PyRx docking results of glucose and ATP with our protein. | These results along with supporting evidence from the other in silico tools allowed us to then conduct in silico docking experiments to further confirm our hypothesis. Below is a figure with the PyRx docking results of glucose and ATP with our protein. | ||
| - | [[Image:PyRx1.png| | + | [[Image:PyRx1.png|px|100]] |
The -5.1 kcal/mol value shows that our protein of interest hypothesis of a glucose kinase is strong. The confidence behind our in silico results allowed us to move into testing our hypothesis in vitro. Because ATP is a commonality amongst sugar kinases, an <scene name='90/904995/3r8ec_w_glc_and_atp/1'>interactive structure</scene> has been provided to represent glucose and ATP in the active site. | The -5.1 kcal/mol value shows that our protein of interest hypothesis of a glucose kinase is strong. The confidence behind our in silico results allowed us to move into testing our hypothesis in vitro. Because ATP is a commonality amongst sugar kinases, an <scene name='90/904995/3r8ec_w_glc_and_atp/1'>interactive structure</scene> has been provided to represent glucose and ATP in the active site. | ||
== Experimental Results/Function == | == Experimental Results/Function == | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
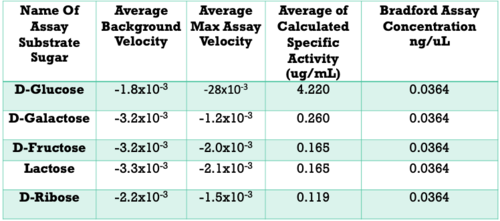
[[Image:KinaseAssayResults.png|500px|]] | [[Image:KinaseAssayResults.png|500px|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | For further validation, we conducted an SDS analysis and provided below is the gel image. Results were not as clear as anticipated, and in future studies, we would need to utilize different chromatography methods to yield higher quality protein concentrations and conduct a pre and post induction to visualize the purity of our protein. | ||
| + | |||
== Project Implications == | == Project Implications == | ||
The goal of this project is to explore the methods it takes to characterize a putative kinase. To do this, we became familiar with online alignment, structure, and function tools, paired with a variety of in vitro lab experiments, such as bacterial protein overexpression, affinity chromatography, coupled kinase assays, and SDS PAGE Gel Electrophoresis. Proteins are biomolecules essential to organisms' survival and understanding how they work in result of their function is pivotal for advances in modern medicine, scientific research, and agriculture. | The goal of this project is to explore the methods it takes to characterize a putative kinase. To do this, we became familiar with online alignment, structure, and function tools, paired with a variety of in vitro lab experiments, such as bacterial protein overexpression, affinity chromatography, coupled kinase assays, and SDS PAGE Gel Electrophoresis. Proteins are biomolecules essential to organisms' survival and understanding how they work in result of their function is pivotal for advances in modern medicine, scientific research, and agriculture. | ||
Revision as of 15:38, 19 September 2022
Characterization of the 3r8e Protein, a Novel Glucose Kinase
| |||||||||||
References
1. Blastp [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): Natiobal Library of Medicine (US), National Center for Biotechnology Information; 2004- [cited 2022 March]. Available from: (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PAGE=Proteins)
2. BASIL. https://basilbiochem.github.io/basil/
3. Holm L (2020) Using Dali for protein structure comparison. Methods Mol. Biol. 2112, 29-42.
4. Small- Molecule Library Screening by Docking with PyRx. .Dallakyan S, Olson AJ Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1263:243-50. The full-text is available at https://www.researchgate.net/publications/2739554875. Small-Molecule Library Screening by Docking with PyRx.
5. Pfam: The Protein families database in 2021 J. Mistry, S. Chuguransky, L. Williams, M. Qureshi, G.A. Salazar, E.L.L. Sonnhammer, S.C.E. Tosatto, L. Paladin, S. Raj, L.J. Richardson, R.D. Finn, A. Bateman Nucleic Acids Research (2020) doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa913
6. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.2r3pre, Schrödinger, LLC.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Dalton Dencklau, Michel Evertsen, Bonnie Hall, Jaime Prilusky