BASIL2022GV3R8E
From Proteopedia
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<StructureSection load='3r8e' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | <StructureSection load='3r8e' size='340' side='right' caption='Caption for this structure' scene=''> | ||
== Abstract == | == Abstract == | ||
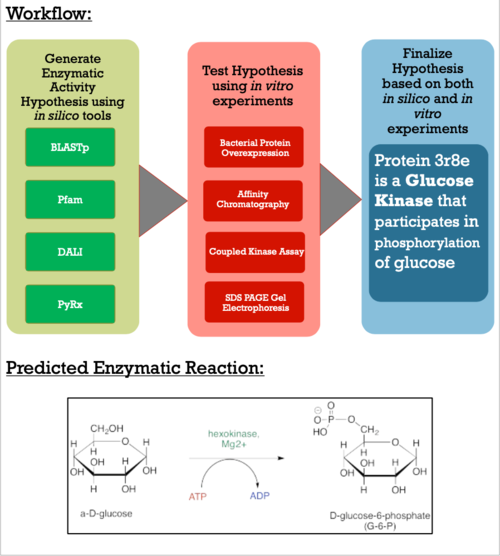
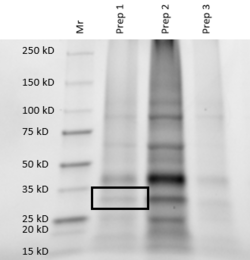
| - | The Protein Data Bank (PDB) contains approximately 188 thousand protein structures, 5000 of which have not been assigned a specific function. As a part of the Biochemistry Authentic Scientific Inquiry Laboratory (BASIL) project, we were tasked with analyzing and determining the function of one of these proteins, PDB ID 3r8e. This protein is a putative kinase, which is of interest due to the key roles kinases play in many cellular processes. Utilizing the modules the BASIL consortium provides, a series of in silico and in vitro experiments were conducted. The 3r8e protein was first studied using a variety of in silico tools, including BLASTp, Pfam, and DALI. Based on our in silico results, glucose was determined to be the most likely substrate for 3r8e and was used for further in vitro characterization of the protein. To confirm the in silico function prediction for the 3r8e protein, bacterial protein overexpression, affinity chromatography purification, coupled kinase activity assays, and SDS PAGE analyses were utilized. Multiple sugar substrates for 3r8e were tested, including glucose. The coupled kinase assay results confirmed that 3r8e likely plays a role in glucose phosphorylation, aligning with our in silico conclusions. Previous and subsequent analysis of protein 3r8e validated our initial in silico and in vitro results. Overall, we have strong preliminary evidence that the our protein of interest (POI) is a glucose kinase. | + | The Protein Data Bank (PDB) contains approximately 188 thousand protein structures, 5000 of which have not been assigned a specific function. As a part of the Biochemistry Authentic Scientific Inquiry Laboratory (BASIL) project, we were tasked with analyzing and determining the function of one of these proteins, PDB ID 3r8e. This protein is a putative kinase, which is of interest due to the key roles kinases play in many cellular processes. Utilizing the modules the BASIL consortium provides, a series of in silico and in vitro experiments were conducted. The 3r8e protein was first studied using a variety of in silico tools, including BLASTp, Pfam, and DALI. Based on our in silico results, glucose was determined to be the most likely substrate for 3r8e and was used for further in vitro characterization of the protein. To confirm the in silico function prediction for the 3r8e protein, bacterial protein overexpression, affinity chromatography purification, coupled kinase activity assays, and SDS PAGE analyses were utilized. Multiple sugar substrates for 3r8e were tested, including glucose. The coupled kinase assay results confirmed that 3r8e likely plays a role in glucose phosphorylation, aligning with our in silico conclusions. Previous and subsequent analysis of protein 3r8e validated our initial in silico and in vitro results. Overall, we have strong preliminary evidence that the our protein of interest (POI) is a <scene name='90/904995/Mesh_backbone_with_atp_glucose/2'>glucose kinase</scene>. |
== Introduction == | == Introduction == | ||
As apart of a research project under the Biochemistry Authentic Scientific Inquiry Laboratory (BASIL) consortium, our group was tasked with characterizing and identifying the function of this protein to provide further insight of the protein's relationship to the bacteria. Like many proteins with solved crystal structures, protein 3r8e has an uncharacterized and unconfirmed function. Previous research has shown that there is relationship between our POI and bacteria found in soil. Current research techniques have made the role more apparent and below is the general workflow detailing how we generated our conclusions. | As apart of a research project under the Biochemistry Authentic Scientific Inquiry Laboratory (BASIL) consortium, our group was tasked with characterizing and identifying the function of this protein to provide further insight of the protein's relationship to the bacteria. Like many proteins with solved crystal structures, protein 3r8e has an uncharacterized and unconfirmed function. Previous research has shown that there is relationship between our POI and bacteria found in soil. Current research techniques have made the role more apparent and below is the general workflow detailing how we generated our conclusions. | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
[[Image:3R8EDALIHMM.png|400px|]] | [[Image:3R8EDALIHMM.png|400px|]] | ||
| - | + | ||
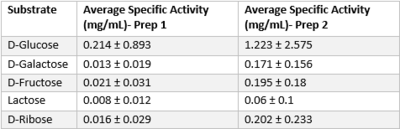
From here, we were able to form the conclusion that our POI interacts with glucose based on the alignment with a known hexokinase. To validate that glucose actually binds and interacts with our protein of interest, we conducted a PyRx in silico docking experiment with a total of five hexose substrates. Other substrates tested include fructose, galactose, lactose, and ribose, however, experimental in silico docking results for those substrates were significantly less than glucose. Along with the PyRx docking, we visualized ATP and glucose (Orange) within the proposed active site in the PyMol visualization below. The binding affinity of glucose was -5.1 kcal/mol, which strengthens our idea that glucose is phosphorylated by our protein of interest. The confidence behind our in silico results allowed us to move into testing our hypothesis in vitro and because ATP aids in the phosphorylation of glucose, an <scene name='90/904995/3r8ec_w_glc_and_atp/1'>interactive structure</scene> has been provided to represent interactions of glucose and ATP in the active site. | From here, we were able to form the conclusion that our POI interacts with glucose based on the alignment with a known hexokinase. To validate that glucose actually binds and interacts with our protein of interest, we conducted a PyRx in silico docking experiment with a total of five hexose substrates. Other substrates tested include fructose, galactose, lactose, and ribose, however, experimental in silico docking results for those substrates were significantly less than glucose. Along with the PyRx docking, we visualized ATP and glucose (Orange) within the proposed active site in the PyMol visualization below. The binding affinity of glucose was -5.1 kcal/mol, which strengthens our idea that glucose is phosphorylated by our protein of interest. The confidence behind our in silico results allowed us to move into testing our hypothesis in vitro and because ATP aids in the phosphorylation of glucose, an <scene name='90/904995/3r8ec_w_glc_and_atp/1'>interactive structure</scene> has been provided to represent interactions of glucose and ATP in the active site. | ||
Revision as of 19:28, 29 September 2022
Characterization of the 3r8e Protein, a Novel Glucose Kinase
| |||||||||||
References
1. Blastp [Internet]. Bethesda (MD): Natiobal Library of Medicine (US), National Center for Biotechnology Information; 2004- [cited 2022 March]. Available from: (https://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi?PAGE=Proteins)
2. BASIL. https://basilbiochem.github.io/basil/
3. Holm L (2020) Using Dali for protein structure comparison. Methods Mol. Biol. 2112, 29-42.
4. Small- Molecule Library Screening by Docking with PyRx. .Dallakyan S, Olson AJ Methods Mol Biol. 2015;1263:243-50. The full-text is available at https://www.researchgate.net/publications/2739554875. Small-Molecule Library Screening by Docking with PyRx.
5. Pfam: The Protein families database in 2021 J. Mistry, S. Chuguransky, L. Williams, M. Qureshi, G.A. Salazar, E.L.L. Sonnhammer, S.C.E. Tosatto, L. Paladin, S. Raj, L.J. Richardson, R.D. Finn, A. Bateman Nucleic Acids Research (2020) doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa913
6. The PyMOL Molecular Graphics System, Version 1.2r3pre, Schrödinger, LLC.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Dalton Dencklau, Michel Evertsen, Bonnie Hall, Jaime Prilusky