This is a default text for your page BASIL2023GVP30646. Click above on edit this page to modify. Be careful with the < and > signs.
You may include any references to papers as in: the use of JSmol in Proteopedia [1] or to the article describing Jmol [2] to the rescue.
Abstract
The Protein Data Bank (PDB) and UniProt contain a wealth of protein structures, many of which do not have a known function. One such protein is P30646, an uncharacterized sugar kinase. Sugar kinases play a role in a variety of metabolic processes within the body, so understanding their functions is of great importance. Our work aimed to further characterize P30646 through the identification of a substrate for this enzyme. Utilizing materials Biochemistry Authentic Scientific Inquiry Laboratory (BASIL) project, our group combined in silico and in vitro data for a full analysis of P30646. Computation tools including BLAST, DALI, SPRITE, and InterPro allowed our group to compare the structural and sequential similarities between P30646 and proteins with known functions. In silico analysis indicated that P30646 had xylulokinase activity, and xylulose was tested as a substrate in vitro using a coupled kinase assay. The kinase assay indicated that P30646 does have strong enzymatic activity for xylulose. The combination of our in silico and in vitro results provide a strong indication that P30646 is a sugar kinase with affinity for xylulose breakdown.
Background
The study of protein structure and function is essential, as the structure of a protein is often closely related to its function. This project investigated the protein P30646 (UniProt), a protein with a known structure but an unknown function. It is understood that P30646 is an uncharacterized sugar kinase that is involved in the metabolic processes of Caenorhabditis elegans. Through the analysis of results obtained through computational and laboratory methods, this work aims to identify the function of P30646 and gain insight into its role in the metabolism of C. elegans.
Workflow
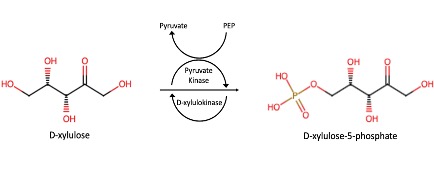
Predicted Mechanism
Methods
To determine the function of P30646 as well as a potential substrate for the enzyme, we first conducted an in silico exploration. We utilized tools including DALI, InterPro, PredictProtein, and BLASTp to gain insight into the potential function P30646. Each of these tools draws upon data for proteins of unknown functions to generate hypotheses about the function of the protein of interest. We then identified potential substrates for our protein of interest through docking tools including SwissDock and PyRx.
The hypotheses we developed through computational tools were tested in vitro by overexpressing and purifying P30646, followed by an experimental analysis of the protein. This analysis involved a Bradford assay, a coupled kinase assay, and SDS-PAGE.

Computational Exploration
Our in silico experiments focused on first determining a potential function for our protein of interest, and then on identifying an ideal substrate. We hypothesized about a function for P30646 through structural and sequential alignments with proteins of known function. A number of similar proteins were identified, including a 4BC3 (PDB), a human D-xylulokinase. 4BC3, along with other xylulokinases, is both structurally and sequentially similar to P30646. This led us to confidently conclude that our protein of interest is a D-xylulokinase.
Image:InterPro.
Laboratory Experiments
Conclusions
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.



