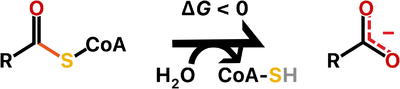This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Mitochondrial hotdog-fold thioesterase
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Overview of thioesterases == | == Overview of thioesterases == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Thioesterase reaction.png | right | 400x89 px]] | ||
Thioesterases are enzymes that catalyze the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrolysis hydrolysis] of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thioester thioester bonds], which are the linkage between a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbonyl_group carbonyl] and a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sulfur sulfur] atom. | Thioesterases are enzymes that catalyze the [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hydrolysis hydrolysis] of [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thioester thioester bonds], which are the linkage between a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carbonyl_group carbonyl] and a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sulfur sulfur] atom. | ||
| + | |||
The ATP-dependent formation of a thioester bond from a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carboxylate carboxylate] and a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thiol thiol] in biomolecules makes them more reactive and is particularly an important commitment step in [[lipid metabolism]]. Therefore, thioesterases counteract this activation by releasing upon hydrolysis a molecule with the more '''stable''' carboxylate group. For this reason, thioesterases are found at the end of some metabolic pathways but they also may act as''' regulators''' of flux. Besides lipid metabolism, thioester bonds also occur in biosynthetic pathways for polyketide and non-ribosomal peptide production, as well as in main metabolites of carbon metabolism such as acetyl-CoA and succinyl-CoA. | The ATP-dependent formation of a thioester bond from a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Carboxylate carboxylate] and a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Thiol thiol] in biomolecules makes them more reactive and is particularly an important commitment step in [[lipid metabolism]]. Therefore, thioesterases counteract this activation by releasing upon hydrolysis a molecule with the more '''stable''' carboxylate group. For this reason, thioesterases are found at the end of some metabolic pathways but they also may act as''' regulators''' of flux. Besides lipid metabolism, thioester bonds also occur in biosynthetic pathways for polyketide and non-ribosomal peptide production, as well as in main metabolites of carbon metabolism such as acetyl-CoA and succinyl-CoA. | ||
| Line 32: | Line 35: | ||
In order to study the binding of acyl-CoA's to Them4, Zhao ''et al.'' (2012) obtained by X-ray crystallography the atomic structure of the <scene name='10/1049462/Monomer-ligand/2'>human Them4 complexed with undecan-2-one-CoA</scene>, which is a structural analog of acyl-CoA's and inhibitor of this protein. Since there are two active sites per dimer,<scene name='10/1049462/Dimer-ligand/1'> two molecules of undecan-2-one-CoA</scene> can bind to Them4. It was reported from the crystal structure that the phosphate groups in the coenzyme A moiety establish electrostatic interactions with <scene name='10/1049462/Arg-lys-ligand/1'>Arg206 and Lys207</scene>. Furthermore, there is a hydrogen bond seen between the C(6)NH<sub>2</sub> from the adenine ring in coenzyme A and Asn193. Nonetheless, Zhao ''et al.'' (2012) point out that such interactions may be minimized by the polar solvent. | In order to study the binding of acyl-CoA's to Them4, Zhao ''et al.'' (2012) obtained by X-ray crystallography the atomic structure of the <scene name='10/1049462/Monomer-ligand/2'>human Them4 complexed with undecan-2-one-CoA</scene>, which is a structural analog of acyl-CoA's and inhibitor of this protein. Since there are two active sites per dimer,<scene name='10/1049462/Dimer-ligand/1'> two molecules of undecan-2-one-CoA</scene> can bind to Them4. It was reported from the crystal structure that the phosphate groups in the coenzyme A moiety establish electrostatic interactions with <scene name='10/1049462/Arg-lys-ligand/1'>Arg206 and Lys207</scene>. Furthermore, there is a hydrogen bond seen between the C(6)NH<sub>2</sub> from the adenine ring in coenzyme A and Asn193. Nonetheless, Zhao ''et al.'' (2012) point out that such interactions may be minimized by the polar solvent. | ||
| + | |||
| + | </StructureSection> | ||
== Function == | == Function == | ||
| Line 44: | Line 49: | ||
Them4 is also called Akt C-Terminal Modulator Protein (CTMP), owing to previous data suggesting that it interacts with the serine-threonine protein kinase Akt1 in an inferred mechanism of regulating apoptosis. However, this putative activity is not well defined yet. Through pull-down assays, Zhao ''et al.'' (2012) verified that Them4 and Akt1 form a stable complex and that Them4 inhibits Akt1 activity'' in vitro'', but Akt1 does not inhibit Them4. | Them4 is also called Akt C-Terminal Modulator Protein (CTMP), owing to previous data suggesting that it interacts with the serine-threonine protein kinase Akt1 in an inferred mechanism of regulating apoptosis. However, this putative activity is not well defined yet. Through pull-down assays, Zhao ''et al.'' (2012) verified that Them4 and Akt1 form a stable complex and that Them4 inhibits Akt1 activity'' in vitro'', but Akt1 does not inhibit Them4. | ||
| - | |||
| - | </StructureSection> | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 13:36, 30 May 2024
Overview of thioesterases
Thioesterases are enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of thioester bonds, which are the linkage between a carbonyl and a sulfur atom.
The ATP-dependent formation of a thioester bond from a carboxylate and a thiol in biomolecules makes them more reactive and is particularly an important commitment step in lipid metabolism. Therefore, thioesterases counteract this activation by releasing upon hydrolysis a molecule with the more stable carboxylate group. For this reason, thioesterases are found at the end of some metabolic pathways but they also may act as regulators of flux. Besides lipid metabolism, thioester bonds also occur in biosynthetic pathways for polyketide and non-ribosomal peptide production, as well as in main metabolites of carbon metabolism such as acetyl-CoA and succinyl-CoA.
There are two main families of thioesterases which are distinguished by their folding, named the α/β-hydrolases and the hotdog-fold hydrolases. Notably, these two different families are evolutionarily distant, so the thioesterase activity is a shared feature owing to convergent evolution.
| |||||||||||
Function
From enzymatic activities in vitro, it was shown that Them4 (Zhao et al., 2009) and Them5 (Zhuravleva et al., 2012) have higher kcat/KM for acyl-CoA's with medium and long hydrocarbon chain, such as myristoyl-CoA (14:0), palmitoyl-CoA (16:0), oleoyl-CoA (18:1) and linoleoyl-CoA (18:2). According to Zhuravleva et al. (2012), linoleoyl-CoA (18:2) was a preferred substrate for Them5. From studies with Them5−/− mice, it was identified by mass spectrometry (MS) that loss of Them5 is related to an increase in the levels of monolysocardiolipin (MLCL), which is a metabolite upstream of the cardiolipin remodeling process in mitochondria. Furthermore, the lipidomics analysis by MS for Them5−/− mice also revealed a 2-fold decrease of free fatty acids, notably linoleic (18:2) and linolenic (18:3) acids. This is consistent with the in vitro assay for the recombinant ∆34Them5 which revealed higher kcat/KM for linoleoyl-CoA (18:2). Moreover, it is observed by two-dimensional electron microscopy (2D-EM) and subsequent 3D reconstruction that in hepatocytes from Them5−/− mice, mitochondria were more elongated and interconnected, with a 2-fold increase in volume. With these data, Zhuravleva et al. (2012) propose that Them5 might be a regulator of cardiolipin remodeling through modulation of the unsaturated acyl-CoA pool in mitochondria. This modulation in turn seems to affect mitochondrial morphology.
Zhao et al. (2012) observed that Them4 shows very weak binding affinity (Ki > 1 mM) for carboxylic acids generated after the thioester bond hydrolysis, suggesting that this enzyme is not regulated by product inhibition.
Them4 is also called Akt C-Terminal Modulator Protein (CTMP), owing to previous data suggesting that it interacts with the serine-threonine protein kinase Akt1 in an inferred mechanism of regulating apoptosis. However, this putative activity is not well defined yet. Through pull-down assays, Zhao et al. (2012) verified that Them4 and Akt1 form a stable complex and that Them4 inhibits Akt1 activity in vitro, but Akt1 does not inhibit Them4.
References
Swarbrick, C. M., Nanson, J. D., Patterson, E. I., & Forwood, J. K. (2020). Structure, function, and regulation of thioesterases. Progress in Lipid Research, 79, 101036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plipres.2020.101036
Caswell, B. T., de Carvalho, C. C., Nguyen, H., Roy, M., Nguyen, T., & Cantu, D. C. (2022). Thioesterase enzyme families: Functions, structures, and mechanisms. Protein Science, 31(3), 652-676. https://doi.org/10.1002/pro.4263
Zhao, H., Martin, B. M., Bisoffi, M., & Dunaway-Mariano, D. (2009). The Akt C-terminal modulator protein is an acyl-CoA thioesterase of the Hotdog-Fold family. Biochemistry, 48(24), 5507-5509. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi900710w
Zhao, H., Lim, K., Choudry, A., Latham, J. A., Pathak, M. C., Dominguez, D., ... & Dunaway-Mariano, D. (2012). Correlation of structure and function in the human hotdog-fold enzyme hTHEM4. Biochemistry, 51(33), 6490-6492. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi300968n
Zhuravleva, E., Gut, H., Hynx, D., Marcellin, D., Bleck, C. K., Genoud, C., ... & Hemmings, B. A. (2012). Acyl coenzyme A thioesterase Them5/Acot15 is involved in cardiolipin remodeling and fatty liver development. Molecular and cellular biology, 32(14), 2685-2697. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00312-12