We apologize for Proteopedia being slow to respond. For the past two years, a new implementation of Proteopedia has been being built. Soon, it will replace this 18-year old system. All existing content will be moved to the new system at a date that will be announced here.
Sandbox Reserved 1851
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
==General Structure== | ==General Structure== | ||
===Active Site=== | ===Active Site=== | ||
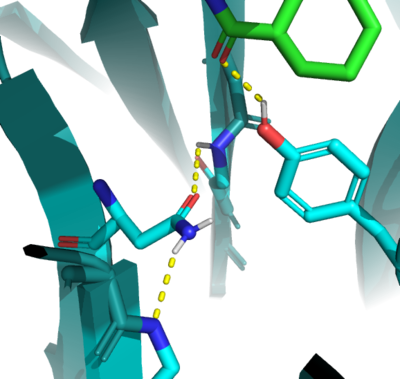
| - | In the active state, there are two catalytic residues | + | In the active state, there are two catalytic <scene name='10/1075253/Active_site_residues/5'>residues</scene> that aim to stabilize the transition state of the Diels-Alder reaction. Y134 acts as a hydrogen bond donor to the oxygen on the <scene name='10/1075253/Ligand/2'>ligand</scene>. Q208 acts as a hydrogen bond acceptor to the nitrogen on the ligand. These interactions help reduce the energetic gap between orbitals allowing the reaction to proceed, outlined in HOMO/LUMO. |
| + | |||
Revision as of 18:47, 3 April 2025
| This Sandbox is Reserved from March 18 through September 1, 2025 for use in the course CH462 Biochemistry II taught by R. Jeremy Johnson and Mark Macbeth at the Butler University, Indianapolis, USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 1828 through Sandbox Reserved 1846. |
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing |
Contents |
Novel Diels-Alder Catalyst Identified Using de novo Design
|
Introduction
General Structure
Active Site
In the active state, there are two catalytic that aim to stabilize the transition state of the Diels-Alder reaction. Y134 acts as a hydrogen bond donor to the oxygen on the . Q208 acts as a hydrogen bond acceptor to the nitrogen on the ligand. These interactions help reduce the energetic gap between orbitals allowing the reaction to proceed, outlined in HOMO/LUMO.
Mechanism
Uncatalyzed Reaction
Orbital Stabilization
Structural Details
Active Site
Conserved Mutations
Relevance
Chemical Applications
Improvements
This is a sample scene created with SAT to by Group, and another to make of the protein. You can make your own scenes on SAT starting from scratch or loading and editing one of these sample scenes.
</StructureSection>
References
Student Collaborators
Micah Zile Kate Thuma Taylor Donahue