This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Leucine-rich repeat
From Proteopedia
m |
m |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<slideshow sequence="random" transition="fade" align="left" refresh="5500"> | <slideshow sequence="random" transition="fade" align="left" refresh="5500"> | ||
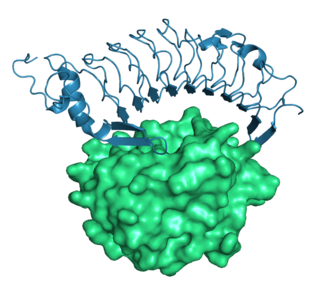
<div>[[Image:1m10complexsurf.png|330px|left|thumb| <span style="font-size:1.2em;">The human leucine-rich repeat family member Glycoprotein Ib alpha (blue) involved in Willebrand disease bound to the von Willebrand Factor A1 Domain (green surface), from [[1m10]].</span>]] </div> | <div>[[Image:1m10complexsurf.png|330px|left|thumb| <span style="font-size:1.2em;">The human leucine-rich repeat family member Glycoprotein Ib alpha (blue) involved in Willebrand disease bound to the von Willebrand Factor A1 Domain (green surface), from [[1m10]].</span>]] </div> | ||
| - | <div>[[Image:1id5polyview3d.png|center|thumb|330px|<span style="font-size:1.2em;">Lingo-1 protein involved in inhibiting effective regrowth of axons after central nervous system damage, from [[2id5]].</span>]] </div> | + | <div>[[Image:1id5polyview3d.png|center|thumb|330px|<span style="font-size:1.2em;">Extracellular domain of Lingo-1 protein involved in inhibiting effective regrowth of axons after central nervous system damage, from [[2id5]].</span>]] </div> |
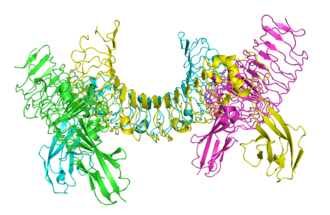
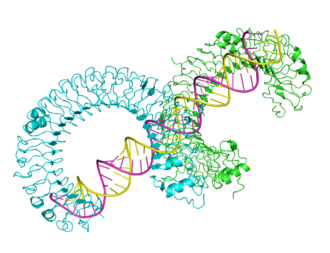
| - | <div>[[Image:3ciyPV3D.png|center|thumb|330px|<span style="font-size:1.2em;"> | + | <div>[[Image:3ciyPV3D.png|center|thumb|330px|<span style="font-size:1.2em;">Extracellular domain of mouse Toll-like receptor bound to dsRNA, from [[3ciy]].</span>]] </div> |
</slideshow> | </slideshow> | ||
Revision as of 02:17, 25 November 2010
The leucine-rich repeat proteins are a large family of over 60,000 proteins found in viruses, bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes that feature horseshoe- or arc-shaped domains made of leucine-rich repeating motifs.[1]
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
<slideshow sequence="random" transition="fade" align="left" refresh="5500">
</slideshow>
Articles in Proteopedia concerning Leucine-rich repeat proteins include:
- Human Follicle Stimulating Hormone Complexed with its Receptor
- Variable Lymphocyte Receptors
- Lamprey Variable Lymphocyte Receptor
- Toll-like receptors (TLRs), such as Mouse Toll-like receptor bound to dsRNA
- Complex of Glycoprotein Ib alpha and the von Willebrand Factor A1 Domain
- Lingo-1 protein involved in inhibiting effective regrowth of axons after central nervous system damage
| |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
To view automatically seeded indices concerning Leucine-rich repeat proteins[2], see:
- Leucine-rich repeat
- Leucine-rich-repeat
- Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 4
- LRR
- Leucine-rich repeat glycoprotein
References
- ↑ Matsushima N, Miyashita H, Mikami T, Kuroki Y. A nested leucine rich repeat (LRR) domain: the precursor of LRRs is a ten or eleven residue motif. BMC Microbiol. 2010 Sep 9;10:235. PMID:20825685 doi:10.1186/1471-2180-10-235
- ↑ Matsushima N, Miyashita H, Mikami T, Kuroki Y. A nested leucine rich repeat (LRR) domain: the precursor of LRRs is a ten or eleven residue motif. BMC Microbiol. 2010 Sep 9;10:235. PMID:20825685 doi:10.1186/1471-2180-10-235
See Also
Additional Literature
- Kobe B, Kajava AV. The leucine-rich repeat as a protein recognition motif. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2001 Dec;11(6):725-32. PMID:11751054
- Matsushima N, Tanaka T, Enkhbayar P, Mikami T, Taga M, Yamada K, Kuroki Y. Comparative sequence analysis of leucine-rich repeats (LRRs) within vertebrate toll-like receptors. BMC Genomics. 2007 May 21;8:124. PMID:17517123 doi:10.1186/1471-2164-8-124
- Matsushima N, Tachi N, Kuroki Y, Enkhbayar P, Osaki M, Kamiya M, Kretsinger RH. Structural analysis of leucine-rich-repeat variants in proteins associated with human diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005 Dec;62(23):2771-91. PMID:16231091 doi:10.1007/s00018-005-5187-z
- Kajava AV, Kobe B. Assessment of the ability to model proteins with leucine-rich repeats in light of the latest structural information. Protein Sci. 2002 May;11(5):1082-90. PMID:11967365 doi:10.1110/ps.4010102
- Jin MS, Lee JO. Application of hybrid LRR technique to protein crystallization. BMB Rep. 2008 May 31;41(5):353-7. PMID:18510864
- Carpenter S, O'Neill LA. Recent insights into the structure of Toll-like receptors and post-translational modifications of their associated signalling proteins. Biochem J. 2009 Jul 29;422(1):1-10. PMID:19627256 doi:10.1042/BJ20090616
