Sandbox Reserved 162
From Proteopedia
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
__TOC__ | __TOC__ | ||
== Background == | == Background == | ||
| - | Human Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a immune protein often categorized under hematopoietins. Since its discoverey, it has been known by many names including: interferon-ß2 (IFN-ß2), 26-kD protein, B-cell stimulatory factor-2 (BSF-2), hepatocyte stimulating factor (HSF), cytotoxic T-cell differentiation factor (CDF), interleukin-HP1 (IL-HP1), monocyte-granulocyte inducer type 2 (MGI-2), and hybridoma/plasmacytoma growth factor (HPGF/HGF). It wasn't until December of 1988 that is was givin the final moniker of IL-6 (PDB: 1IL6). | + | Human Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a immune protein often categorized under hematopoietins. Since its discoverey, it has been known by many names including: interferon-ß2 (IFN-ß2), 26-kD protein, B-cell stimulatory factor-2 (BSF-2), hepatocyte stimulating factor (HSF), cytotoxic T-cell differentiation factor (CDF), interleukin-HP1 (IL-HP1), monocyte-granulocyte inducer type 2 (MGI-2), and hybridoma/plasmacytoma growth factor (HPGF/HGF). It wasn't until December of 1988 that is was givin the final moniker of IL-6 (PDB: 1IL6). Interleukin 6 (IL6) is a potent pleiotropic cytokine that regulates cell growth and differentiation and plays an important role in immune response. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of the receptor complex for IL6. |
== Structure == | == Structure == | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== Clinical Applications == | == Clinical Applications == | ||
| + | Dysregulated production of IL6 and this receptor are implicated in the pathogenesis of many diseases, such as multiple myeloma, autoimmune diseases and prostate cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been reported. | ||
== Additional Resources == | == Additional Resources == | ||
Revision as of 15:49, 26 March 2011
|
Contents |
Background
Human Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a immune protein often categorized under hematopoietins. Since its discoverey, it has been known by many names including: interferon-ß2 (IFN-ß2), 26-kD protein, B-cell stimulatory factor-2 (BSF-2), hepatocyte stimulating factor (HSF), cytotoxic T-cell differentiation factor (CDF), interleukin-HP1 (IL-HP1), monocyte-granulocyte inducer type 2 (MGI-2), and hybridoma/plasmacytoma growth factor (HPGF/HGF). It wasn't until December of 1988 that is was givin the final moniker of IL-6 (PDB: 1IL6). Interleukin 6 (IL6) is a potent pleiotropic cytokine that regulates cell growth and differentiation and plays an important role in immune response. The protein encoded by this gene is a subunit of the receptor complex for IL6.
Structure
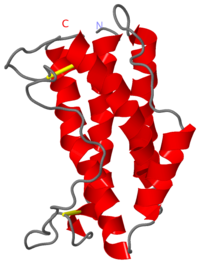
IL-6 is a monomer of 185 amino acids produced from T-Cells, macrophages, and endothelial cells found on a single gene at locus 7p21. It contains five alpha-helices and four of these helices constitute a classical four-helix bundle with the fifth helix located in the CD loop.
Functions
IL-6 Receptor
|
Clinical Applications
Dysregulated production of IL6 and this receptor are implicated in the pathogenesis of many diseases, such as multiple myeloma, autoimmune diseases and prostate cancer. Alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms have been reported.