User:Jakob Raphael Käppler/Sandbox218
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| - | [[Image:1aus.png| | + | [[Image:1aus.png|350px|left|thumb| Spinach Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphat Carboxylase Oxygenase, [[1aus]]]] |
{{STRUCTURE_1aus| right| PDB=1aus | SCENE= |CAPTION=Crystal Structure of Spinach Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphat Carboxylase Oxygenase, [[1aus]] }} | {{STRUCTURE_1aus| right| PDB=1aus | SCENE= |CAPTION=Crystal Structure of Spinach Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphat Carboxylase Oxygenase, [[1aus]] }} | ||
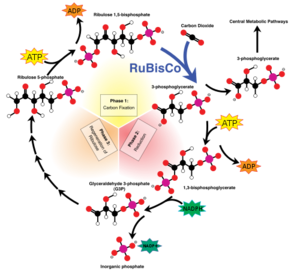
| - | + | [[Image:Calvin cycle en wikipedia.giv.png|300px|left|thumb|Overview of the calvin cycle]] | |
| + | |||
'''Rubisco''' ('''Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase''') EC 4.1.1.39, quite likely the most occurring enzyme of the world[1], is found also in plants and bacteria. It simplifies the first step in the Calvin-Benson-bassham-cycle: the catalytic binding of inorganic carbon dioxide to Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate by a condensation reaction. The enzyme a hexadecamer with the molecular mass 550 kDa, consists out of 16 subunits (L8S8) which are divided into 8 large 50 – 55 kDa units and 8 small 12 – 18 kDa units. The genes which encode for the large subunits are located in the chloroplast whereas the genes for the small subunits are located in the nucleus. | '''Rubisco''' ('''Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase''') EC 4.1.1.39, quite likely the most occurring enzyme of the world[1], is found also in plants and bacteria. It simplifies the first step in the Calvin-Benson-bassham-cycle: the catalytic binding of inorganic carbon dioxide to Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate by a condensation reaction. The enzyme a hexadecamer with the molecular mass 550 kDa, consists out of 16 subunits (L8S8) which are divided into 8 large 50 – 55 kDa units and 8 small 12 – 18 kDa units. The genes which encode for the large subunits are located in the chloroplast whereas the genes for the small subunits are located in the nucleus. | ||
==Biological role== | ==Biological role== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
==General structure== | ==General structure== | ||
Revision as of 21:21, 20 December 2011
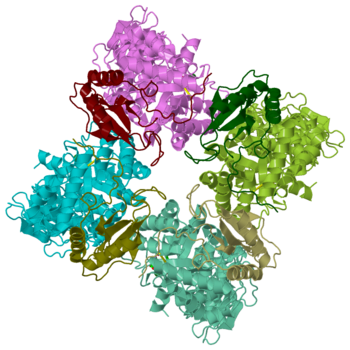
Spinach Ribulose-1,5-Bisphosphat Carboxylase Oxygenase, 1aus
Rubisco (Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase) EC 4.1.1.39, quite likely the most occurring enzyme of the world[1], is found also in plants and bacteria. It simplifies the first step in the Calvin-Benson-bassham-cycle: the catalytic binding of inorganic carbon dioxide to Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate by a condensation reaction. The enzyme a hexadecamer with the molecular mass 550 kDa, consists out of 16 subunits (L8S8) which are divided into 8 large 50 – 55 kDa units and 8 small 12 – 18 kDa units. The genes which encode for the large subunits are located in the chloroplast whereas the genes for the small subunits are located in the nucleus.
Contents |
Biological role
General structure
detailed structure
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors
Nicolai Rügen and Jakob Raphael Käppler