User:Jakob Raphael Käppler/Sandbox218
From Proteopedia
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
[[Image:Calvin cycle en wikipedia.giv.png|300px|left|thumb|Overview of the calvin cycle <ref>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Calvin-cycle4.svg Image of the Calvin cycle]was obtained from Wikipedia</ref>]] | [[Image:Calvin cycle en wikipedia.giv.png|300px|left|thumb|Overview of the calvin cycle <ref>[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Calvin-cycle4.svg Image of the Calvin cycle]was obtained from Wikipedia</ref>]] | ||
| - | '''Rubisco''' ('''Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase''') EC 4.1.1.39, quite likely the most | + | '''Rubisco''' ('''Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase''') EC 4.1.1.39, quite likely the most frequently found enzyme of the world[1], appears in plants as well as bacteria. It simplifies the first step in the Calvin-Benson-bassham-cycle by a condensation reaction, where inorganic carbon dioxide binds in catalysis to Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate. The enzyme, a hexadecamer with the molecular mass of 550 kDa, consists of 16 subunits (L8S8) which are divided into 8 large 50 – 55 kDa subunits and 8 small 12 – 18 kDa subunits. The genes which encode for the large subunits are located in the chloroplast whereas the genes for the small subunits are located in the nucleus. Rubisco not only catalyze the carbon fixation, it also has an oxygenase reaction. These two reactions are in competition to each other. |
==Biological role== | ==Biological role== | ||
Revision as of 15:06, 2 January 2012
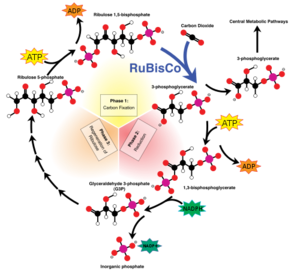
Rubisco (Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase oxygenase) EC 4.1.1.39, quite likely the most frequently found enzyme of the world[1], appears in plants as well as bacteria. It simplifies the first step in the Calvin-Benson-bassham-cycle by a condensation reaction, where inorganic carbon dioxide binds in catalysis to Ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate. The enzyme, a hexadecamer with the molecular mass of 550 kDa, consists of 16 subunits (L8S8) which are divided into 8 large 50 – 55 kDa subunits and 8 small 12 – 18 kDa subunits. The genes which encode for the large subunits are located in the chloroplast whereas the genes for the small subunits are located in the nucleus. Rubisco not only catalyze the carbon fixation, it also has an oxygenase reaction. These two reactions are in competition to each other.
Contents |
Biological role
General structure
detailed structure
3D Structures of RuBisCO
Updated December 2011
RuBisCO
3rg6 – RBCO – Synechococcus elongatus
3qfw - RBCO large subunit – Rhodopseudomonas palustris
1uzh, 1gk8 – CrRBCO – Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
1uw9, 1uwa – CrRBCO (mutant)
1svd – RBCD – Halothiobacillus neapolitanus
1bxn – RBCO – Cupriavidus necator
1aus - spRBCO – spinach
1rba - RrRBCO (mutant) – Rhododpirillum rubrum
5rub - RrRBCO
2wvw – RBCO – Anabena – Cryo EM
2vdh, 2vdi, 2v67, 2v68, 2v63, 2v69, 2v6a - CrRBCO (mutant)
1mlv - pRBCO LSMT – pea
2cxe, 2cwx – PhRBCO - Pyrococcus horikoshii
1uzd – CrRBCO/spRBCO
1geh – TkRBCO – Thermococcus kodakaraensis
1iwa - GpRBCO – Galdieria partita
1tel – RBCO large subunit – Chlorobium tepidum
RuBisCO complex with inhibitor 2-CABP
3kdn, 3a12 – TkRBCO III + 2-CABP
3kdo, 3a13 - TkRBCO III (mutant) + 2-CABP
1ir2 - CrRBCO + 2-CABP
1upm, 1upp, 1rbo, 3ruc, 8ruc - spRBCO + 2-CABP + Cation
1ir1 - spRBCO + 2-CABP + CO2 + Mg
1wdd – RBCO + 2-CABP – rice
1bwv - GpRBCO + 2-CABP
RuBisCO complex with product
1aa1 – spRBCO + phosphoglycerate
1rus - RrRBCO + phosphoglycerate
RuBisCO complex with substrate
1rcx, 1rxo – spRBCO + ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate
RuBisCO complexes
2h21 – pRBCO LSMT + AdoMet
2h23 - pRBCO LSMT + AdoHcy
2h2e, 1ozv, 1p0y - pRBCO LSMT + AdoMet + lysine
2h2j - pRBCO LSMT + sinefungin
2d69 – PhRBCO + sulfate
1rco - spRBCO + xylulose-diol-1,5-bisphosphate
2rus - RrRBCO + CO2 + Mg
1ej7 – RBCO + phosphate - tobacco
Notes and Literarture References
- ↑ Image of the Calvin cyclewas obtained from Wikipedia
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors
Nicolai Rügen and Jakob Raphael Käppler