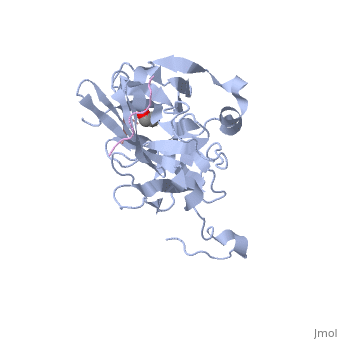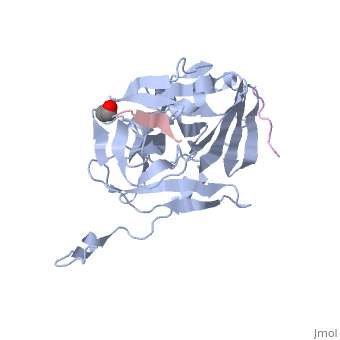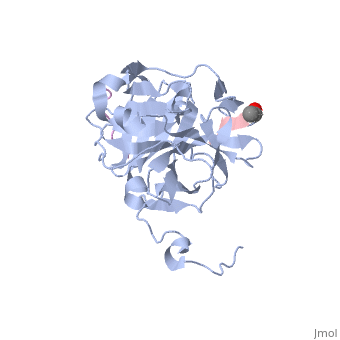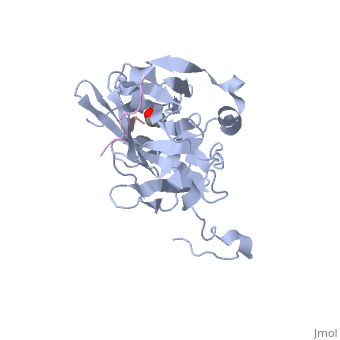
The tobacco etch virus (TEV) is a member of the Potyviridae family of positive-strand RNA viruses [1]. Unlike its name suggests, TEV can infect not only the tobacco plant, but a number of other plants including some flowers (baby's breath and zinnias) and fruits/vegetables (eggplant, peppers, and tomatoes). The 5' end of the RNA genome is covalently linked to a 49 kDa virus-encoded protein or VPg (viral protein genome-linked).The positive sense genome is translated by the host's ribosomes into a large polyprotein precursor that is cleaved soon after translation to form independent protein products [2]. The TEV nuclear inclusion a (NIa) protease (shown to the right co-crystallized with peptide product in purple, with the catalytic residues highlighted as green ball and stick models) [3] is a 27 kDa 3C-type cysteine protease, part of the VPg, and responsible for the processing of the original polyprotein into functional viral proteins. TEV protease resembles well-known serine proteases, such as trypsin and chymotrypsin, except that the TEV protease utilizes the nucleophilic thiol of the active site cysteine residue, as opposed to the serine hydroxyl used in serine proteases. Ultimately, the biological importance of the TEV protease requires that the enzyme have very stringent sequence specificity to ensure proper production of viral proteins, and it is based on this stringency that the TEV protease has increasingly been used to remove affinity tags from recombinant proteins. See also Ashley Steere/Tobacco Etch Virus (TEV) Protease.
Structure of TEV Protease
TEV protease is classified as an all β protein which adopts a antiparallel β-barrel fold, typical of trypsin-like serine proteases, where the β sheet in the first domain folds to form an antiparallel (cyan and the β sheet in the second domain is open (red). Like typical serine proteases, the β-barrel contains a motif. Located at the interface between the two domains is the , composed of His46, Asp81, and Cys151. A structural comparison with related proteins reveals that the TEV protease fold is most similar to that of other 3C-type cysteine proteases from the Picornaviridae virus family, such as the hepatitis A virus, the poliovirus, the foot and mouth disease virus and rhinovirus, which serve a similar function as the TEV protease in their respective viruses. However, although the overall fold of TEV protease and these related proteins is indeed very similar, the actual atomic coordinates are very different, with the root mean square deviation for α carbons between 2.4 to 3.5 Å [3].
Classification
The TEV protease is classified by the EC number: 3.4.22.44. A breakdown of this classification is as follows:
Enzymes
- 3. Hydrolases
- 3.4 Acting on peptide bonds (peptidases)
- 3.4.22 Cysteine endopeptidases
- 3.4.22.44 Nuclear inclusion a (NIa) endopeptidase (A.K.A. TEV protease)
Enzymatic Mechanism
Given the catalytic cysteine residue yet the overall serine protease-like fold possessed by 3C-type
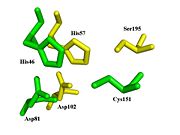
Spatial comparison of the catalytic triads from bovine
chymotrypsin and the
TEV protease. PDB Files:
1YPH and
1LVM.
cysteine proteases like the TEV protease, it has long been debated whether these proteases (from both the Picornaviruses and Potyviruses) catalyze the cleavage of a peptide bond in a manner similar to conventional cysteine proteases (e.g., the plant enzyme papain) or via a similar mechanism as serine proteases (e.g., chymotrypsin). Traditional cysteine proteases utilize a thiolate-imidizolium ion pair to function which ultimately gives rise to the characteristic bell-shaped pH dependency observed of such proteases. On the other hand, traditional serine proteases utilize a characteristic Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad. The two types of proteases display a number of well-described mechanistic differences.
Due to the similar spatial arrangement of catalytic residues, proteolysis by the TEV protease (and other 3C-type viral proteases) is thought to occur through general base assisted nucleophilic catalysis homologous to chymotrypsin-like serine proteases and analogous to papain-like cysteine proteases [4] [5]. However, the exact details of the catalytic mechanism of the TEV protease have yet to be elucidated. Provided is a brief description of the proposed catalytic mechanism-closely resembling that of chymotrypsin-like serine proteases.
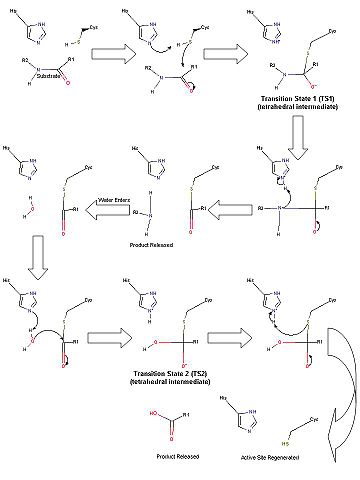
Scheme 1. Proposed catalytic mechanism of the TEV protease.
In the first half of the reaction (please refer to Scheme 1), the acylation step, the catalytic histidine (His46 in TEV protease numbering) acts as a general base to abstract a proton from Cys151 and produce the catalytic thiolate. (This is a major difference between chymotrypsin-like cysteine proteases and traditional cysteine proteases; the role of the catalytic His in traditional cysteine proteases is not to abstract a proton from the catalytic cysteine residue, but instead to donate a proton to the substrate.) This thiolate nucleophile then attacks the carbonyl atom of the scissile bond, ultimately leading to the formation of the first tetrahedral intermediate (TS1). The negative oxygen ion, after accepting electrons from the carbonyl double bond, is stabilized through a network of hydrogen bond interactions with the backbone atoms of residues 149 and 151 in what is termed the oxyanion hole. This stabilization of the negative charge generated in the TS is a critical part in the catalytic mechanism. In fact, most viral 3C-type cysteine proteases contain highly conserved small amino acids around the catalytic cysteine residue in order to properly orient the residue for nucleophilic attack as well as properly position the backbone atoms for the formation of the oxyanion hole. Collapse of this intermediate leads to release of the C-terminal product fragment and a covalent thioester enzyme-substrate complex. The second half of the reaction involves subsequent release of the N-terminal product fragment and regeneration of the enzyme in what is called the deacylation step. To accomplish this, a water molecule (activated by His46 to a nucleophilic OH-) attacks the thioester carbonyl carbon, forming the second tetrahedral intermediate (T2). As with T1, this second transition state is stabilized by the oxyanion hole within the enzyme. Breakdown of the second transition state regenerates the catalytic cysteine residue and cleavage of the target peptide bond is complete [4]. Importantly, the aspartic acid residue of the catalytic triad (Asp81) serves to correctly orient the histidine residue (His46) throughout the catalytic process.
Low-Barrier Hydrogen Bond
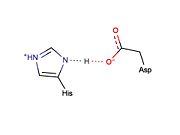
Potential LBHB formed between catalytic residues His46 and Asp81 that may aid in catalysis through stabilization of the tetrahedral intermediate (based on mechanistic homology with chymotrypsin).
Low-barrier hydrogen bonds (LBHBs) are short, strong hydrogen bonds thought to be formed under certain circumstances and play a role in enzymatic catalysis [6]. Although the existence of LBHBs is highly debated, a great deal of spectroscopic evidence suggests that a LBHB may form between the catalytic His and Asp residues during the mechanism of chymotrypsin [7]. It is proposed that bridging of the proton between the His and Asp residue through a LBHB may aid in stabilization of the tetrahedral intermediate [7]. It is thought that the LBHB shared between the His and Asp residues of the catalytic triad in serine proteases increases the nucleophilicity of the catalytic serine essentially by increasing the basicity of the His residue. Traditional cysteine proteases (e.g., papain) are thought not to require the formation of a LBHB because: (1) they do not contain a counterpart to the catalytic Asp residue found in serine proteases and (2) the active site cysteine exists as a thiolate ion, which is highly nucleophilic and does not require its nucleophilicity to be enhanced to facilitate catalysis. Given that catalysis by the TEV protease is thought to occur in a manner similar to chymotrypsin, it is possible that a similar LBHB may form between the catalytic residues, His46 and Asp81, although there is no experimental spectroscopic evidence to support this hypothesis. However, X-ray crystal structures of the TEV protease may support LBHB formation between His46 and Asp181. Depending on the crystal structure, the distance between these two residues appears to vary between ~3.0 Å (typical of weak regular hydrogen bonds) and ~2.6 Å (typical of stronger LBHB).
Substrate Specificity
The canonical recognition site of the TEV protease is the seven amino acid sequence ENLYFQ/G,

TEV protease substrate recognition sequence and numbering.
with cleavage occurring after the glutamine residue. All 3C type proteases exhibit a strong preference for glutamine at the P1 position and for small aliphatic residues (glycine or serine) at the P1’ position
[3]. However, the requirement for a Gly or Ser in the P1’ position may not be as stringent as originally thought. Kapust et al. substituted this position with various amino acids and assessed the impact the P1’ position had on the catalytic efficiency of the TEV protease
[8]. The amino acids tested were ranked as follows:
- G>S>A>M>C>N>H>Y>K>D>Q>F>T>W>R>L>E>I>V>P
Furthermore, even though Val was ranked one of the least favorable amino acids at the P1’ position, cleavage was nearly 50% as efficient as when the most favorable amino acid (Gly) was in this position [8]. Additionally, residues at the P6 and P3 positions have been found critical to binding of the substrate and subsequent cleavage by the TEV protease [9].
The substrate binding pockets of the enzyme account for the specific substrate specificity of the TEV protease. In the S1 binding pocket both the N- ε2 and O- ε1 of the P1 Gln residue are involved in hydrogen bonding with TEV protease (specifically residues His167 and Thr146) [3]. Similar interactions have been observed in the rhinovirus 3C-type protease [3]. The S2, S3, and S4 binding pockets of the TEV protease are lined with mainly hydrophobic residues (Val209, Trp211, Val216, Met218, Phe139, Ala169, His214, Tyr178, and Val216) which serve to stabilize substrate binding through hydrophobic interactions with the Phe, Tyr, and Leu found at positions P2, P3 and P4. Interestingly, there is no S5 pocket in the TEV protease. The side chain in this position points away from the enzyme, therefore practically any residue can occupy the P5 position with little to no impact on catalytic efficiency [3]. The presence of a Glu at the P6 position is a stringent requirement for TEV protease substrates as the P6 residue is involved in an intricate network of hydrogen bonding interactions in the S6 binding pocket [3]. On the other side of the cleavage point, a shallow narrow groove on surface of TEV protease makes up the S1’ binding pocket [3]. The crystal structure of an inactive form of the TEV protease (C151A mutant) bound to peptide substrate indicates that the side chain of the P1’ residue is partially exposed to solvent rather than completely buried within the enzyme-substrate complex. This may explain the findings of Kapust et al. [8] which indicate that the enzyme can tolerate a number of substitutions at this position with short aliphatic residues being the best-most efficiently cleaved.
Inhibition
Given that the catalytic cysteine residue is critical to catalysis by the TEV protease, any alkylating agents that directly target and modify cysteine residues are potent inhibitors of this enzyme. Moreover, the TEV protease is inhibited by a number of different detergents generally used in purification of integral membrane proteins [10]. High concentrations of certain metals, such as zinc (5 mM), are also potent inhibitors of the TEV protease. A number of common protease inhibitors are known to be ineffective against the TEV protease including: TLCK, EDTA, and commercially available protease inhibitor cocktails.
Autoinhibition
The canonical recognition site of the TEV protease is the seven amino acid sequence ENLYFQ/G, with cleavage occurring after the glutamine residue. Although quite specific, TEV protease does have a tendency to undergo intramolecular self-cleavage at a (KVFM/S) which follows residue 218, yielding a truncated enzyme with diminished catalytic activity [11]. Based on biochemical and structural data, it appears that the C-terminal region of the protein is relatively unstructured and flexible, allowing the scissile bond between Met218 and Ser219 to come dangerously close to the active site, where it is readily cleaved. Crystallization of the catalytically inactive TEV protease mutant (C151A) reveals that the of the protease (shown in yellow, active site residues in green) actually binds tightly within the active site in the absence of natural substrate. Based on available structural and biochemical data, the mode of substrate binding appears to be very different between the normal proteolytic activity and the autolytic activity of the TEV protease. It is proposed that after cleavage at the non-canonical site, the free C-terminal peptide comprised of residues 219-242 of the TEV protease, binds within the active site of the enzyme in some type of auto-inhibitory mechanism [9]. This C-terminal peptide has no known counterpart in any other trypsin-like proteases and it is believed that in the presence of an appropriate substrate the C-terminus would be displaced from the active site, thus re-activating the enzyme. Mutation of Ser 219 to a number of other amino acids (Asp, Val, Pro) functions to limit the mobility of the peptide bond between residues 218 and 219, and has led to the production of TEV protease constructs resistant to this auto-proteolytic/auto-inhibitory activity with no affect on the normal catalytic function.
Evolutionarily Related Enzymes
Most, if not all, Potyviruses encode a 3C type protease functionally similar to the TEV protease. A more complete list of Potyviruses can be found here. An intriguing theory by Gorbalenya et al.[12] suggested (based on primary sequence alignments)suggests that typical serine proteases (chymotrypsin), typical cysteine proteases (papain)and 3C-type proteases (TEV protease) may share a common, yet distant evolutionary origin. Therefore, it is thought that these three types of proteases comprise a single superfamily of proteases that now differ through divergent evolution, yet maintain similar structures, functions and characteristics.
Proteases related to the TEV protease from the Picornaviruses have been the subject of a great deal of research. This has mainly been targeted towards developing inhibitors for clinical use due to their ability to cause disease in humans and animals. For more information on these related viruses and their respective 3C proteases, please follow the links provided:
- Rhinovirus, 2b0f
- Poliovirus, 1l1n
- Foot and mouth disease, 2wv4
- Hepatitis A virus
3D structures of TEV protease
1q31 – TEV (mutant) – Tobacco etch virus
1lvb, 1lvm – TEV catalytic domain (mutant) + oligopeptide substrate
Additional Resources
For additional information, See: Viral Infections
References
- ↑ Ryan MD, Flint M. Virus-encoded proteinases of the picornavirus super-group. J Gen Virol. 1997 Apr;78 ( Pt 4):699-723. PMID:9129643
- ↑ Stanway G. Structure, function and evolution of picornaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1990 Nov;71 ( Pt 11):2483-501. PMID:2254747
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 3.2 3.3 3.4 3.5 3.6 3.7 Phan J, Zdanov A, Evdokimov AG, Tropea JE, Peters HK 3rd, Kapust RB, Li M, Wlodawer A, Waugh DS. Structural basis for the substrate specificity of tobacco etch virus protease. J Biol Chem. 2002 Dec 27;277(52):50564-72. Epub 2002 Oct 10. PMID:12377789 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M207224200
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 Yin J, Niu C, Cherney MM, Zhang J, Huitema C, Eltis LD, Vederas JC, James MN. A mechanistic view of enzyme inhibition and peptide hydrolysis in the active site of the SARS-CoV 3C-like peptidase. J Mol Biol. 2007 Aug 24;371(4):1060-74. Epub 2007 Jun 8. PMID:17599357 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2007.06.001
- ↑ Arad D, Kreisberg R, Shokhen M. Structural and mechanistic aspects of 3C proteases from the Picornavirus family. J Chem Inf Comput Sci. 1993 May-Jun;33(3):345-9. PMID:8320292
- ↑ Cleland WW, Frey PA, Gerlt JA. The low barrier hydrogen bond in enzymatic catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1998 Oct 2;273(40):25529-32. PMID:9748211
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 Cassidy CS, Lin J, Frey PA. A new concept for the mechanism of action of chymotrypsin: the role of the low-barrier hydrogen bond. Biochemistry. 1997 Apr 15;36(15):4576-84. PMID:9109667 doi:10.1021/bi962013o
- ↑ 8.0 8.1 8.2 Kapust RB, Tozser J, Copeland TD, Waugh DS. The P1' specificity of tobacco etch virus protease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002 Jun 28;294(5):949-55. PMID:12074568 doi:10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00574-0
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Nunn CM, Jeeves M, Cliff MJ, Urquhart GT, George RR, Chao LH, Tscuchia Y, Djordjevic S. Crystal structure of tobacco etch virus protease shows the protein C terminus bound within the active site. J Mol Biol. 2005 Jul 1;350(1):145-55. PMID:15919091 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.04.013
- ↑ Mohanty AK, Simmons CR, Wiener MC. Inhibition of tobacco etch virus protease activity by detergents. Protein Expr Purif. 2003 Jan;27(1):109-14. PMID:12509992
- ↑ Kapust RB, Tozser J, Fox JD, Anderson DE, Cherry S, Copeland TD, Waugh DS. Tobacco etch virus protease: mechanism of autolysis and rational design of stable mutants with wild-type catalytic proficiency. Protein Eng. 2001 Dec;14(12):993-1000. PMID:11809930
- ↑ Gorbalenya AE, Blinov VM, Donchenko AP. Poliovirus-encoded proteinase 3C: a possible evolutionary link between cellular serine and cysteine proteinase families. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 6;194(2):253-7. PMID:3000829