This old version of Proteopedia is provided for student assignments while the new version is undergoing repairs. Content and edits done in this old version of Proteopedia after March 1, 2026 will eventually be lost when it is retired in about June of 2026.
Apply for new accounts at the new Proteopedia. Your logins will work in both the old and new versions.
Acyl carrier protein synthase
From Proteopedia
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
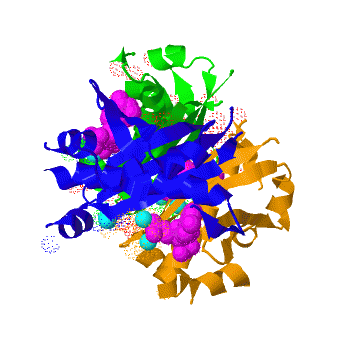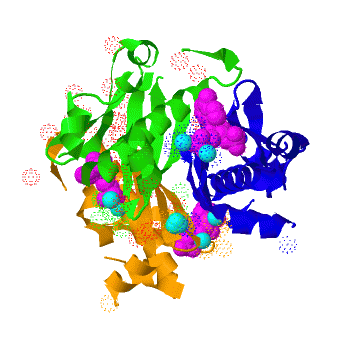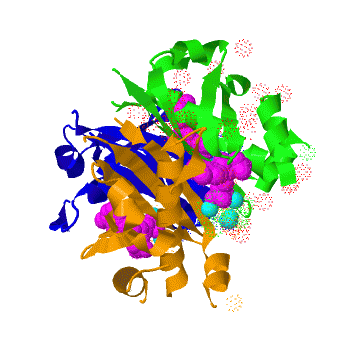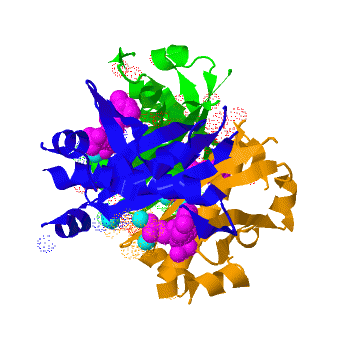
<StructureSection load='3hqj' size='500' frame='true' align='right' scene='3hqj/Trimer/1' caption="Acyl carrier protein synthase complex with CoA and Mg+2 ion [[3hqj]]" > | <StructureSection load='3hqj' size='500' frame='true' align='right' scene='3hqj/Trimer/1' caption="Acyl carrier protein synthase complex with CoA and Mg+2 ion [[3hqj]]" > | ||
| - | The crystal structure of '''Acyl carrier protein synthase (AcpS)''' from [http://http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycobacterium_tuberculosis ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''] (''Mtb'') was solved at 1.95 Å. It crystallized as one <scene name='3hqj/Trimer/2'>monomer</scene> per asymmetric unit. Since ''Mtb'' AcpS has biologically active trimeric arrangement, <scene name='3hqj/Trimer/3'>AcpS trimer</scene> (in <font color='lime'><b>lime</b></font>, <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font>, and <font color='orange'><b>orange</b></font>) was constructed using the 3-fold crystallographic symmetry in the ''P''23 space group | + | The crystal structure of '''Acyl carrier protein synthase (AcpS)''' from [http://http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mycobacterium_tuberculosis ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''] (''Mtb'') was solved at 1.95 Å ([[3hqj]]). It crystallized as one <scene name='3hqj/Trimer/2'>monomer</scene> per asymmetric unit. Since ''Mtb'' AcpS has biologically active trimeric arrangement, <scene name='3hqj/Trimer/3'>AcpS trimer</scene> (in <font color='lime'><b>lime</b></font>, <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font>, and <font color='orange'><b>orange</b></font>) was constructed using the 3-fold crystallographic symmetry in the ''P''23 space group. |
The 3′,5′-ADP moieties of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coenzyme_A coenzyme A] (<font color='magenta'><b>CoA, colored magenta</b></font>), are positioned in the cleft between each of two monomers forming three active sites within AcpS trimer. The <scene name='3hqj/Trimer/5'>active site</scene> is formed by the residues <font color='lime'><b>D9 (highly conserved), E58, L62, and S65</b></font> from monomer <font color='lime'><b>A</b></font> and by <font color='orange'><b>R92, P93, R53, H116, and T115</b></font> from the neighboring monomer <font color='orange'><b>B</b></font>. The residues labeled and shown as sticks (A and B in the brackets point on the name of the monomer). Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines with interatomic distances in Å. The magnesium (Mg) atoms are shown in spacefill representation and colored in <font color='cyan'><b>cyan</b></font>. The <font color='magenta'><b>CoA</b></font> is shown in stick representation and colored <font color='magenta'><b>magenta</b></font>. <font color='blue'><b>Nitrogen</b></font> and <font color='red'><b>oxygen</b></font> atoms of the CoA 3′,5′-ADP moiety and of the active site resudues are colored <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font> and <font color='red'><b>red</b></font>, respectively. | The 3′,5′-ADP moieties of the [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Coenzyme_A coenzyme A] (<font color='magenta'><b>CoA, colored magenta</b></font>), are positioned in the cleft between each of two monomers forming three active sites within AcpS trimer. The <scene name='3hqj/Trimer/5'>active site</scene> is formed by the residues <font color='lime'><b>D9 (highly conserved), E58, L62, and S65</b></font> from monomer <font color='lime'><b>A</b></font> and by <font color='orange'><b>R92, P93, R53, H116, and T115</b></font> from the neighboring monomer <font color='orange'><b>B</b></font>. The residues labeled and shown as sticks (A and B in the brackets point on the name of the monomer). Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines with interatomic distances in Å. The magnesium (Mg) atoms are shown in spacefill representation and colored in <font color='cyan'><b>cyan</b></font>. The <font color='magenta'><b>CoA</b></font> is shown in stick representation and colored <font color='magenta'><b>magenta</b></font>. <font color='blue'><b>Nitrogen</b></font> and <font color='red'><b>oxygen</b></font> atoms of the CoA 3′,5′-ADP moiety and of the active site resudues are colored <font color='blue'><b>blue</b></font> and <font color='red'><b>red</b></font>, respectively. | ||
{{Clear}} | {{Clear}} | ||
Revision as of 09:13, 15 July 2012
| |||||||||||
3D structures of acyl carrier protein synthase
1af8, 2af8, 2kg8, 2kg9, 2kga, 2kgc, 2kgd, 2kge – ScACPS – Streptomyces coelicolor – NMR
2jca - ScACPS
1fte, 1ftf - SpACPS – Streptococcus pneumoniae
1f7l, 1f7t - BsACPS (mutant) – Bacillus subtilis
3f09 - SaACPS – Staphylococcus aureus
3hqj, 3h7q, 3ne1, 3ne3, 3ne9, 3nfd - MtACPS – Mycobacterium tuberculosis
3gwm - ACPS – Mycobacterium smegmatis
3qmn - ACPS – Vibrio cholera
ACPS complex
2jbz - ScACPS + CoA
2wds, 2wdy - ScACPS (mutant) + CoA
2wdo - ScACPS + acetyl-CoA
1fth – SpACPS + ADP
1f80 - BsACPS (mutant) + ACP
2qg8 - ACPS + ADP – Plasmodium yoelii
4dxe - SaACPS + ACP
3hyk - ACPS + ADP – Bacillus anthracis
β-ketoacyl-ACPS
1w0i - AtACPS – Arabidopsis thaliana
2ix4 - AtACPS + hexanoic acid
2c9h, 2iwy, 3hhd – hACPS – human
2iwz - hACPS + hexanoic acid
β-ketoacyl-ACPS I
1dd8, 1g5x, 2buh, 2aq7, 2vb7, 2vb9 - EcACPS I - Escherichia coli
1h4f, 2byw, 2byy, 2bz4 - EcACPS I (mutant)
2wgd - MtACPS I
2wgf - MtACPS I (mutant)
2was - yACPS I PPT domain – yeast
3oyt - ACPS I – Yersinia psetis
ACPS I complex
1fj4, 1fj8, 2aqb, 2vb8 - EcACPS I + antibiotic
2vba - EcACPS I + inhibitor
1ek4 - EcACPS I (mutant) + dodecanoic acid
2bui - EcACPS I + octanoic acid
1f91, 2byx, 2byz, 2bz3 - EcACPS I (mutant) + fatty acid substrate
2wge - MtACPS I + antibiotic
2wgg - MtACPS I (mutant) + antibiotic
2wat - yACPS I PPT domain + CoA
β-ketoacyl-ACPS II
1e5m - ACPS II – Synechocytosis
1j3n - TtACPS II – Thermus thermophilus
1ox0, 1oxh - SpACPS II
2alm, 2rjt - MtACPS II (mutant)
2gqd - SaACPS II
2gp6 - MtACPS II
3e60 – ACPS II – Bartonella henselae
3kzu - ACPS II – Brucella melitensis
3o04 - ACPS II – Listeria monocytogenes
4ddo - BvACPS II – Burkholderia vietnamiensis
1kas, 2gfw – EcACPS II
2gfv - EcACPS II (mutant)
ACPS II complex
1b3n - EcACPS II + antibiotic
2gfx, 3g0y, 3g11, 3hnz, 3ho2, 3ho9, 3i8p - EcACPS II (mutant) + antibiotic
2gfy - EcACPS II (mutant) + dodecanoic acid
4f32 - BvACPS II + antibiotic
β-ketoacyl-ACPS III
1hzp, 1m1m - MtACPS III
1u6e, 2ahb, 2aj9 - MtACPS III (mutant)
1mzj - ACPS III – Streptomyces
1zow, 3il7 - SaACPS III
2ebd - ACPS III – Aquifex aeolicus
3gwa, 3gwe - ACPS III – Burkholderia pseudomallei
4dfe, 4efi - ACPS III – Burkholderia xenovorans
3il3 - ACPS III – Haemophilus influenza
3fk5 - ACPS III – Xanthomonas oryzae
3led - ACPS III – Pseudonomas palustris
2x3e - ACPS III – Pseudonomas aeruginosa
1ebl, 1hn9, 1hnk, 3il9 - EcACPS III
ACPS III complex
1hnd, 1hnh, 2gyo, 2eft - EcACPS III + CoA
1hnj - EcACPS III + malonyl-CoA
2qx1 - EcACPS III + decyl-CoA
1mzs - EcACPS III + inhibitor
1u6s - MtACPS III (mutant) + lauroyl-CoA
2qnx, 2qo1 - MtACPS III + undecanoic acid
2qo0 - MtACPS III (mutant) + undecanoic acid
2qnz - MtACPS III + decyl formate
2qny - MtACPS III (mutant) + decyl formate
1ub7 - TtACPS III (mutant)
3il4 - EfACPS III + CoA – Enterococcus faecalis
3il5 - EfACPS III + benzoic acid derivative
3il6 - EfACPS III (mutant) + benzoic acid derivative
References
- Parris KD, Lin L, Tam A, Mathew R, Hixon J, Stahl M, Fritz CC, Seehra J, Somers WS. Crystal structures of substrate binding to Bacillus subtilis holo-(acyl carrier protein) synthase reveal a novel trimeric arrangement of molecules resulting in three active sites. Structure. 2000 Aug 15;8(8):883-95. PMID:10997907
- Dym O, Albeck S, Peleg Y, Schwarz A, Shakked Z, Burstein Y, Zimhony O. Structure-function analysis of the acyl carrier protein synthase (AcpS) from Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J Mol Biol. 2009 Nov 6;393(4):937-50. Epub 2009 Sep 3. PMID:19733180 doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2009.08.065
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
Categories: Topic Page | Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Albeck,S. | Burstein,Y. | Dym,O. | ISPC, Israel Structural Proteomics Center. | Peleg,Y. | Schwarz,A. | Shakked,Z. | Zimhony,O. | An/fold | Cytoplasm | Fatty acid biosynthesis | ISPC | Israel Structural Proteomics Center | Lipid synthesis | Magnesium | Metal-binding | Structural genomic | Transferase