Sandbox Reserved 641
From Proteopedia
(→'''Introduction''') |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== '''Introduction''' == | == '''Introduction''' == | ||
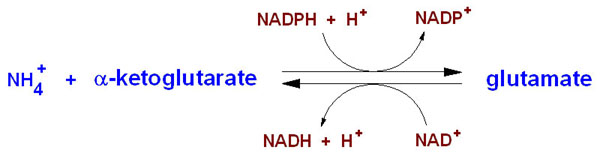
| - | Glutamate Dehydrogenase (GDH)is used to remove the ketone group and replace it with an α-amine group on the α-carbon. | + | :::::Glutamate Dehydrogenase (GDH)is used to remove the ketone group and replace it with an α-amine group on the α-carbon, which forms glutaamte. Glutamate is one of the 20 essential amino acids. This is done in reverse to supply α-ketoglutarate to the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. GDH is an oxidoreductase, which is an enzyme that transfers electrons from one molecule (reductant/electron donor) to another molecule (oxidant/electron acceptor). |
| + | ::::: | ||
== '''Structure''' == | == '''Structure''' == | ||
Revision as of 00:16, 8 November 2012
| This Sandbox is Reserved from 30/08/2012, through 01/02/2013 for use in the course "Proteins and Molecular Mechanisms" taught by Robert B. Rose at the North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC USA. This reservation includes Sandbox Reserved 636 through Sandbox Reserved 685. | |||||||
To get started:
More help: Help:Editing For more help, look at this link: http://proteopedia.org/w/Help:Getting_Started_in_Proteopedia
Glutamate Dehydrogenase
Introduction
StructureGlutamate Dehydrogenase is a hexamer that is comprised of two trimer subunits. These two subunits are stacked and composed of three domains. The top of each domain contains a "NAD-binding domain" that has the conserved nucleotide-binding motif. A larger helix-loop-helix structure rises above this and is referred to as an "antenna." This antenna contains approximately 50 amino acids and plays a major role in regulation of the enzyme. (1) MechanismNH4+ + α-ketoglutarate + NADPH + 2 H+ → glutamate + NADP+ + H2O
|