Sandbox BCMB402 Ricin
From Proteopedia
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<StructureSection load='3rtj' size='400' side='right' caption='Ricin bound to adenine (PDB entry [[3rtj]])'> | <StructureSection load='3rtj' size='400' side='right' caption='Ricin bound to adenine (PDB entry [[3rtj]])'> | ||
| - | + | __notoc__ | |
==Structure== | ==Structure== | ||
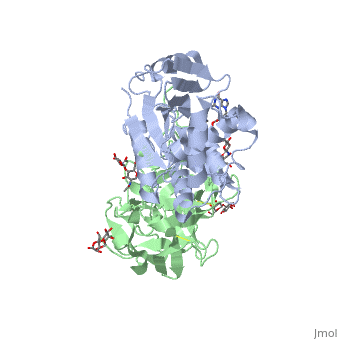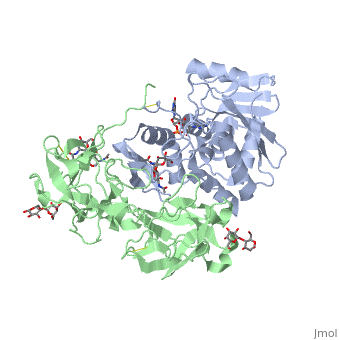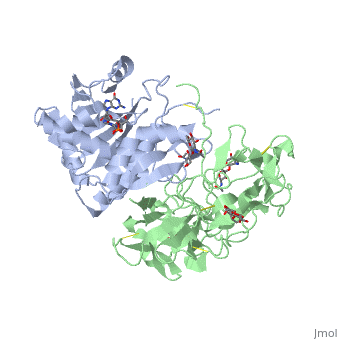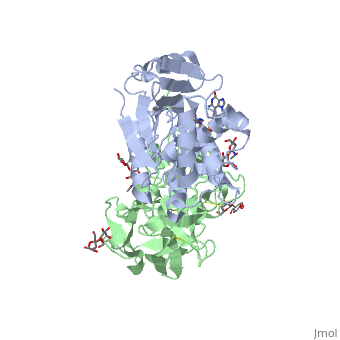
Ricin is a heterodimer that consists of a 32 kilodalton A chain glycoprotein (light blue) linked by a <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/Dihedral_link_between_subunits/1'>disulfide bond</scene> to a 32 kilodalton <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/B_subunit/1'>B chain</scene> glycoprotein<ref name="montfort" /> (green). | Ricin is a heterodimer that consists of a 32 kilodalton A chain glycoprotein (light blue) linked by a <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/Dihedral_link_between_subunits/1'>disulfide bond</scene> to a 32 kilodalton <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/B_subunit/1'>B chain</scene> glycoprotein<ref name="montfort" /> (green). | ||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
The B chain is a lectin<ref name="lord" /> that <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/Carbohydrate_binding/1'>binds</scene> to galactose-containing surface receptors. Originally it was thought that the mode of action of Ricin poisoning was due to hemagglutination due to a closely related, co-isolating lectin, RCA. | The B chain is a lectin<ref name="lord" /> that <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/Carbohydrate_binding/1'>binds</scene> to galactose-containing surface receptors. Originally it was thought that the mode of action of Ricin poisoning was due to hemagglutination due to a closely related, co-isolating lectin, RCA. | ||
| - | + | __notoc__ | |
==Mechanism of action== | ==Mechanism of action== | ||
The mechanism deployed by Ricin to gain entry to a host cell involves the poison's heterogenic properties. First, the B subunit binds to two carbohydrates on the cell surface, either glycolipids or glycoproteins, which both terminate with galactose. The interaction is facilitated by hydrogen bonds to <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/B_chain_bind_lactose_1/2'>lysine 40 and asparagine 46</scene> in one domain<ref name = "Rutenber">PMID: 3561502</ref> and <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/B_chain_bind_lactose_2/1'>asparagine 255</scene> in the other domain. Once bound, the ricin-glycoprotein complex is taken into the cells via endocytosis, and the toxin is released into the cells. This association between the A and B chain is essential for toxicity <ref name="montfort" /> without it the Ricin would not be able to gain access to the cell, rendering it useless<ref name = "rapak">PMID: 9108055</ref>.. | The mechanism deployed by Ricin to gain entry to a host cell involves the poison's heterogenic properties. First, the B subunit binds to two carbohydrates on the cell surface, either glycolipids or glycoproteins, which both terminate with galactose. The interaction is facilitated by hydrogen bonds to <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/B_chain_bind_lactose_1/2'>lysine 40 and asparagine 46</scene> in one domain<ref name = "Rutenber">PMID: 3561502</ref> and <scene name='Sandbox_BCMB402_Ricin/B_chain_bind_lactose_2/1'>asparagine 255</scene> in the other domain. Once bound, the ricin-glycoprotein complex is taken into the cells via endocytosis, and the toxin is released into the cells. This association between the A and B chain is essential for toxicity <ref name="montfort" /> without it the Ricin would not be able to gain access to the cell, rendering it useless<ref name = "rapak">PMID: 9108055</ref>.. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
''Updated April 2013'' | ''Updated April 2013'' | ||
| - | + | __notoc__ | |
===Ricin A chain (RTA)=== | ===Ricin A chain (RTA)=== | ||
[[1j1m]], [[1ift]], [[2aai]], [[1rtc]] – RTA<br /> | [[1j1m]], [[1ift]], [[2aai]], [[1rtc]] – RTA<br /> | ||
[[3lc9]], [[3mk9]], [[2vc4]], [[1uq4]], [[1uq5]], [[1obs]], [[3bjg]], [[3srp]] – RTA (mutant) | [[3lc9]], [[3mk9]], [[2vc4]], [[1uq4]], [[1uq5]], [[1obs]], [[3bjg]], [[3srp]] – RTA (mutant) | ||
| - | + | __notoc__ | |
===Ricin A chain binary complexes=== | ===Ricin A chain binary complexes=== | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
[[1apg]] – RTA + RNA | [[1apg]] – RTA + RNA | ||
[[3px8]] – RTA + formycin monophosphate<br /> | [[3px8]] – RTA + formycin monophosphate<br /> | ||
| - | + | __notoc__ | |
===Ricin B chain (RTB)=== | ===Ricin B chain (RTB)=== | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
[[3nbe]] – CnRTB + lactose derivative<br /> | [[3nbe]] – CnRTB + lactose derivative<br /> | ||
[[3phz]] – RTB + glycoside – ''Polyporus squamosus'' | [[3phz]] – RTB + glycoside – ''Polyporus squamosus'' | ||
| - | + | __notoc__ | |
===Ricin A+B chains=== | ===Ricin A+B chains=== | ||
| Line 59: | Line 59: | ||
[[3rtj]] - RTA + RTB + dinucleotide | [[3rtj]] - RTA + RTB + dinucleotide | ||
| - | + | __notoc__ | |
==See Also== | ==See Also== | ||
* [[Ribosome]] | * [[Ribosome]] | ||
* [[Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula|Large Ribosomal Subunit]] | * [[Large Ribosomal Subunit of Haloarcula|Large Ribosomal Subunit]] | ||
* [[Translation]] | * [[Translation]] | ||
| - | + | __notoc__ | |
==References== | ==References== | ||
{{Reflist}} | {{Reflist}} | ||
Revision as of 20:10, 24 April 2013
Ricin is a potent cytotoxin that is synthesized in the endosperm cells of maturing seeds of the castor oil plant (Ricinus communis)[1]. Ricin belongs to a small multi-gene family[2] that is composed of eight members. Ricin is classified as a type II heterodimeric Ribosome Inactivating Protein[1] or RIPs. For toxins in Proteopedia see Toxins.
| |||||||||||
Updated April 2013
Ricin A chain (RTA)
1j1m, 1ift, 2aai, 1rtc – RTA
3lc9, 3mk9, 2vc4, 1uq4, 1uq5, 1obs, 3bjg, 3srp – RTA (mutant)
Ricin A chain binary complexes
3px8 – RTA preproricin + 7-carboxy-pterin
1br5, 1br6 - RTA + pterin derivative
3px9 - RTA preproricin + furanylmethyl-carbamoyl-pterin
3lc9, 3mk9, 2vc4, 1uq4, 1uq5, 1obs – RTA (mutant)
3hio – RTA + tetranucleotide
3ej5, 1il5 – RTA pyrimidine derivative
2p8n, 1ifs – RTA + adenine
2pjo, 2r2x – RTA + urea derivative
2r3d – RTA + acetamide
2vc3 - RTA (mutant) + acetate
1il3, 1il4, 1il9 – RTA + guanine derivative
1ifu, 1fmp – RTA + formycin
1obt - RTA (mutant) + AMP
1apg – RTA + RNA
3px8 – RTA + formycin monophosphate
Ricin B chain (RTB)
3nbc, 3nbd – CnRTB + lactose – Clitocybe nebularis
3nbe – CnRTB + lactose derivative
3phz – RTB + glycoside – Polyporus squamosus
Ricin A+B chains
2aai - RTA + RTB
3rtj - RTA + RTB + dinucleotide
See Also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 Lord JM, Roberts LM, Robertus JD. Ricin: structure, mode of action, and some current applications. FASEB J. 1994 Feb;8(2):201-8. PMID:8119491
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 2.2 Montfort W, Villafranca JE, Monzingo AF, Ernst SR, Katzin B, Rutenber E, Xuong NH, Hamlin R, Robertus JD. The three-dimensional structure of ricin at 2.8 A. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5398-403. PMID:3558397
- ↑ Weston SA, Tucker AD, Thatcher DR, Derbyshire DJ, Pauptit RA. X-ray structure of recombinant ricin A-chain at 1.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1994 Dec 9;244(4):410-22. PMID:7990130 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.1994.1739
- ↑ Rutenber E, Ready M, Robertus JD. Structure and evolution of ricin B chain. Nature. 1987 Apr 9-15;326(6113):624-6. PMID:3561502 doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/326624a0
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 Rapak A, Falnes PO, Olsnes S. Retrograde transport of mutant ricin to the endoplasmic reticulum with subsequent translocation to cytosol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997 Apr 15;94(8):3783-8. PMID:9108055
- ↑ Holmberg L, Nygard O. Depurination of A4256 in 28 S rRNA by the ribosome-inactivating proteins from barley and ricin results in different ribosome conformations. J Mol Biol. 1996 May 31;259(1):81-94. PMID:8648651 doi:10.1006/jmbi.1996.0303