Ciprofloxacin
From Proteopedia
(Difference between revisions)
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
== Historical Information == | == Historical Information == | ||
| - | Although the official patented introduction of Ciprofloxacin by Bayer Pharmaceuticals occurred in 1987, some reports | + | Although the official patented introduction of Ciprofloxacin by Bayer Pharmaceuticals occurred in 1987, some reports indicate that at least two European patents for similar drugs pre-dated the Bayer patent by five years<ref>Ciprofloxacin. (2010). Pcm.me. http://pcm.me/ciprofloxacin/.</ref>. On October 27, 1987, the FDA approved the [[Pharmaceutical Drugs|drug]] for use in the United States for the treatment of certain bacterial infections. The effectiveness of Ciprofloxacin as an antibiotic went unchallenged by all alternative antibiotics<ref>Ciprofloxacin - Activity, Business Aspects/Bayer Pharmaceutical. Encyclopedia.jrank.org. http://encyclopedia.jrank.org/articles/pages/1398940/Ciprofloxacin.html</ref>. Consequently, other pharmaceutical companies were forced to offer their alternative antibiotics at lower costs (compared to the cost of Ciprofloxacin) so as to engage any sort of competition with Bayer Pharmaceuticals. Because of the increasingly common tendency of physicians to prescribe lower-cost medication, Bayer Pharmaceuticals could not expand into the international pharmaceutical market (which, as a whole, was declining) and, consequently, was forced to downsize at the turn of the century. Thus, the competitive effectiveness of Ciprofloxacin did not overcome the competitive pricing of drugs released by other pharmaceutical companies. Faced with the impending expiration of its patent for Ciprofloxacin in the early years of the millennium, Bayer Pharmaceuticals attempted to release variations of Ciprofloxacin. The release of Ciprofloxacin variations such as Pediatric Ciprofloxacin and Once-daily Ciprofloxacin allowed for the extension of the Ciprofloxacin patent. The popularity of Ciprofloxacin rose sharply after September 11, 2001 due to its characteristic targeting of ''Bacillus anthracis'', which was projected as a means of bioterrorism. The prescription of Ciprofloxacin for treatment of bacterial infections continues to this day. |
== Structure and Administration == | == Structure and Administration == | ||
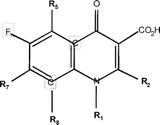
=== General Quinolone-Fluoroquinolone Structure === | === General Quinolone-Fluoroquinolone Structure === | ||
| - | + | Ciprofloxacin is identified as a "quinolone" because of its heterocyclic (with an inner-ring Nitrogen), bicyclic core-containing structure. This structure is characteristic of all quinolones<ref>Siegmund, K., et al. (2005). Molecular details of quinolone-DNA interactions: solution structure of an unusually stable DNA duplex with covalently linked nalidixic acid residues and non-covalent complexes derived from it. ''Nucleic Acids [Research], 33(15)'', 4838-4848.</ref>. Specifically, Ciprofloxacin is characterized as a "fluoroquinolone" since it contains a fluorine atom at the R6 position of its bicyclic core<ref>Peterson, L. (2001). Quinolone-Molecular Structure-Activity Relationships: What We Have Learned About Improving Antimicrobial Activity. ''Clinical Infectious Diseases, 33(3)'', S180-S186.</ref>. All fluoroquinolones contain this R6 fluorine moiety. A general molecular structure for all fluoroquinolones is shown. The R6 fluorine occurs on the left ring of the bicyclic core. | |
[[Image:Flg.jpg]]<ref>Image from: http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/33/Supplement_3/S180.full.</ref> | [[Image:Flg.jpg]]<ref>Image from: http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/33/Supplement_3/S180.full.</ref> | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
=== Administration === | === Administration === | ||
| - | Ciprofloxacin is | + | Usually, Ciprofloxacin is administered either as CIPRO® Oral Suspension (Ciprofloxacin), or as CIPRO® Tablets (Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride)<ref>CIPRO® (ciprofloxacin hydrochloride) TABLETS - CIPRO® (ciprofloxacin*) ORAL SUSPENSION - Drug Information Packet. Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. Schering Plough Corporation.</ref>. Both administration types are oral. |
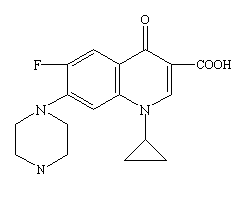
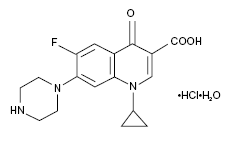
CIPRO® Oral Suspension (Ciprofloxacin) is a 1-cyclopropyl-6-floro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid with empirical formula: C₁₇H₁₈FN₃O₃. Ciprofloxacin has a molecular weight of 331.35 g/mol and occurs as a yellowish, crystalline substance<ref>Molecular weight from Chemexper.com.</ref><ref>CIPRO® (ciprofloxacin hydrochloride) TABLETS - CIPRO® (ciprofloxacin*) ORAL SUSPENSION - Drug Information Packet. Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. Schering Plough Corporation.</ref>. A simple molecular structure of Ciprofloxacin is shown (base empirical formula). | CIPRO® Oral Suspension (Ciprofloxacin) is a 1-cyclopropyl-6-floro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid with empirical formula: C₁₇H₁₈FN₃O₃. Ciprofloxacin has a molecular weight of 331.35 g/mol and occurs as a yellowish, crystalline substance<ref>Molecular weight from Chemexper.com.</ref><ref>CIPRO® (ciprofloxacin hydrochloride) TABLETS - CIPRO® (ciprofloxacin*) ORAL SUSPENSION - Drug Information Packet. Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. Schering Plough Corporation.</ref>. A simple molecular structure of Ciprofloxacin is shown (base empirical formula). | ||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
[[Image:ciproHCl.gif]]<ref>Image from: http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://images.rxlist.com/images/rxlist/ciloxan_s.gif&imgrefurl=http://www.rxlist.com/ciloxan_ophthalmic_ointment-drug.htm&usg=__UqTKseSe8hD85c5RLGIz2_dbAg0=&h=142&w=232&sz=2&hl=en&start=16&zoom=1&tbnid=70Q2WG5hppsQ5M:&tbnh=100&tbnw=164&ei=T010TenMFYH_8Aa6gvDKDw&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dciprofloxacin%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26client%3Dfirefox-a%26sa%3DN%26rls%3Dorg.mozilla:en-US:official%26biw%3D1280%26bih%3D647%26tbs%3Disch:10%2C624&um=1&itbs=1&iact=hc&vpx=1064&vpy=399&dur=309&hovh=106&hovw=174&tx=98&ty=76&oei=EU10TcvOCMbdtge5msiLDw&page=2&ndsp=18&ved=1t:429,r:17,s:16&biw=1280&bih=647.</ref> | [[Image:ciproHCl.gif]]<ref>Image from: http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://images.rxlist.com/images/rxlist/ciloxan_s.gif&imgrefurl=http://www.rxlist.com/ciloxan_ophthalmic_ointment-drug.htm&usg=__UqTKseSe8hD85c5RLGIz2_dbAg0=&h=142&w=232&sz=2&hl=en&start=16&zoom=1&tbnid=70Q2WG5hppsQ5M:&tbnh=100&tbnw=164&ei=T010TenMFYH_8Aa6gvDKDw&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dciprofloxacin%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26client%3Dfirefox-a%26sa%3DN%26rls%3Dorg.mozilla:en-US:official%26biw%3D1280%26bih%3D647%26tbs%3Disch:10%2C624&um=1&itbs=1&iact=hc&vpx=1064&vpy=399&dur=309&hovh=106&hovw=174&tx=98&ty=76&oei=EU10TcvOCMbdtge5msiLDw&page=2&ndsp=18&ved=1t:429,r:17,s:16&biw=1280&bih=647.</ref> | ||
| - | Ciprofloxacin | + | Ciprofloxacin also may be administered intravenously and in the form of eye drops or ear drops<ref>Ciprofloxacin. (2010). Pcm.me. http://pcm.me/ciprofloxacin/.</ref>. |
Revision as of 15:15, 2 September 2013
| |||||||||||
References
- ↑ CIPRO® (ciprofloxacin hydrochloride) TABLETS - CIPRO® (ciprofloxacin*) ORAL SUSPENSION - Drug Information Packet. Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. Schering Plough Corporation.
- ↑ CIPRO® (ciprofloxacin hydrochloride) TABLETS - CIPRO® (ciprofloxacin*) ORAL SUSPENSION - Drug Information Packet. Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. Schering Plough Corporation.
- ↑ 2011. Ciprofloxacin. Medicine Plus. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists Inc. 2011. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a688016.html.
- ↑ 2001. Information on Cipro (Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride) for Inhalation Anthrax for Consumers: Questions and Answers. Fda.gov. http://www.fda.gov/Drugs/EmergencyPreparedness/BioterrorismandDrugPreparedness/ucm130711.htm. Last updated, 2009.
- ↑ 2011. Ciprofloxacin. Medicine Plus. American Society of Health-System Pharmacists Inc. 2011. http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/druginfo/meds/a688016.html.
- ↑ Ciprofloxacin. (2010). Pcm.me. http://pcm.me/ciprofloxacin/.
- ↑ Ciprofloxacin - Activity, Business Aspects/Bayer Pharmaceutical. Encyclopedia.jrank.org. http://encyclopedia.jrank.org/articles/pages/1398940/Ciprofloxacin.html
- ↑ Siegmund, K., et al. (2005). Molecular details of quinolone-DNA interactions: solution structure of an unusually stable DNA duplex with covalently linked nalidixic acid residues and non-covalent complexes derived from it. Nucleic Acids [Research], 33(15), 4838-4848.
- ↑ Peterson, L. (2001). Quinolone-Molecular Structure-Activity Relationships: What We Have Learned About Improving Antimicrobial Activity. Clinical Infectious Diseases, 33(3), S180-S186.
- ↑ Image from: http://cid.oxfordjournals.org/content/33/Supplement_3/S180.full.
- ↑ CIPRO® (ciprofloxacin hydrochloride) TABLETS - CIPRO® (ciprofloxacin*) ORAL SUSPENSION - Drug Information Packet. Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. Schering Plough Corporation.
- ↑ Molecular weight from Chemexper.com.
- ↑ CIPRO® (ciprofloxacin hydrochloride) TABLETS - CIPRO® (ciprofloxacin*) ORAL SUSPENSION - Drug Information Packet. Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. Schering Plough Corporation.
- ↑ Image from: http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://textbookofbacteriology.net/themicrobialworld/cipro.gif&imgrefurl=http://textbookofbacteriology.net/themicrobialworld/control.html&usg=__wtzKLHB3NssfnODEB224br5-Bcw=&h=200&w=250&sz=2&hl=en&start=0&zoom=1&tbnid=o7VT7s6FFIUrWM:&tbnh=160&tbnw=199&ei=Hk10TaypBcL58AbyvIjKDw&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dciprofloxacin%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26client%3Dfirefox-a%26sa%3DN%26rls%3Dorg.mozilla:en-US:official%26biw%3D1280%26bih%3D647%26tbs%3Disch:1&um=1&itbs=1&iact=hc&vpx=527&vpy=300&dur=1709&hovh=160&hovw=200&tx=155&ty=82&oei=EU10TcvOCMbdtge5msiLDw&page=1&ndsp=16&ved=1t:429,r:7,s:0.
- ↑ Molecular weight from: CIPRO® (ciprofloxacin hydrochloride) TABLETS - CIPRO® (ciprofloxacin*) ORAL SUSPENSION - Drug Information Packet. Bayer HealthCare Pharmaceuticals. Schering Plough Corporation.
- ↑ Image from: http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://images.rxlist.com/images/rxlist/ciloxan_s.gif&imgrefurl=http://www.rxlist.com/ciloxan_ophthalmic_ointment-drug.htm&usg=__UqTKseSe8hD85c5RLGIz2_dbAg0=&h=142&w=232&sz=2&hl=en&start=16&zoom=1&tbnid=70Q2WG5hppsQ5M:&tbnh=100&tbnw=164&ei=T010TenMFYH_8Aa6gvDKDw&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dciprofloxacin%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26client%3Dfirefox-a%26sa%3DN%26rls%3Dorg.mozilla:en-US:official%26biw%3D1280%26bih%3D647%26tbs%3Disch:10%2C624&um=1&itbs=1&iact=hc&vpx=1064&vpy=399&dur=309&hovh=106&hovw=174&tx=98&ty=76&oei=EU10TcvOCMbdtge5msiLDw&page=2&ndsp=18&ved=1t:429,r:17,s:16&biw=1280&bih=647.
- ↑ Ciprofloxacin. (2010). Pcm.me. http://pcm.me/ciprofloxacin/.
- ↑ Image from: http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://www.chemdrug.com/databases/SYNTHESIS/SYN/09/09000601a.gif&imgrefurl=http://www.chemdrug.com/databases/8_0_dvpytumicutbciwa.html&usg=__TxiDuzCve6C_crxmcPYTpfW5d4s=&h=555&w=678&sz=6&hl=en&start=0&zoom=1&tbnid=xhquLksJBbMnjM:&tbnh=165&tbnw=201&ei=0Y93TdbGI-yI0QGspa25Bw&prev=/images%3Fq%3Dsynthesis%2Bof%2Bciprofloxacin%26um%3D1%26hl%3Den%26client%3Dfirefox-a%26sa%3DN%26rls%3Dorg.mozilla:en-US:official%26biw%3D1280%26bih%3D647%26tbs%3Disch:1&um=1&itbs=1&iact=hc&vpx=346&vpy=105&dur=63&hovh=203&hovw=248&tx=170&ty=128&oei=0Y93TdbGI-yI0QGspa25Bw&page=1&ndsp=16&ved=1t:429,r:1,s:0
- ↑ Ciprofloxacin Oral - Monograph - Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride. 2009. Medscape.com. http://www.medscape.com/druginfo/monograph cid=med&drugid=7748&drugname=Ciprofloxacin+Oral&monotype=monograph&secid=8.
- ↑ Su, Chih-Chia, et al. (2006). Conformation of the AcrB Multidrug Efflux Pump in Mutants of the Putative Proton Relay Pathway. Journal of Bacteriology, 188(20), 7290-7296.
- ↑ Husain, F., Nikaido, H. (2010). Substrate path in the AcrB multidrug efflux pump of Escherichia coli. Molecular Microbiology, 78(2), 320-330.
- ↑ Su, Chih-Chia, et al. (2006). Conformation of the AcrB Multidrug Efflux Pump in Mutants of the Putative Proton Relay Pathway. Journal of Bacteriology, 188(20), 7290-7296.
Proteopedia Page Contributors and Editors (what is this?)
John Ripollone, John E. Ripollone, Alexander Berchansky, David Canner